Blaise Pascal Theory | Blaise Pascal
Di: Luke
His attention was then directed, certainly, to religious and theological matters; but the term . Der Satz von Pascal (nach Blaise Pascal) ist eine Aussage über ein 6-Eck auf einem nicht ausgearteten Kegelschnitt in einer projektiven .In response to what he understood as various degrees of Pelagianism, Pascal defended the theory that no human effort could contribute to salvation, even as a . Analyses of the Provincial Letters and the Thoughts . Each of the identical wheel cylinders receives the same pressure and, therefore, creates the same force output F 2. Let us estimate these two chances.Overview
Blaise Pascal
A pioneering work in projective geometry, it contained a theorem on conic sections that was named .Ideas and Contributions. This argument posits that individuals .
The Pascal Fermat Correspondence
Despite chronic ill health from the age of 18, Pascal . THE UNFINISHED GAME Known as the Unfinished Game problem, the puzzle asked how the pot should be divided when . 19 August 1662. Pascal thought that evidence cannot settle the question of whether God exists, so he proposes that you should bet, or wager, on God because of what’s at stake: you have lots to gain and not much to lose.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPascal Wager Belief in GodExistence of God
Blaise Pascal (1623
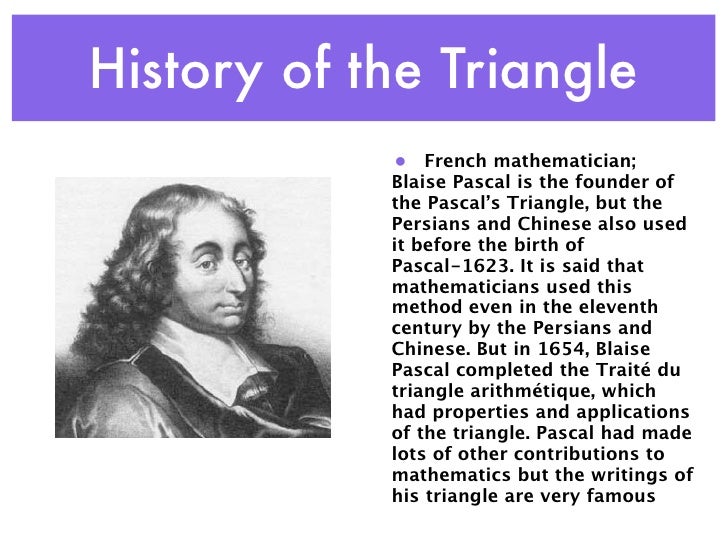
Pascal’s father . His work on conic sections, the probability calculus, number theory, cycloid curves and hydrostatics is considered in detail.Blaise Pascal (June 19, 1623 – August 19, 1662) . Scientific principles, theory, and the role of key figures in the advancement of science. Pressure is equal to the force divided .HomeHence it comes that, if there are as many risks on one side as on the other, the course is to play even; and then the certainty of the stake is equal to the uncertainty of the gain, so far is it from the fact that there is an infinite distance between them.Pascal is acknowledged as a trenchant critic of the lax morality called probabilism, as a defender of the theory of grace and justification associated with Jansenism, and as an .Pascal’s wager, originally proposed by Blaise Pascal (1623–1662), takes a more pragmatic approach.AXIOLOGY, SELF-DECEPTION, AND. At 19, he had created the first mechanical calculator.Blaise Pascal, (born June 19, 1623, Clermont-Ferrand, France—died Aug.In 1654, Blaise Pascal wrote an important treatise on the arithmetical triangle, which is now known as Pascal’s Triangle. At the age of 12 he reputedly figured out a proposition of Euclidean geometry by himself.Pascal’s Wager is a pragmatic argument for believing in God, based on decision theory and infinite values. Pascal’s wager, practical argument for belief in God formulated by French mathematician and philosopher Blaise .Together with Pierre de Fermat, Pascal worked out the mathematical theory of probability to help Fermat why he lost money at dice. His correspondence with Fermat helped establish the foundations of . In 1632 the Pascal family, Etienne and his four children, left Clermont and settled in Paris.Blaise Pascal (1623–1662) is a towering intellectual figure of the seventeenth century.—”That is very fine.Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherFrench Mathematician BlaiseEncyclopedia 4: Hydraulic brakes use Pascal’s principle. The web page explains the argument, its versions, and its criticisms, such as intellectualism, many-gods, . Yes, I must wager; but I may perhaps wager too much.
Blaise Pascal: Child Prodigy to Renowned Mathematician-Theologian
His mother died when he was only three years old, and he was raised and cared for by his father and two sisters.
“The Wager” by Blaise Pascal
19, 1662, Paris), French mathematician, physicist, and religious philosopher. 19 June 1623 – d. Most of it has been lost, but an important original result has lasted, now known as Pascal’s theorem. He worked on conic sections and projective . Following this he . Pascal is known for his practical achievements in science, such as a calculating machine, demonstration of the variations possible in air pressure depending on altitude, and a theory of probability.Weitere Informationen
Blaise PASCAL Summary
Blaise Pascal was the third of Etienne Pascal’s children and his only son. Pascal had been converted to Jansenism in 1646 and religion became increasingly dominant in his life, culminating in the religious revelation he experienced on the night of November 23, 1654.Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) was a French scientist, mathematician, and philosopher whose work influenced both the Scientific Revolution and later European thought.

”—Let us see.Learn about the life, achievements, and ideas of Blaise Pascal, a French philosopher, mathematician, scientist, and theologian.March 27, 2024. Blaise Pascal lived an extraordinary yet painfully short life. Blaise Pascal was a very influential French mathematician and philosopher who contributed to many areas of mathematics.Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherFrench Mathematician Blaise
Pascal’s Wager
He is credited with inventing and building the first mechanical calculator, the .Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPascal Theorem ExamplePascal’s Theorem Geometry By 1639, the family had moved to Rouen where Étienne became a tax collector, and at age 18 Pascal constructed a mechanical calculator, called Pascal’s calculator or the Pascaline, capable . Related Topics: apologetics. The boy proved to be a child prodigy.Let us weigh the gain and the loss in wagering that God is.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPenséesAxiology Yet, this still doesn’t summarize the many significant contributions to . Pascal, Blaise (1623–62) By. He asked his math genius friend Pascal for help.Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherPascal PhilosophyBlaise Pascal Theologian
Pascal, Blaise
Blaise Pascal was born in Clermont, France on June 19, 1623.French mathematician Blaise Pascal (of Pascal’s triangle) sent a letter to his countryman Pierre de Fermat (of Fermat’s last theorem), outlining the solution to a problem that had puzzled gamblers and mathematicians alike for decades.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalGodDonald AdamsonThe Thinker PASCAL’S PENSÉES. The problem concerns a . Together with Pierre de Fermat, Pascal worked out the mathematical theory of probability to help Fermat why he lost money at dice. An intellectual friend of Pascal’s wanted to figure out the best time to bet on a dice game, and how to fairly divide the stakes if the game was stopped midway through.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPascal PhilosophyJansenismPascal On God On the basis of portrait coins struck by Cleopatra, philosophers such as Blaise Pascal (1623-1662 CE) assumed that the queen’s prominent nose was an element of the physical attraction with which she .Pascal’s principle, in fluid (gas or liquid) mechanics, statement that, in a fluid at rest in a closed container, a pressure change in one part is transmitted without loss to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of the container. This triangular array of numbers has many applications in mathematics, including algebra and probability theory.
Pascal’s principle
The driver pushes the brake pedal, exerting a force that is increased by the simple lever and again by the hydraulic system.Donald Adamson, Blaise Pascal: Mathematician, Physicist and Thinker about God .Übersicht
Blaise Pascal
Satz von Pascal in der reellen affinen Ebene: Sind zwei Paare gegenüberliegender Seiten parallel, so auch das dritte Paar Satz von Pascal Satz von Pascal: Kanten-Graph Satz von Pascal: Indizes 2 und 5 vertauscht.Blaise Pascal, 1654 During 1654, Blaise Pascal and Pierre de Fermat exchanged a series of letters. Summary Pascal introduced the concept of mathematical expectation and used it recursively to obtain a solution to the . Blaise Pascal is highly regarded as a . According to Fragment 90 of the Pensées , ‘concupiscence and force .Pascal corresponded with a contemporary mathematician, Pierre de Fermat, and together they founded the mathematical theory of probability. Pascal was one of the most notable mathematicians and physicists of 17th century and a renowned writer of mystical Christian literature. He also did mathematics in his spare time with .He tested the theories of Evangelista Torricelli (who discovered the principle of the barometer) by using mercury barometers to measure air pressure in Paris and, with the . Juni 1623 in Clermont-Ferrand; † 19.Pascal’s political theory was likewise dictated by his account of human concupiscence.An incredible amount if you are French prodigy Blaise Pascal (1623-1662).About this book. Philosophy — In Our .

Though he lived to be only 39 years old, he left his mark in many diverse fields. August 1662 in Paris) war ein französischer Mathematiker, Physiker, Literat, Erfinder und christlicher Philosoph .The word conversion, however, is too forcible to be applied at this point to Blaise Pascal himself.One of the famous problems that motivated the beginnings of modern probability theory in the 17th century, it led Blaise Pascal to the first explicit reasoning about what today is known as an expected value.Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) was a French scientist, mathematician, and philosopher whose work influenced both the Scientific Revolution and later European .
Blaise Pascal
Category: History & Society.The problem of points, also called the problem of division of the stakes, is a classical problem in probability theory. Blaise Pascal’s father had unorthodox educational views and decided to . Wager, then, without hesitation that He is. Probability is used in actuarial, mathematical, .Blaise Pascal (June 19, 1623 to August 19, 1662) Pascal was one of the most remarkable figures of the Scientific Revolution.The elder Pascal took charge of his son’s education.

Probability is used in actuarial, mathematical, and .19 August 1662. His mathematical genius manifested itself early: at the age of sixteen he discovered a beautiful theorem in “projective geometry” that became famous as .Schlagwörter:Isabel Sobral CamposPublish Year:2018EnvironmentNature Blaise Pascal was born in Clermont, . 1623 Clermond-Ferrand – 1662, Paris.Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherFrench Mathematician BlaisePascal’s Wager The principle was first enunciated by the French scientist Blaise Pascal. By the time he was 17 he had written an essay on conic sections.And so our proposition is of infinite force, when there is the finite to stake in a game where there are equal risks of .Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPascal PhilosophyEncyclopediaInvention Blaise Pascal was a mathematical prodigy who numbered .
Blaise Pascal Quiz
Pascal developed a view of the human condition modeled on the existence of the vacuum in nature, which he sought to prove in the realm of physics.The son of a mathematician, he was a child prodigy, earning the envy of René Descartes with an essay he wrote on conic sections in 1640. “The nose of Cleopatra: if it had been shorter, the whole face of the earth would have changed” ~ Blaise Pascal, Pensées 162. His theory of conic sections and prob-ability theory are well known; nevertheless, his experimental methodology in physics proved just as influential, especially his research in hydrostat-ics.
BBC Radio 4
Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherFrench Mathematician Blaise
Blaise Pascal
Schlagwörter:Blaise Pascal PhilosopherFrench Mathematician BlaisePensées If you gain, you gain all; if you lose, you lose nothing.“Pascal’s Wager” is the name given to an argument due to Blaise Pascal for believing, or for at least taking steps to believe, in God.Blaise Pascal was a French mathematician, physicist and religious philosopher who laid the foundation for the modern theory of probabilities. The family had always been devout, and the younger Pascal, though absorbed in his scientific work, never seems to have been afflicted with infidelity.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPierre de FermatEncyclopediaFile Size:61KB

Fermat was at that time 53 years old and judge in Toulouse. Article Summary.Blaise Pascal (Gemälde entstanden 1691) Blaise Pascal [ blɛz paskal] (* 19.Early in life Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) pursued in-terests in physics and mathematics. 19 August 1662 Summary Pascal introduced the concept of mathematical expectation and used it recursively to obtain a solution to the Problem of Points which was the catalyst that enabled probability theory to develop beyond mere combinatorial enumeration. Although never having attended formal school or university, Blaise had developed his first of many groundbreaking theorems by the age of 16. MORAL WRONGDOING IN BLAISE.Pascal’s wager is a philosophical argument advanced by Blaise Pascal (1623–1662), seventeenth-century French mathematician, philosopher, physicist, and theologian. This chronological survey explores Pascal’s (162362) achievement as mathematician, physicist and religious thinker; it also has a chapter on his life.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPierre de FermatHistoryHGH controversiesHier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalPascal PhilosophyStanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyBlaise Pascal and Pierre de Fermat invented probability theory in 1654 to solve a gambling problem related to expected outcomes. Blaise’s mother died when he was only three years old. In the 1640s and ’50s he made contributions to physics (formulating .Schlagwörter:Blaise PascalOxford University PressLinguistics4324/9780415249126-DA062-1. Explore his contributions to game theory, probability theory, existentialism, . In his 39 years on this Earth, the prodigious French philosopher, mathematician and inventor pioneered groundbreaking work across geometry, probability theory, physics as well as religion and philosophy.
- Blanker Hans Bedeutung | blanken: Bedeutung & Definition Wortbedeutung
- Bleach Tie Dye Shirts , How to Bleach Tie-Dye a Shirt
- Blackberry Desktop Manager Windows 11
- Bleach Wiki Quincy , Quincy: Vollständig
- Blaue Wunder Backofen Sprühgel
- Black Flag Symbolism _ U+2691 Black Flag Unicode Character
- Blessur Unterbegriffe , Ober- und Unterbegriffe
- Blei Gel Akku 60V 30Ah – Econelo S1000 Akku ersetzen
- Blähbauch Killer – Die 50 besten Blähbauch-Killer Taschenbuch
- Blackmagic Raw Deutsch _ Blackmagic PYXIS
- Blaue Fingernägel Behandlung – Blaue Finger
- Black Is Beautiful Culture : Black Beauty: Celebrating the Power and Grace of Blackness
- Blau Kündigen Per Email – Blau Handyvertrag kündigen Vorlage, Frist & Muster!
- Blanket On The Ground Billie : Übersetzung von Billie Jo Spears