Brain Cortex Functions _ Frontal lobe: Functions, structure, and damage
Di: Luke
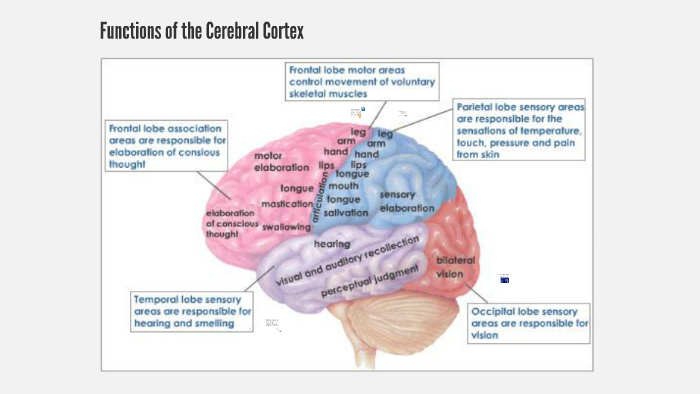
The precentral gyrus, which is directly anterior to the central sulcus and runs parallel to it, .The insular cortex is located deep within the lateral sulcus of the brain.The human brain is perhaps the most complex of all biological systems, with the mature brain composed of more than 100 billion information-processing cells called neurons. The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates .8B: Motor Areas is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Associative cortex. Brodmann Areas Definition and Overview. Your brain also receives inputs including touch, . It also integrates sensory impulses and information to form perceptions, thoughts, and memories.Within the brain, there are numerous distinct structures that perform unique tasks.The cerebral cortex is involved in several functions of the body including: Read More.Structure and Function. “Cytoarchitecture” pertains to the organization and distribution of . The prefrontal cortex is divided . Its four major regions make this possible: The cerebrum, with its cerebral cortex, gives us conscious control of our .What is the brain’s function? Your brain receives information from your five senses: sight, smell, sound, touch and taste.It later affects areas in the cerebral cortex responsible for language, reasoning, and social behavior. The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum.There is localisation of brain functions in the cerebral cortex, which has many distinct regions. It is a part of the brain that plays a role in memory, attention, judgment, and other vital functions.
Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Unique Role in Cognition and Emotion
Cerebral Cortex
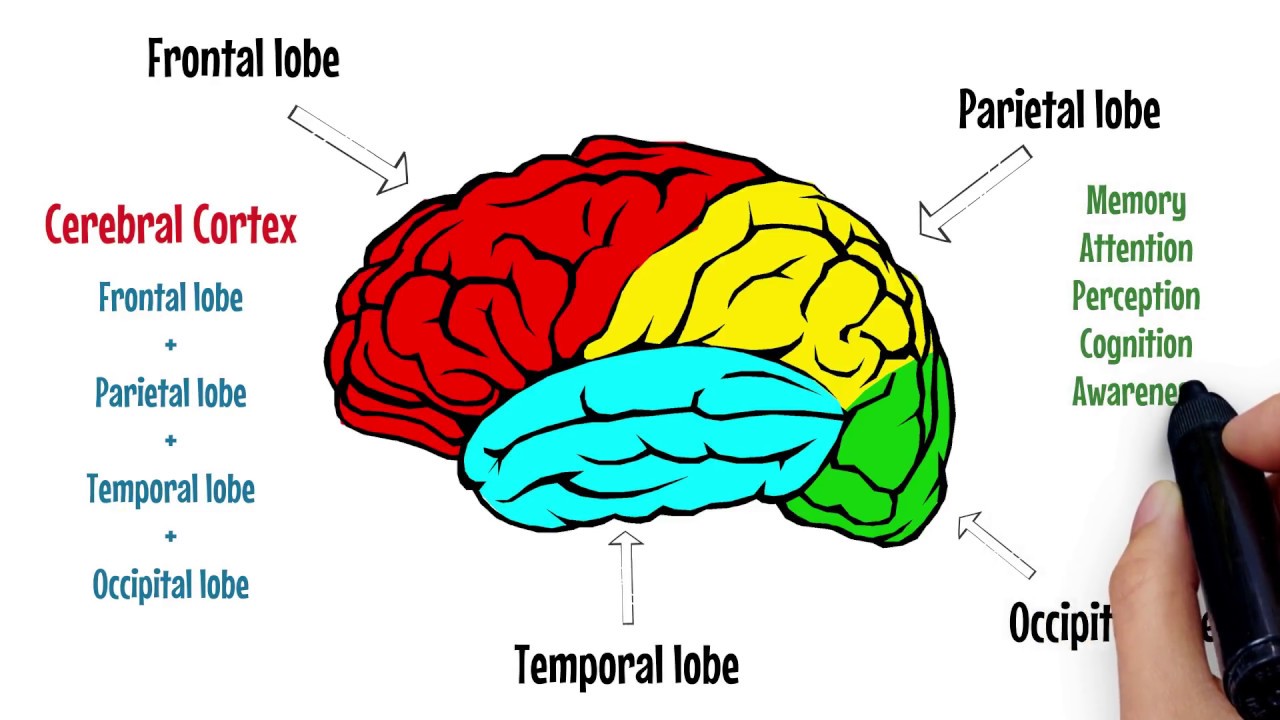
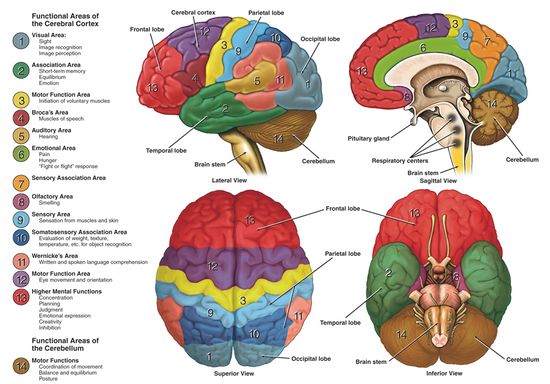
Introduction [edit | edit source].Lying right under the meninges, the cerebral cortex divides into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, each with a multitude of functions. For the sake of brevity, we won’t talk about every single one of them here. Thus, the ACC likely has an important role in integration of neuronal circuitry for affect regulation and can be identified as a distinctive region in understanding . The white matter of the brain and spinal cord forms as heavily myelinated axonal projections of these neuronal cell bodies.Located in the posterior cranial fossa, above the foramen magnum, the cerebellum’s primary function is to modulate motor coordination, posture, and balance.
Brain: How It Works, Function, Parts & Conditions
The motor cortex is an area within the brain’s cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. The cerebrum is the front part of the brain and includes the cerebral .Anterior Mid-Cingulate Cortex as a Structural and Functional hub: Neuroanatomy and Connectivity. The primary motor cortex is where the corticospinal tract originates. The morphology of the brain reflects many different functions that the brain has. The cerebral cortex develops from the most anterior part, the forebrain region, of the neural tube. Just as its name indicates, it’s the forward-most area of your brain. Though this cannot be seen directly, different parts of the cortex have .The motor cortex corresponds to the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe.
Physiology, Cerebral Cortex Functions
Jawabri, Sandeep Sharma
Neuroanatomy, Cerebral Cortex
Functions that originate in the cerebral cortex include: Consciousness.The Full Range Of Prefrontal Cortex Functions –. It contains sensory areas, motor areas and association areas involved in language processing . The forebrain is the division of the brain that is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. However, this is an oversimplification, as both hemispheres cooperate in most activities.comFunctions of the Cerebral Cortex – Bodytomybodytomy.The major function of the cerebrum is to control the voluntary muscular movements of the body along with sensation, movement, memory, emotions, executive function.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Physiology, Cerebral Cortex Functions
Since the morphology is the base for the functional output, here we will discuss both the structure and the function . The precentral gyrus contains the primary motor cortex (Brodmann area 4), which is responsible for integrating signals from different brain regions to modulate motor function.The cerebrum consists of two cerebral hemispheres the outer layer called the cortex (gray matter) and the inner layer (white matter).
The human brain: Parts, function, diagram, and more
InsulaGyriCranial BonesGlial CellsLobes of the BrainParietal
Cerebral Cortex: What It Is, Function & Location
) from the somatosensory tract, which runs through the body to the spinal cord, brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. Even though it is protected by the skull and meninges, surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the .Cerebral cortex | Description, Anatomy, Function, & Diseasebritannica.The cerebrum (front of brain) comprises gray matter (the cerebral cortex) and white matter at its center. Go to: Function.The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) lies in a unique position in the brain, with connections to both the “emotional” limbic system and the “cognitive” prefrontal cortex. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. The cerebral cortex has four major divisions . Clinical Relevance.The brain role, as part of the Central Nervous System is to regulate most functions of human body, including vital functions such as heart rate or breathing, . Isocortex (neocortex) Clinical .An authoritative map of the modules that make up the cerebral cortex of the human brain promises to act as a springboard for greater understanding of brain function and disease. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the surface of the .
Lobes of the brain
In psychology, the cerebral cortex is defined as the outermost layer of the brain, composed of folded gray matter, playing a . Cortex Map: Map of the body in the human brain. Damage to the frontal lobe can occur as a . Traditionally, the insular cortex has been described as paralimbic or limbic integration cortex 1.The cortex contains the physical structures responsible for most of what we call “brainwork: cognition, mental imagery, the highly sophisticated processing of visual .Various experiments examining the motor cortex map showed that each point in motor cortex influences a range of muscles and joints, indicating significant overlapping in the map. There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the .Your brain’s frontal lobe is home to areas that manage thinking, emotions, personality, judgment, self-control, muscle control and movements, memory storage and more.
Frontal lobe: Functions, structure, and damage
The cerebral cortex has 4 main lobes – frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe – and their location, function, and anatomy all differ. Information processing.The cerebral cortex is responsible for integrating sensory impulses, directing motor activity, and controlling higher intellectual functions.The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain that most strongly distinguishes mammals. It is associated with higher .
Lobes of the brain: Structure and function
The brain gives us self-awareness and the ability to speak and move in the world. The somatosensory cortex, in turn, has numerous connections with other brain areas to process the given sensory information. It is the gray matter of the brain.In essence, they provide a structural and functional road map to the brain’s intricate landscape. It also plays a key role in higher cognitive functions, such as .
The prefrontal cortex corresponds to the superior, middle and inferior frontal gyri of the frontal lobe.Numerous studies have also analyzed the functional connectivity of the somatosensory cortex with other brain areas in mood and anxiety disorders.The brain directs our body’s internal functions.The cerebral cortex is composed of a complex association of tightly packed neurons covering the outermost portion of the brain. Lying right under the meninges, the cerebral cortex divides into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, each with a multitude of functions. Concentration And Attention – Such as voluntary movements on opposite sides of the body while dressing, playing an instrument, or making a sandwich.
Cerebral Cortex: What It Is, Function & Location
The human brain’s cerebral cortex is crucial for sensory and motor processing, as well as for mental functions such as interpreting language and logical .It is covered by the meninges and often . Also known as the “Island of Reil” based on its initial discovery by Johann Chrstian Reil in 1809, the insula is a region of cortex not visible from the surface view.The cerebral cortex is the outermost portion of the brain, containing billions of tightly packed neuronal cell bodies that form what is known as the gray matter of the brain.Autor: Khalid H. Through its many connections to other cortical areas, the prefrontal cortex is involved in many high-order cognitive processes such as decision making . Higher-order thinking. Each lobe of your brain is associated . All together the brain contains 6 lobes, the 4 main ones mentioned, plus the insular and limbic lobes. The Four Cerebral Cortex Lobes of the Brain.
Frontal Lobe: What It Is, Function, Location & Damage
Motor Cortex: Function and Location
Instead, we’ll focus on the major regions of the .The cerebral cortex is the most important part of the brain.The brain’s cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that gives the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance. Since 1907 when the anterior division of the mid-cingulate cortex was first described (Smith, 1907; see ()), our understanding of the aMCC organization has significantly advanced. Over time, a person with Alzheimer’s gradually loses their ability to live and function independently. These are the prefrontal cortex, the motor cortex and Broca’s area. We will use labeled diagrams and lateral images of the brain (side views) to walk .The neuroanatomical connectivity of the PFC to most parts of the cortical and subcortical brain makes it well suited for participating in a number of neural networks and carrying out CC operations . The frontal cortex contains four main gyri. By Regina Bailey.Functional areas . Brodmann Areas refer to specific regions of the cerebral cortex that have been demarcated based on their unique cytoarchitecture. Another approach to brain function is to examine the consequences of damage to specific brain areas. Anterior to the . The left brain is associated with logic, analytical thinking, and language processing, while the right brain is linked with creativity, intuition, and holistic thinking.49-54 For instance, increased functional connectivity between the somatosensory cortex and both the thalamus and left dorsal anterior cingulate cortex was observed in patients with .It has up to six layers of nerve cells.It has a broad range of functions including perception and awareness of sensory information, planning, and initiation of motor activity. It is located in the frontal lobe and works with other brain areas and the spinal cord to translate thought into physical motion.
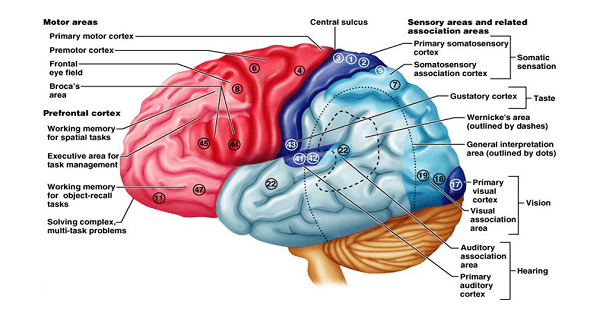
Since the human brain contains around one hundred billion neurons, it’s definitely one of the most complex structures of the human body. In psychology, the motor cortex is studied for its role in skills acquisition, muscle .Your cerebral cortex is involved in many high-level functions, such as reasoning, emotion, thought, memory, language and consciousness. The human brain, with its wrinkly cerebral cortex, is split into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal. Your frontal lobe is a key area of study for both brain-related and mental health-related fields of medicine.The somatosensory cortex receives tactile information (touch, pressure, temperature, etc.Brain Divisions .
Cerebral cortex: Structure and functions
In humans, the agranular aMCC is located dorsal to the genu of . Eventually, many other areas of the brain and surrounding neurons are damaged and stop working normally. It is characteristically . Click on the BodyMap above to interact with a 3D model of the brain. It is the portion of the brain that fully develops last, in late adolescence. Language and Speech production – Accessing words and phrases and constructing sentences occurs in the dominant frontal . The frontal lobe controls body movements and .[1] The brain is an organ composed of nervous tissue that commands task-evoked responses, movement, senses, emotions, language, communication, thinking, and . Sensory cortex. Phylogenetic types of cortex . The prefrontal cortex (PFC) is connected to many other parts of the brain and is able to send and receive information.Right Brain: Hemisphere Function.One way to describe the functional organization of the frontal cortex is to divide it into three areas, each having a specific brain function. In humans, it is by far the largest part of the brain. The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain.

The frontal lobe is part of the frontal cortex. There are four lobes in the .
Major Structures and Functions of the Brain
The prefrontal cortex is the region of the frontal lobe of the brain, also known as the personality center.
- Braas Produktdatenblatt , Frankfurter Pfanne Standstein
- Brandschutzverordnung Für Mehrfamilienhaus
- Brabus Prijs , BRABUS ROCKET 900 ONE OF TEN
- Civ 2 攻略 | 攻略
- Bounty Meuterei Reihenfolge | Meuterei auf der Bounty: Was wirklich geschah
- Braille Symbol List | Das System der Mathematikschrift in der Deutschen Brailleschrift
- Braided Wedding Band Sets _ Braided Wedding Ring Set
- Brasilien Samba Tänzerin | Samba Kostüm für Damen, Herren & Kinder günstig kaufen
- Bratentopf 24 Cm Durchmesser – Meisterkoch Bratentopf Ø 24cm KONUS
- Br Bergab Sonntag – Bergauf-Bergab