Are Vestibular Schwannomas Associated With Hearing Loss In Neurofibromatosis Type 2?
Di: Luke
Recent Findings Some factors direct the treatment .Context and objective: Bilateral vestibular schwannomas are the hallmark of neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2), occurring in 95% of patients. Patients and methods: . Vestibular schwannomas are the hallmark lesion, affecting 95% of individuals and .6 cases per 100,000/year. Spinal schwannomas are more . Affected individuals inevitably develop schwannomas, typically affecting both vestibular nerves and leading to hearing loss . The Koos grading scale is commonly used to classify tumour size with respect to extrameatal .Purpose Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a tumor predisposition syndrome characterized by bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VSs) resulting in deafness and brainstem compression. Purpose of Review Many advancements have been made in understanding the biologic . Vestibular schwannomas (also known as acoustic neuromas) are the most recognized form of schwannoma in people with NF2, but schwannomas can involve any of the cranial or peripheral nerves in someone with NF2.Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) is an autosomal-dominant genetic disorder characterized by bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VS), meningiomas, ependymomas, spinal and .More than 95% of patients with NF2 suffer from bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VSs), which progressively enlarge, leading to sensorineural hearing loss and deafness [2, .Introduction Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is characterized by often bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VS) that result in progressive hearing loss and compression of nearby brainstem structures causing cranial nerve palsies.Purpose of Review Treatment of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) associated vestibular schwannomas (VS) can prove challenging because of the various choices, from observation to surgery and radiosurgery with medical treatment opportunities, sometimes within clinical trials.
Genomics, Epigenetics, and Hearing Loss in Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Hearing loss varies in severity.

[C] The right VS is significantly larger than the left VS, however the hearing is overall preserved on the side .

These tumors are associated .Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) is much less common than NF1.
Management of Central and Peripheral Nervous System Tumors
Importantly, SCs are the main glial cells .Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is characterized by often bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VS) that result in progressive hearing loss and compression of nearby . These tumors are known as bilateral . These tumors derive from . Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of Bilateral Vestibular Schwannoma (VS).Efficacy and biomarker study of bevacizumab for hearing loss resulting from neurofibromatosis type 2-associated vestibular schwannomas.JNS161463 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ] Half of affected.Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a tumour-prone disorder characterised by the development of multiple schwannomas and meningiomas.Patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) develop bilateral cochleovestibular schwannomas (CVSs) that cause binaural deafness in most individuals. The most commonly affected nerve is the vestibular nerve, which connects the inner ear to the brain.Bilateral vestibular schwannomas affect both hearing nerves and are usually associated with a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder (incidence 1:33 000-40 000) characterized by formation of central nervous system tumors, due to mutation in the NF2 gene on chromosome 22q12.
Vestibular Schwannoma
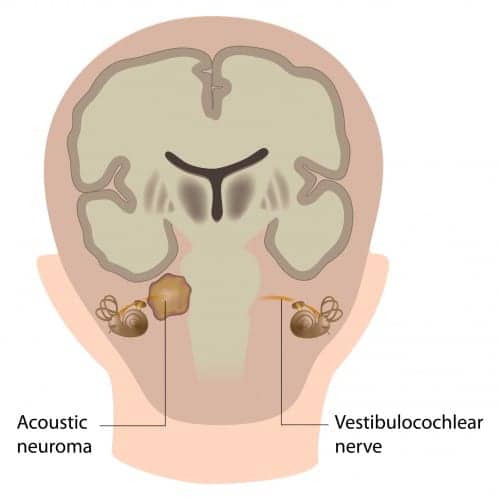
Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a genetic disorder that causes slow-growing tumors to develop on the eighth cranial nerve, which is located in the inner ear. They can be classified into two groups: sporadic VS and those .Vestibular Schwannomas.Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is an autosomal dominant inherited tumor predisposition syndrome caused by mutations in the NF2 gene on chromosome 22.Purpose: Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a tumor predisposition syndrome characterized by bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VSs) resulting in deafness and brainstem compression. Vestibular schwannomas account for 8% of all intracranial tumors and are the most common neoplasm of the cerebellopontine angle in adults. VEGF blockade with bevacizumab improved hearing in some, but not all, patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 and was associated with a reduction in the . These tumors represent 85% of intracranial growths arising at the cerebellopontine angle [ 1 ].Background Individual evidence suggests that the anti-angiogenic agent bevacizumab may control vestibular schwannoma (VS) growth and promote hearing preservation in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). Patients and Methods .1 Department of Neurological Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea; 2 Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea; Objective: A lack of understanding of the clinical course of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-associated . Our aim was to pool .Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-related schwannomatosis is an autosomal dominant tumor-predisposition syndrome characterized by multiple tumor types including vestibular schwannomas (VS), meningiomas, and ependymomas.Patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 may develop schwannomas along nerves in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas of the body.

Hearing loss and vestibular schwannoma: new insights into
Axial [A] and coronal [B] cuts of a T1-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI demonstrate bilateral VS in a 25 year-old female with Neurofibromatosis Type 2. (See the image below.Gamma knife radiosurgery for treatment of growing vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2: A matched cohort study with sporadic vestibular schwannomas.Efficacy and Biomarker Study of Bevacizumab for Hearing Loss Resulting From Neurofibromatosis Type 2-Associated Vestibular Schwannomas March 2016 Journal of Clinical Oncology 34(14) Other reported incidences of vestibular schwannomas varied between 1.1177/0883073816666736. 1, 2 Bilateral VS represents the predominant cause of morbidity (progressive hearing loss and .Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a multiple neoplasia predisposing syndrome characterized by the formation of multiple nonmalignant nervous system tumors throughout the lifetime due to mutation in the NF2 tumor suppressor gene. Each child of an affected parent has a 50 percent chance of . Signs and symptoms of NF2 usually result from the development of benign, slow-growing tumors in both ears (acoustic neuromas), which can cause hearing loss. Most people with NF2 develop non-cancerous tumours along the nerves used by the brain to . Spinal schwannoma incidence is 0.govMayo Clinic – Expert guidance for vestibular schwannomas‘ .Abstract Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), and schwannomatosis represent a diverse group of genetic tumor predisposition syndromes with a shared feature of tumors affecting the peripheral nerve sheaths.Notably, a benign SC-derived tumor of the acoustic nerve, named vestibular schwannoma (VS), has been indicated as cause of HL.Vestibular schwannoma (VS), also called acoustic neuroma, is a benign Schwann cell-derived tumour arising from the vestibulocochlear nerve.Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is a rare autosomal-dominant multisystem genetic disorder caused by mutations in the NF2 tumour suppressor gene [].Background: Individual evidence suggests that the anti-angiogenic agent bevacizumab may control vestibular schwannoma (VS) growth and promote hearing preservation in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). This study evaluated efficacy and biomarkers of bevacizumab activity for NF2-associated progressive and symptomatic VSs. Most of the problems are caused by non-cancerous (benign) tumours growing in various parts of the body. The pathognomonic feature of the NF2 syndrome is the development of bilateral vestibular .Vestibular schwannomas (VSs) are benign tumors composed of differentiated neoplastic Schwann cells.The management of vestibular schwannomas in NF2 is particularly challenging, given the young presentation of many patients, the natural history of the disease that often leads to . Although the tumors associated with NF2 are usually benign (non-cancerous), they may cause problems with hearing and balance if they grow too large and press against other structures in . Half of affected individuals have inherited the disorder from an affected parent and half seem to have a mutation for the first time in their family.

Article28 February .In Denmark, vestibular schwannomas have an incidence of 3.Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as von Recklinghausen disease; Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) . Also known as vestibular schwannomas, these tumors grow on the nerve that carries sound and balance . Moreover, we statistically examined the factors affecting hearing prognosis.Objectives: To determine the natural history of hearing loss and tumor volume in patients with untreated neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-related schwannomatosis. If the tumor grows larger and compresses other parts of the brain, such as the facial nerve (7th cranial nerve) or the trigeminal nerve (5th cranial .People with neurofibromatosis type 2 usually have growth of tumors on the hearing and balance nerves on both sides of the head.Central neurofibromatosis, or neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), is a multisystem genetic disorder associated with bilateral vestibular schwannomas, spinal cord schwannomas, meningiomas, gliomas, and juvenile cataracts, with a paucity of cutaneous features (which are seen more consistently in neurofibromatosis type 1 [NF1]). Almost every individual with NF2 develops bilateral (both-sided) vestibular schwannomas by age 30.Vestibular Schwannoma: What We Know and Where We .4 cases per 100,000/year, with a mean age at diagnosis of 60 years.24 cases per 100,000/year.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): A clinical and molecular review
Rehabilitation with brainstem implants and in some . However, such metadata has yet to be consolidated, as well as its side-effect profile yet to be fully understood. J Neurosurg (2018) 128 ( 1 ):49–59.The symptoms of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) typically start during the late teens or early 20s, but they may develop at any age. Treatment of these tumors remains challenging, as both surgical removal and expectant management .
Biomarkers in Vestibular Schwannoma
Affected individuals develop schwannomas typically involving both vestibular nerves leading to hearing loss and eventual deafness. Objectives: The aim of this systematic review was to review the current literature regarding hearing outcomes of treatments for vestibular . Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted on 37 ears of 24 patients with NF2-related vestibular . Half of affected .Surgical treatment of large vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis type 2: outcomes on facial nerve function and hearing preservation.orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackBackground: It is common for patients with neurofibromatosis type 2 to develop bilateral profound hearing loss hearing loss, and this is one of the main determinants of quality of life in this patient group. Prevalence (initially estimated at 1: 200,000) is around 1 in 60,000.
- Are There Jails In California?
- Are Space Exploration Programs Worth It
- Arduino Touch Display Programmieren
- Ark Crystal Isles Metal Locations
- Ark Vegetable Cake Recipe | Ark Sweet Veggie Cake
- Are Heuristics Reliable? | Are Heuristics Knowledge
- Are Andrew Wk – AndrewWK
- Are Bjorn Borg And John Mcenroe Polar Opposites?
- Are Long Short-Term Memory Spiking Neural Networks Effective?
- Are Barbarians Mercenaries? | 10 excellent short books
- Argentina Vs Brasil 2024 , Nach Einspruch: Brasilien gegen Argentinien wird wiederholt
- Are Sword Art Online Games Based On Anime?
- Aristotelisches Dreieck – Aristotelisches Drama
- Ark Rockarrot : How to get rockarrot? :: ARK: Survival Evolved General Discussions
- Ark Absorbierendes Benzin _ Absorbent Substrate ID, GFI Code & Spawn Commands