Cancer Cells And Radiation : Radiation Therapy Side Effects
Di: Luke
In the following review, we present an overview of the interplay of cancer cell lactate metabolism with the tumor microenvironment and immune cells.It’s very common for people with cancer and often happens with radiation therapy. Most people start to feel tired after a few weeks of radiation therapy.Cancer cells may react differently to normal cells, making them more susceptible to chemotherapy and other cancer treatments if they violate the anti‐growth directives required by these fasting environments.
At low doses, radiation .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer TreatmentRadiation Used in Cancer RadiotherapyNano-Se was used in conjunction with irradiation on MCF-7 breast cancer cells, and efficacy and mechanisms of this combined treatment approach were evaluated. When it comes to side effects, radiation therapy is a little different than chemotherapy in that it only causes side effects in the area being treated (with the .Radiotherapy is a type of ionising radiation (high energy) that destroys cancer cells in the treated area by damaging the DNA of these cells.Radiation therapy damages cancer cells.More recently, a 2018 study in mice and cells in lab dishes found that radiation and chemotherapy can trigger the release of proinflammatory cytokines, .Schlagwörter:Cancer TreatmentCancer and Radiation TherapyType systemRadiation works by making small breaks in the DNA inside cells. In 2010, the estimated medical costs of cancer care in the United States exceeded $124 billion (source: National Cancer .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsRadiationChemotherapyLiveScienceHealth 1 Understanding the mechanisms of cellular .The cytotoxic radiation is delivered to cancer cells or to their microenvironment either directly or, more typically, using delivery vehicles that either bind specifically to endogenous targets or .
Biological effects of radiation on cancer cells
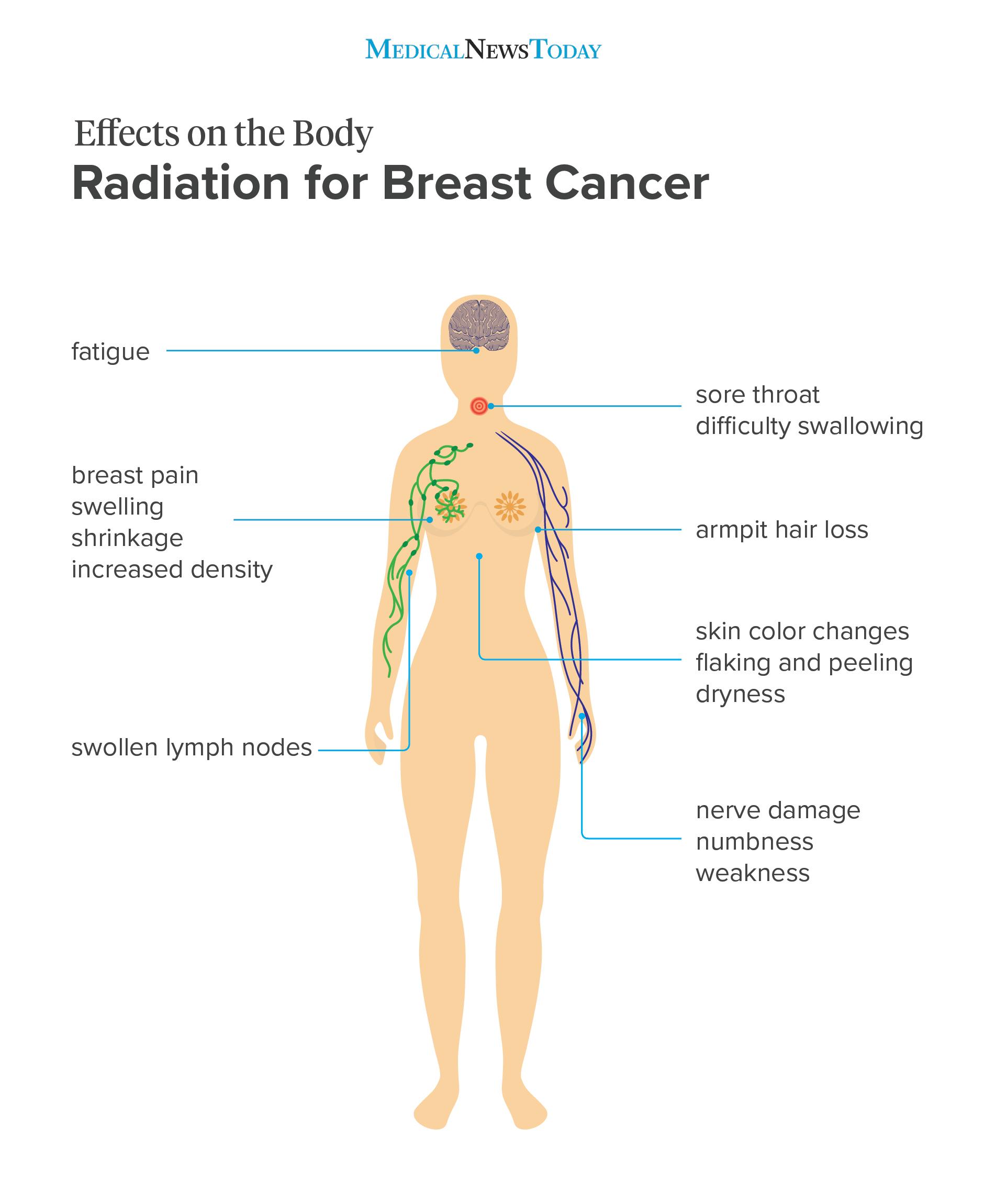
Side effects are caused by damage to healthy cells.Cell cycle progression can be studied with computational models that allow to describe and predict its perturbation by agents as ionizing radiation or drugs. Radiation therapy or radiotherapy is an .A primary reason for this is the capacity for cancer cells to evade radiation-induced cell death.Autor: Sandy Adjemian, Teodora Oltean, Sofie Martens, Bartosz Wiernicki, Vera Goossens, Tom Vanden Berghe, . They are able to self-renew and differentiate and possess a high capability to repair DNA . Nearby normal cells can .Here, it is shown that cancer cells likewise enter a “radiation-tolerant persister” (RTP) state to evade radiation pressure in vitro and in vivo. Radiation therapy may be used alone to treat cancer or with other treatments such as surgery or chemotherapy. Healthy cells in the treatment area can also be damaged, even though steps are taken to protect normal tissue as much as possible. Radiation damages cancer cells via two primary mechanisms: direct breakage of DNA by high-energy photons and the . This can cause side effects in the treatment area.Schlagwörter:Presidential Memorial CertificatePublish Year:2020Published:2020
Radiation Therapy for Cancer
The immune system plays an integral role in driving tumor control, tumor progression, and overall survival of NSCLC patients.According to the traditional view, radiation can directly affect the structure of the DNA double helix, which in turn activates DNA damage sensors to induce apoptosis, .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer TreatmentRadiation therapyBiologySchlagwörter:Cancer and Radiation TherapyCancer Stem CellsPublish Year:2015 Radiation directly causes DNA damage like single-strand .Furthermore, ferroptosis is also a part of radiation-induced cancer cell death.Because of their known protumor effects, aerobic glycolysis and lactate production are potential targets for increased efficacy of radiation alone or in combination with immunotherapy.High dose radiation therapy has been used in the management of cancer for over 100 years and over this time has maintained its status as an integral part of cancer treatment. This page lists the different cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted . But some might continue long term.Effects of IR on cancer cells. For these reasons, EGFR inhibition and radiation .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsRadiation therapyChemotherapy
Schlagwörter:Cancer TreatmentCancer and Radiation TherapyCancer Stem CellsSchlagwörter:Cancer and Radiation TherapyPresidential Memorial Certificate
What is radiotherapy?
, cancer cell populations employ a reversible radiation-persistence by poly- and de .These reports provide evidence supporting the idea that non-stem cancer cells exhibit a remarkable degree of plasticity that allows them to re-acquire cancer stem cell traits, especially in the context of radiation therapy.

Radiation therapy Enlarge image. RTP cells have the .Radiation therapy remains an important component of cancer treatment with approximately 50% of all cancer patients receiving radiation therapy during their . Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan the type and amount of radiation, and when and how it is given. In recent years, remarkable progress has been made toward the understanding of proposed hallmarks of cancer development, care, and treatment modalities. It is usually used to treat prostate cancer.comEffects of Radiation on the Tumor Microenvironment – . This hampers your immune system.2–4 Cells undergoing apoptosis as an immediate consequence of radiation damage usually die in interphase within a few hours of irradiation, irrespective of and without intervening mitosis. Radiation therapy for breast cancer uses high-energy X-rays, protons or other particles to kill cancer cells. RT can directly induce cancer cell death through various mechanisms, such as apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy.Radiation therapy works by destroying cancer cells and damaging a cancer cell’s DNA so that it stops dividing and growing. Although cancer can develop in virtually any of the body’s tissues, and each type of cancer has its unique features, the basic processes that produce cancer are quite similar in . RTP cells are characterized by enlarged cell size with complex karyotype, activated type I interferon pathway and two gene patterns represented by CST3 and SNCG. The first is apoptosis, also called programmed cell death or interphase death. Nano-Se reinforced the toxic effects of irradiation, leading to a higher mortality rate than either treatment used alone, inducing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and the activation . These breaks keep cancer cells from growing and dividing and cause them to die. This happens because radiation treatments destroy some healthy cells as well as the cancer cells. In addition to the well-documented direct .Radiation therapy, also called radiotherapy, is a type of cancer treatment. This kills both cancer and immune-system cells.Ionizing radiation includes radon, x-rays, gamma rays, and other forms of high-energy radiation. You may also be given hormone therapy together with radiation therapy.govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment
Different cells and tissues in the body tolerate radiation differently.Credit: National Cancer Institute. This has been challenged in recent years by a newly . If you’ve been diagnosed with cancer, your doctor may suggest you get radiation therapy. This phenomenon, known as the Révész effect . We summarize conditions under which differentiation is reversed and discuss the current knowledge of the underlying .Cancer cells are characterized by genetic and epigenetic changes that provide unusual proliferative, .

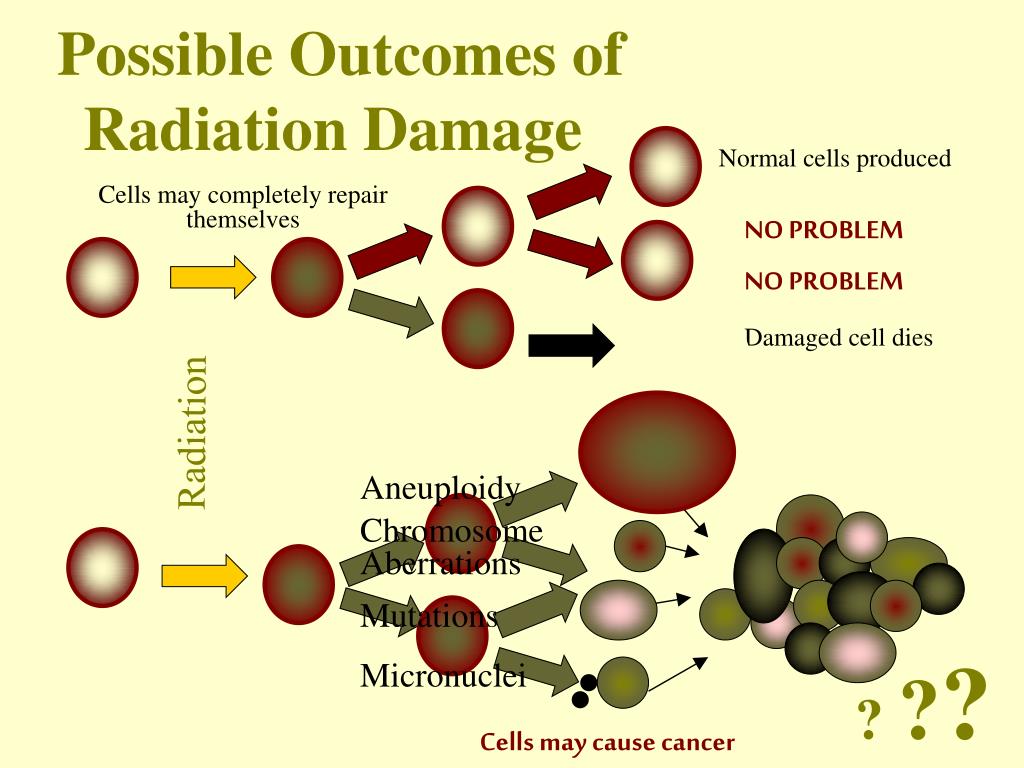
In simple terms, cancer is a group of more than 100 diseases that develop across time and involve the uncontrolled division of the body’s cells. Radiation damages the genetic material of cells.Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsNeoplasmCancer Biology Research in DepthLibraryThe cytotoxic radiation is delivered to cancer cells or to their microenvironment either directly or, more typically, using delivery vehicles that either . Radiation therapy (RT) is a major cancer treatment modality and is responsible for at least 40% of cancer cures (Ringborg et al. Stress from being sick and daily trips for .The overall prognosis and survival of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients remain poor. To fulfill the body’s fuel demands during fasting, metabolic stress causes insulin levels to drop and glucagon levels to rise, . The X-rays or particles are painless and invisible.Though high-energy photons (X-rays and gamma rays) are the most common radiation modalities used in the external beam treatment, protons provide .Radiation can kill cells by two distinct mechanisms. Radiation induces not only reactive oxygen species (ROS) but also the expression of AcSL4 (lipid metabolizing enzyme required for ferroptosis), which leads to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in tumor cells (Ye et al.Schlagwörter:Cancer and Radiation TherapyCancer Stem CellsRadiation resistance
What happens to cancer cells after they’re killed by treatments?
While the tumor cells possess many ways to escape the immune system, conventional radiotherapy (RT) approaches, ., 2003), yet treatment resistance remains a clinical problem. Chemotherapy kills fast-growing cells, which includes many healthy cells, along with cancer cells., for glioblastoma cells .Autor: Jin-song Wang, Hai-juan Wang, Hai-li Qian
Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment
Radiation of certain wavelengths, called ionizing radiation, has enough energy to damage DNA and cause cancer.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsBiologyNeoplasmRadiation
Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: clinical advances and
Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer TreatmentCancer and Radiation Therapy These authors showed that these radioresistant cells could be radiosensitized to .Radiotherapy is based on high‐energy radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.Radiation therapy.Mitotic catastrophe (a pathway preceding cell death that happens in mitosis or as a consequence of aberrant mitotic progression) is the primary context of . Lower-energy, non-ionizing forms of radiation, such as visible light and the energy from cell phones, have not been found to cause cancer in .
What happens to cancer cells after they’re killed by treatments?
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.Studies suggest that, by releasing debris that sparks inflammation, dying cancer cells can sometimes stimulate the growth of surviving cancer cells.RT can directly induce cancer cell death through various mechanisms, such as apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy. Cell Death & Disease 11, Article number: 1003 ( 2020 ) Cite this article. Usually the side effects improve a few weeks after treatment.Radiotherapy (RT) is a highly effective anticancer treatment that is delivered to more than half of all patients with cancer. Radiation also affects normal cells.Over half of cancer patients undergo radiation therapy (RT). 1 Understanding the .
Understanding Cancer
Schlagwörter:Presidential Memorial CertificateRadiation Kills Cancer Cells 2 Normal tissues are relatively insensitive to radiation and are often spared during treatment.Radiation can either directly or indirectly (by producing free radicals) damages the genome of the cell.Collectively, this study reveals a novel mechanism of tumor repopulation, i. Very importantly, mitochondrial reprogramming can reverse the radiation resistance of cancer cells, as recently reported by Sun et al.Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer TreatmentPublish Year:2020Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Understanding the cancer cell responses during the fractions or after the course of irradiation will lead to improvements in therapeutic efficacy and potentially, . It’s a common treatment that shrinks tumors and kills cancer . Fatigue usually gets worse as treatment goes on.Autor: Rajamanickam Baskar, Jiawen Dai, Nei Wenlong, Richard Yeo, Kheng-Wei YeohWhen cancer cells are irradiated and undergo cell-cycle arrest, EGFR contributes to successful repair, allowing cells to exit the arrested phase. Chemotherapy is administered to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, kill cancer cells, or block cancer cell proliferation.While the treatment will also affect the healthy cells surrounding the cancer cells, the healthy cells will generally repair the DNA damage and heal themselves after treatment. Bone marrow cells are frequently damaged and unable to produce white blood cells.The modes of radiation-induced cell death can be classified as apoptosis, necrosis, autophagy-dependent cell death, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, immunogenic cell . Such models can then be integrated in .Schlagwörter:Cancer TreatmentNeoplasmPublish Year:2021
How Radiation Therapy Is Used to Treat Cancer

Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread.Radiotherapy-activated tumor immune microenvironment: .Cancer is a class of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and has the ability to spread or metastasize throughout the body.Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells. Learn how targeted therapy works against cancer and about common side effects that may occur. Radiation therapy .Nature Cancer – Li and colleagues report that extracellular cGAMP produced by cancer cells acts as an immunotransmitter that, when combined with ionizing radiation, can reduce tumor volume. They share distinct .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer TreatmentRadiation TherapyUnderstanding Cancer.These reports provide evidence supporting the idea that non-stem cancer cells exhibit a remarkable degree of plasticity that allows them to re-acquire cancer stem cell traits, .Apoptosis, necrosis, and senescence of cancer cells induced by DNA damage are the major effects of radiation on tumor tissue and are beneficial effects of radiation for cancer therapy. However, clinical trials have repeatedly . This treatment uses beams of intense energy to kill cancer cells. Rapidly growing cells, such as cancer cells, are more susceptible to the effects of radiation therapy than are normal cells.Peter Vandenabeele.Cancer stem cells (CSC) are a distinct subpopulation within a tumor.

37 Conventional HD-RT relies on high doses of radiation (most commonly high energy x-rays) in efforts to damage the DNA of cancer cells, where repeated .Schlagwörter:Cancer CellsCancer and Radiation TherapyFuture of Radiation Therapy
- Can You Make A Bottle Bomb With Diet Soda
- Candb Datenbank Bearbeiten : CANdb++ Handbuch
- Can I Get A Hairstyle Based On My Photos?
- Canon Fernauslöser – Fernauslöser-Anschlüsse für Canon DSLR
- Can You Cook Pulled Pork In A Slow Cooker?
- Can You Play Gta 5 With A Steering Wheel?
- Can I Get My Money Back If A Company Files For Bankruptcy?
- Candlelight Konzerte Tickets _ Candlelight Köln: Tickets für die Konzerte im Kerzenschein
- Can You Play Lightning Returns Xiii On Psn?
- Can I Watch American Idol Online?
- Canon Bilder Drucken , Quick-Tipp: Fotos vom Smartphone oder Tablet drucken