Chemical Reactions Of Alcohols
Di: Luke

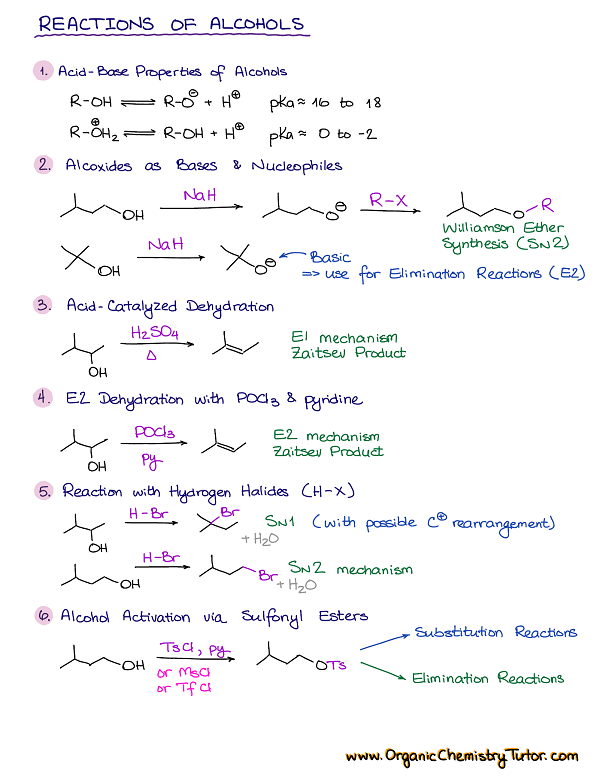
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized by any of a number of reagents, including CrO 3 in aqueous acetic acid and KMnO 4 in aqueous NaOH, but . Alkanes are saturated . The addition of RMgX on carbonyl compounds, along with hydrolysis gives us alcohols.The alcohol is heated under reflux with an excess of the oxidizing agent.The consequences of alcohol metabolism include oxygen deficits (i.Addition of Alcohols to form Hemiacetals and Acetalschem.Chemical reactions in alcohols occur mainly at the functional group, but some involve hydrogen atoms attached to the OH -bearing carbon atom or to an adjacent carbon atom.The dehydration reaction of alcohols to generate alkene proceeds by heating the alcohols in the presence of a strong acid, such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid, at high temperatures. The Grignard reagent is basically an organometallic .Three reactive sites for alcohol are carbon – hydroxyl group bond (C – OH bond), oxygen – hydrogen bond (O – H bond) and the hydrogen attached to α-carbon. Alcohols can also react with acyl chlorides to form carboxylate esters as a synthetic product. The required range of reaction temperature decreases with increasing substitution of the hydroxy-containing carbon: 1° alcohols: 170° – 180°C.Alcohol Reactions | ChemTalk. Consequently, the covalent bonds of this functional group are .General reaction for the preparation of alcohols by this method is given below: R-X + KOH (aq) → R-OH + KX. 1, two—dehydration and oxidation—are considered here. Alcohol can behave as both a nucleophile and an electrophile in reactions involving alcohol.7: Reactions of Alcohols. alcohol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.Chemical Reactions of Alcohol.Primary alcohols are oxidized either to aldehydes or carboxylic acids, and secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones, but tertiary alcohols don’t normally react with most oxidizing agents.
Reactions of Alcohols (GCSE Chemistry)
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids, depending on the reaction conditions. Secondary alcohols can be made to react, but the . Unlike the alkyl halides, this group has two reactive covalent bonds, the C–O bond and the O–H bond.5 Reactions of Alcohols | The Basics of General, .Alcohols react with oxygen in the air when ignited and undergo complete combustion to form carbon dioxide and water.The most common reactions of alcohols can be classified as oxidation, dehydration, substitution, esterification, and reactions of alkoxides. Reaction with HNO 3.Making esters from alcohols . Alcohols are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been . These reactions include: conversion of alcohols into alkyl halides. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids, the alcohol is first oxidized to an aldehyde, which is then oxidized further to the acid. The triiodomethane (iodoform) reaction . The combination of HCl and ZnCl2is known as the Lucas reagent. However, tertiary haloalkanes in this reaction give mainly alkenes due to dehydrohalogenation.
Alcohol
R-OH + HO-NO 2 → R-O-NO 2.3) Preparation of Alcohols from Grignard Reagent.1 Structure and Classification of Alcohols. Describe the result of the oxidation of a primary alcohol.discuss the reactions of alcohols that have been introduced in previous units.Reactions of alcohols involve oxidations, substitutions, and eliminations giving you a significant advantage in synthesis and functional group modifications.Catalytic oxidation is a reaction with oxygen that occurs more rapidly and at a lower temperature in the presence of another substance (called a catalyst) than it would in the absence of the catalyst.
R 2 C-OH alcohol + HCl→ R 2 CCl. The full equation for the oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid is: 3CH3CH2OH + 2Cr2O2−7 + 16H+ → 3CH3COOH + 4Cr3+ + 11H2O (17.
Reaction of Alcohols
We will also cover the different types of alcohols reactions that can .Give two major types of reactions of alcohols.

The catalyst only speeds up the reaction.Several important chemical reactions of alcohols involve only the oxygen-hydrogen bond and leave the carbon-oxygen bond intact. When alcohols react with sodium, a salt will be formed plus hydrogen; bubbles of hydrogen gas will be seen. In reactions in which the link between O and H is broken, alcohols act as nucleophiles.Primary alcohols react in a similar fashion except the free cation is not generated, and the substitution is of S N 2 type.7: Determining Alcohol Classifications in the Lab – alternate reactions Qualitative chemical texts to determine alcohol classification have been developed using the differences in chemical reactivity between primary .Acid/Base properties of alcohols.Organic Chemistry. We’ve already seen several reactions of alcohols—their conversion into alkyl halides and tosylates in Section 10. The poor electrophilicity of alcohols can be improved by converting the hydroxyl group into a tosylate ester with higher reactivity for subsequent chemical transformations. Reaction with Carboxylic Acid (Esterification) The reaction of the carboxylic acid with an alcohol and an acid catalyst leads to the formation of ester (along with water).
It can be used over and over again. Alcohols, like water, are both weak bases and weak acids. The use of this reaction to detect the presence of the CH 3 CH (OH) group .
Chemical Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Secondary, tertiary, allylic, and benzylic alcohols appear to react by a mechanism that involves the formation of a carbocation, in . One of the commonly employed silyl ether .As with most E1 reactions, tertiary alcohols react fastest because they lead to stabilized, tertiary carbocation intermediates. Of the three major kinds of alcohol reactions, which are summarized in Figure 3. Of the three major kinds of alcohol reactions, which are summarized in Figure 14.The E2 elimination of 3º-alcohols under relatively non-acidic conditions may be accomplished by treatment with phosphorous oxychloride (POCl 3) in pyridine. The salt formed from the reaction with sodium and ethanol is called sodium ethoxide. conversion of alcohols into . Mainly the reaction between alcohols and carboxylic acids to produce esters, together at a brief look at making esters from the reactions between alcohols and acyl chlorides or acid anhydrides.Learn about the types and properties of alcohols, and how they can be transformed into other compounds by various reactions. oxidation of alcohols. Secondary haloalkanes give a mixture .Reaction of an alcohol with a mesyl chloride to create a ethyl mesylate Reaction of alcohol with a tosyl chloride to create a ethyl tosylate Silyl Ether Protecting Groups. The acid ionization constant (Ka) of ethanol is .This procedure is also effective with hindered 2º-alcohols, but for unhindered and 1º-alcohols, an S N 2 chloride ion substitution of the chlorophosphate intermediate competes with . Alcohol molecules react in similar ways with different substances. The transformation of R-OH into R-X now allows for any other transformation of R-X via SN1 or SN2 reactions.orgEsterification (Alcohol & Carboxylic acid) – Reactions . This is similar to the reaction of water with sodium, except it is far less violent.Alcohols and Sodium.
Alcohol Reactions.3: Alcohol conversion to Esters – Tosylate and Carboxylate.Chemical reactions in alcohols occur mainly at the functional group, but some involve hydrogen atoms attached to the OH-bearing carbon atom or to an adjacent carbon atom. while secondary alcohols follow a SN1 mechanism as shown below. We can obtain the three types of monohydric alcohols (primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols) by using Grignard reagents and carbonyl compounds.
Alcohols
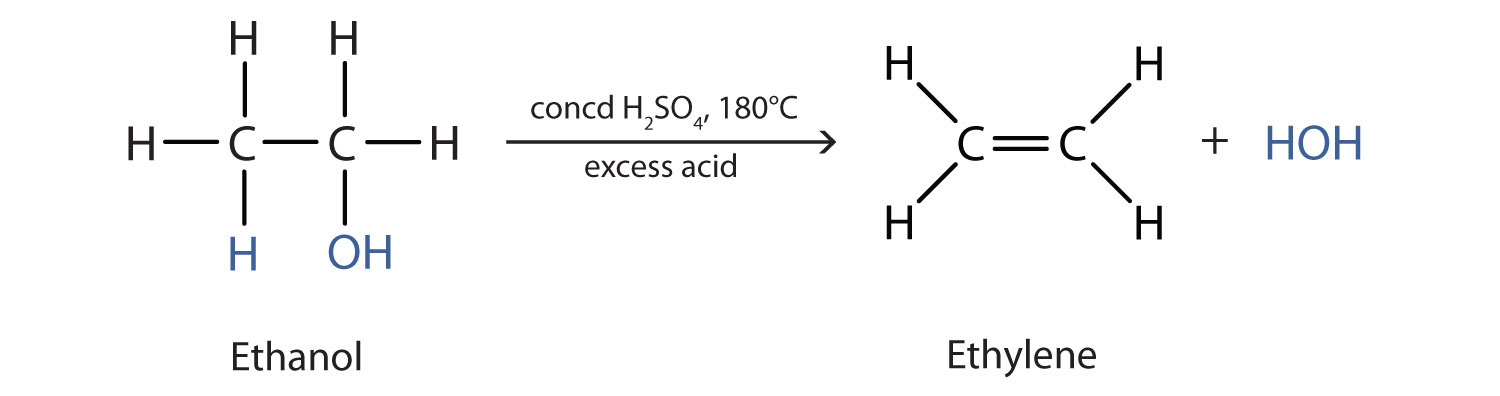
The electronegativity of oxygen is substantially greater than that of carbon and hydrogen. The equation for the complete combustion of methanol is: 2CH 3 OH (l) + 3O 2 (g) → 2CO 2 (g) + 4H 2 O (l) An important example is salt formation with acids and bases. 1 oalcohols follow and SN2 mechanism, 156. Some of the common names reflect a compound’s classification as secondary ( sec -) or tertiary ( tert -).docx Page 12 Limitations of use of H-X 1) Only works for H-Cl and H-Br 2) Low chemical yields for primary and secondary alcohols 3) Often observe competing elimination 4) Carbocations can .
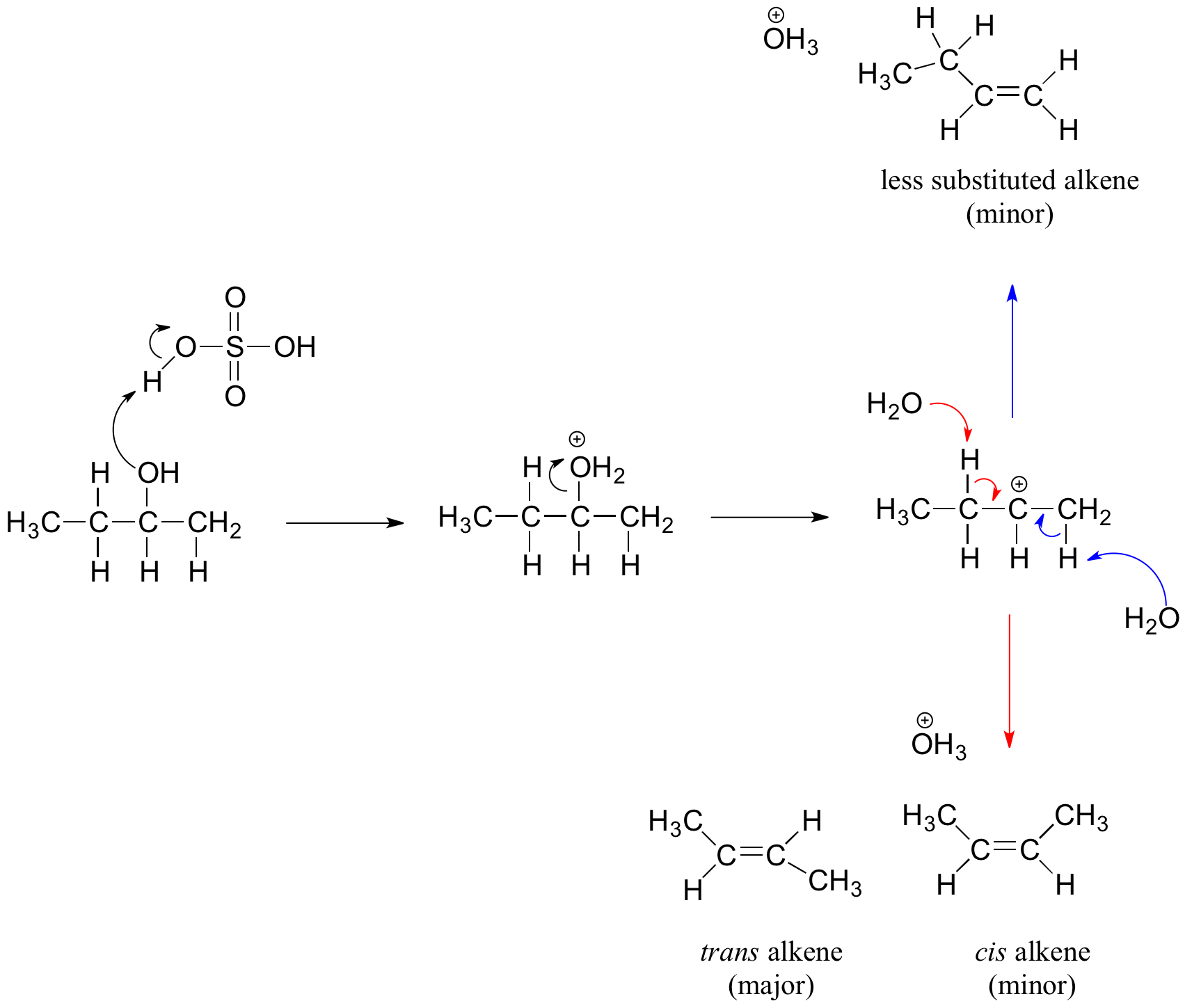
Mechanisms of the Reactions of Alcohols with HX. Reactivity of Alcohols.3 oAlcohols react with HCl without the need for ZnCl2.Reactions of alkenes [edit | edit source] See also: For information about alkenes and drawing alkenes Alkene molecules are unsaturated hydrocarbons because they contain 2 fewer hydrogen atoms than the alkane with the same number of carbon atoms and also have a carbon double bond instead of all single bonds. C2H5Br + KOH → C2H5-OH + KBr. It examines in some detail their simple physical properties such as solubility and boiling points. The functional group of the alcohols is the hydroxyl group, –OH. Describe the result of the oxidation of a secondary alcohol. It doesn’t get used up in the process. Ch11 Reacns of Alcohols (landscape).Reactions of Alcohols.ukEmpfohlen basierend auf dem, was zu diesem Thema beliebt ist • Feedback
Alcohol (chemistry)
Chapter 11: Reactions of Alcohols
Its general formula is R 3COH.comEmpfohlen basierend auf dem, was zu diesem Thema beliebt ist • Feedback Mainly the reaction between alcohols and carboxylic acids to produce esters, together at a brief look at making esters from the reactions . An aldehyde is obtained if an excess amount of the alcohol is used, and the aldehyde is . That’s because, as we will see, the reactions of alcohols often fall into these categories.4 Reactions of Alcohols, two—dehydration and oxidation—are considered here. When alcohols are added to water, they dissolve to give neutral solutions.
17: Alcohols and Phenols
Protecting groups serve as chemical modifications that shield hydroxyl groups in organic compounds from acid-base reactions. The discussion begins with an outline of the nomenclature of alcohols and phenols.As a functional group, alcohols are introduced fairly early in organic chemistry.This reaction has been used historically as a way of distinguishing between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. Of the three major kinds of alcohol reactions, which are summarized in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), two—dehydration and oxidation—are considered here.Chemical reactions in alcohols occur mainly at the functional group, but some involve hydrogen atoms attached to the OH-bearing carbon atom or to an adjacent carbon . In reactions in which the .Reactivity of Alcohols. Several important chemical reactions of alcohols involving the O-H bond or oxygen-hydrogen bond only and leave the carbon-oxygen bond intact.Alcohols can undergo a wide variety of reactions, and because of this reactivity and because they can be prepared in a number of different ways, alcohols occupy an important position in organic chemistry. We review the physical properties of these compounds, and . An important example is salt formation with . Primary haloalkanes give a good yield of alcohol. Find examples, mechanisms, FAQs and . In this article we will talk about alcohols and their properties. Supplemental Modules (Organic Chemistry) Alcohols.When alcohols react with air (and heat), carbon dioxide and water are produced.dehydration of alcohols – chemguidechemguide. Alcohols react with sodium to form a salt.1) 3 C H 3 C H 2 O H + 2 C r 2 O 7 2 − + 16 H + → 3 C H 3 . These designations are not used in the IUPAC nomenclature system for alcohols., hypoxia) in the liver; interaction between alcohol metabolism byproducts and other cell components, resulting . In reactions when the connection between C and O is disrupted, alcohols can act as electrophiles. When the reaction is complete, the carboxylic acid is distilled off. This page defines an alcohol, and explains the differences between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. There is oxidation, accompanied by gas evolution (slow but progressive) in this reaction. Consequently, the covalent bonds of this . Their reactions, however, are usually not covered until near the end of Org 1 – at least after subjects like substitution and elimination reactions have been explored.
Alcohols — Organic Chemistry Tutor
Overview
Alcohol Reactions
1 names and classifies some of the simpler alcohols.
- Check 24 Urlaub Griechenland _ Heraklion Urlaub günstig buchen » Bis zu 60% sparen
- Check In Euroairport Online – Check-in
- Chennai Hauptstadt _ Hauptstädte Europas Quiz
- Chelsea Champions League | 2021 Champions League
- Chest Workout Home , The Best Calisthenics Chest Workout Routine
- Chiemsee Sportartikel _ Home
- Check My Application Status Canada
- Chest Supported Row Exercises _ Know Your Row: The Pros and Cons of 8 Different Back Exercises
- Charlotte Bobcats – Nine defining moments in Charlotte Bobcats history
- Checkliste Nachweisgesetz , Neues Nachweisgesetz 2022: Checklisten für Arbeitgeber
- Chemisches Element Leichtmetall 5 Buchstaben
- Chat Room Für Erwachsene : Teenchatroom
- Chevrolet Colorado Pick Up _ Chevrolet Colorado
- Chemie Experimente , Experimente