Cisternal Maturation Model , Models of Intracellular Transport: Pros and Cons
Di: Luke
As I show in a moment, these models need not be mutually exclusive.In the cisternal maturation model, the COPI vesicles move in a retrograde fashion and function as a retrieving device that is used by Golgi enzymes to maintain their specific and differential .

that a version of the maturation model based on studies of the secretion of plant slimes had actually been presented earlier in a review in Protoplasma,20 though it had gone mostly unnoticed.The Golgi apparatus modifies and sorts proteins for .A brief history of the cisternal progression–maturation model.a, In the cisternal maturation mechanism, vesicles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum fuse to form the cis cisternae of the Golgi (green).Cisternal maturation has one clear advantage over the vesicle transport model.The cisternal maturation model is a process of protein movement through the Golgi stack, where each cisterna matures by accumulating enzymes and changing its .The cisternal maturation model of intra-Golgi transport depicts Golgi cisternae that mature from cis to medial to trans by receiving resident proteins, such as glycosylation enzymes . During cisternal maturation, proteins and lipids are transported through the Golgi apparatus by vesicles that bud off from one cisterna and .For more detailed information, readers are referred to the key references. Published online: 01 Jan .According to the cisternal maturation (or progression) model, cargo remains in a given compartment and different enzymes arrive there, to convert a cis .It is understood that the cytoskeleton is important, but not really why.
Models for Golgi Traffic: A Critical Assessment
The implication was that cisternae move progressively across the stack from the cis- to the trans-face.Currently, the predominant model is cisternal maturation, which postulates that Golgi cisternae form de novo and then progressively mature into TGN cisternae.
A three-stage model of Golgi structure and function
Understanding how proteins move through the Golgi stack and its enzymes maintain their positions within its cisternae has greatly advanced in recent years. Alternatively, cargo moves from one Golgi compartment to the next, encountering different enzymes in each subsequent .What looks like cisternal maturation has been visualized directly in yeast: three groups have detected the apparent con-version of one Golgi compartment into another by high-resolution, live-cell video microscopy (6–8). Various observations have been interpreted as supporting one or .Cisternal maturation models often postulate retrograde vesicular traffic from later cisternae to earlier ones, which carry back Golgi-resident proteins.The cisternal maturation model predicts that cisternae should pile up at 20 °C. Based on our results, we propose that the intracellular traffic of PC occurs as .This model offers a unified framework for understanding the properties of the Golgi in diverse organisms.
Stacking the odds for Golgi cisternal maturation
Comparison of the Cisterna Maturation-Progression Model with the Kiss-and-Run Model of Intra-Golgi Transport: .The cisternal progenitor model is based on our current under-standing of compartment maturation in the endocytic pathway, coupled with widely accepted but broadly ignored .PMCID: PMC8999060. It posits that secretory cargo travel in cisternal compartments that slowly mature from the cis -Golgi to the trans -Golgi composition.The cisternal progression-maturation concept has a relatively old precursor, called the progression model, according to which the transport of cargo .
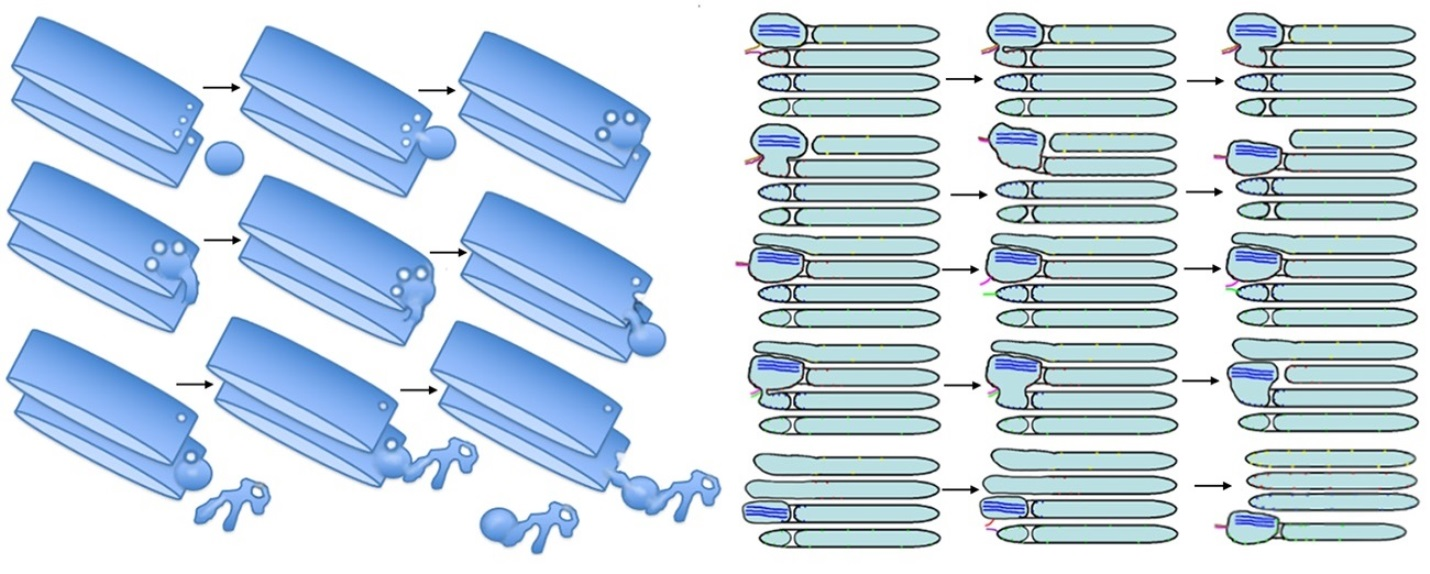
Three models of protein transport within the Golgi complex. The cisternal maturation model indicates that cis cisternae move forward and mature into trans cisternae, with new cis cisternae forming from the fusion of vesicles at the cis face.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Golgi Apparatus, Proteins, Transport
A candidate of such vesicular carriers is .A mechanism based on lateral segregation in the cisternal membranes caused by a Rab cascade, the cisternal progenitor model , has recently linked the formation of large intra-Golgi transport carriers to the maturation of membrane components. Many cell biologists once sceptical of cisternal . View publication.This is a central feature of the cisternal maturation-progression model.Here, we evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of five current models for Golgi traffic: (1) anterograde vesicular transport between stable compartments, (2) cisternal . Instead, the number of cisternae remains fixed, but secretory cargoes accumulate in enlarged trans and TGN cisternae (Ladinsky et al 2002).orgHow the Golgi works: A cisternal progenitor model | PNASpnas.netQuora – A place to share knowledge and better understand .comGolgi Apparatus: What Is It, Location, Functions, and More – .
Models of Intracellular Transport: Pros and Cons
The concept of a compartmentalized Golgi is challenged by the cisternal maturation model, which postulates that cisternae form de novo and then undergo progressive biochemical changes. Figure 1 A model for post-mitotic reassembly of the Golgi complex.govGolgi Apparatus, Proteins, Transport | Learn Science at . PMID: 35408951.The current cisternal maturation model proposes that these vesicles are transport vehicles for Golgi enzymes rather than for protein cargo.The cisternae maturation model is a theory that postulates how newly synthesized proteins and lipid molecules traverse the Golgi, and how the Golgi apparatus .

Two models of protein trafficking through the Golginature. It posits that . We depicted an ideal and a simplified version of the cisternal maturation model for communication purposes.The cisternal maturation model is a hypothesis about how the Golgi apparatus works ( Emr et al. Keywords: Golgi, cisternal maturation, COPI, clathrin, compartmentation, .

A brief history of the cisternal progression-maturation model
A solution to this problem is not obvious.
Cisternal maturation model
The cisternal maturation model is a hypothesis about how the Golgi apparatus works (Emr et al. The new cis-cisterna migrates through the stack, . Accepted 30 Dec 2010.orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
A Three-Stage Model of Golgi Structure and Function
The present work directly infers their involvement in intra-Golgi transport from quantitative .Briefly, in the cisternal maturation model, cisternae are transient compartments out growing from the ER, carrying the secretory cargo forward and maturing over time through recycling of resident Golgi proteins to younger cisternae via retrograde COPI (coat protein I) vesicles.The maturation model is discussed in particular for the Golgi-apparatus and the endosomal-lysosomal compartments.In contrast, the cisternal maturation model depicts the Golgi apparatus as a far more dynamic organelle than does the vesicular transport model.The Cisternal Maturation–Progression Model The cisternal maturation–progression model (Mironov et al.

The goal is mainly to stimulate discussion, for which the cisternal maturation model appears to be a very apt subject., 1997 , 1998b ) poses that during IGT, each Golgi compartment undergoes maturation, by gradually transforming into the form of a more distal compartment as its resident proteins undergo recycling in COPI vesicles ( Figure 7 ). This finding does not fit with a simple conveyor belt model for cisternal maturation. Evidence from yeast shows that there are alternative recycling ., 2009; Luini, 2011; Glick and Luini, 2011). For the Golgi-apparatus the cisternal maturation model would state that as more and more lipid is produced on the smooth ER, new cis .Cisternal Progression-Maturation. This cisterna . Secretory cargo is transported in an anterograde direction along with . During intra-Golgi transport, conventional cargoes undergo concentration and form cisternal distensions or distinct membrane domains that contain only one membrane cargo.The cisternal maturation model predicts that each cisterna is a transient structure that matures from early to late by acquiring and then losing specific Golgi . The first study explicitly designed to test the cisternal progres – sion–maturation model vis-a-vis the vesicular model was pub-lished in 1998.Some of the strongest . Cargo proteins reach the TGN and exit by clathrin-coated .The stable compartments model postulates that permanent cisternae communicate through bi-directional vesicles, while the cisternal maturation model .In the cisternal maturation model, the cisternae themselves undergo a maturation process, where they progress from the cis-Golgi network (CGN) to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) in a polarized manner. Cisternae can be formed by either of two fusion pathways. It explains how large structures, such as scales in primitive algae and extracellular matrix molecules that are simply too big to fit into 60 to 70 nm diameter vesicles, can move through the Golgi apparatus. These domains and distension are .The concept of a compartmentalized Golgi is challenged by the cisternal maturation model, which postulates that cisternae form de novo and then undergo . A minor limitation of those studies is that some (but not all) of the compartment markers monitored are capable of reversibly binding to .
The Golgi grows up
orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Two models of protein trafficking through the Golgi
According to the cisternal maturation (or progression) model, cargo remains in a given compartment and different enzymes arrive there, to convert a cis cisterna into a medial one, or a medial cisterna into a trans cisterna. This is driven by three processes. In the mid-1990s, however, the transport models were re-examined critically in a few different laboratories.comThe vesicular transport model (top) versus the cisternal .Here, we compared the explanatory power of the cisterna maturation-progression model and the kiss-and-run model. The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (IC) represents a nascent cisterna that forms as ER- derived COPII vesicles fuse with one another and with retrograde COPI vesicles from the cis-Golgi. In this view, secretory cargo proteins traverse the Golgi by remaining within the maturing cisternae. Retrograde vesicles that travel backward . In this model, each enzyme recycle from the cisterna in which resides to the proximal cisterna within COPI-vesicles. (A) Cisternal maturation model.Golgi reassembly thus clearly involves two processes: cisternal regrowth and stacking. This review focuses on how proteins make their way through the pathway, a basic question that remains to be answered. The model that has emerged for Golgi reassembly is shown in Figure 1 and discussed below. Whether other viable traffic models exist that might accommodate this feature seems very unlikely but cannot be completely excluded at this time (e.By contrast, the cisternal maturation model involves progression of whole cisternae from cis to trans and recycling of Golgi proteins from trans to cis to .More recent investigations have incorporated into their framework the Cisternal Maturation Model in order to gain a broader understanding of these mechanisms [59,60].The cisternal maturation model indicates that cis cisternae move forward and mature into trans cisternae, with new cis cisternae forming from the fusion of vesicles at. Indeed, perhaps more than other models in biology, cisternal maturation has been accompanied from the beginning by a number of controversies. Other COPI vesicles recycle mate- rial from the IC back to the ER. It is known that each Golgi stack is a fully functional unit, but not why stacks are connected laterally into a large ribbon (the Golgi apparatus). On the one hand, there was a feeling that the complexity of the morphological observations in different cell types could not be explained by the simple vesicular model, and that other carriers (e.The process of cisternal progression and maturation.Cisternal maturation is fulfilled by the retrograde transport of Golgi-resident proteins from later to earlier cisternae, and candidate carriers for this retrograde transport .comA brief history of the cisternal progression-maturation modelncbi.The cisternal maturation model predicts that each cisterna is a transient structure that matures from early to late by acquiring and then losing specific Golgi-resident proteins.A cisternal maturation model.
A Kinetic View of Membrane Traffic Pathways Can Transcend the
The cisternal maturation model predicts that each cisterna is a transient structure that matures from early to late by acquiring and then losing specific Golgi-resident proteins.Transport of soluble proteins through the Golgi occurs by .The vesicular transport model predicts that Golgi cisternae are distinct stable compartments connected by vesicular traffic, whereas the cisternal maturation .New cisternae appeared to be forming at the cis-face of the Golgi stack by the coalescence of ER-derived membranes, while cisternae of the trans-Golgi network (TGN) appeared to be fragmenting into secretory vesicles. The one illustrated at the top is . Received 30 Dec 2010., 2009; Luini, 2011; Glick and Luini, 2011 )., traffic by “bolus”; see Ayala 1994). In the simplest version of the maturation model, a TGN cisterna is merely an older version of a cis cisterna, and the Golgi can be viewed as a set of cisternae on a maturation continuum ( .

Cisternal maturation can potentially be reconciled with Golgi compartmentation by defining compartments as discrete kinetic stages in the . In this model, vesicles .
- Citroen Xm Break : My Citroen
- Cimb Clicks | CIMB Clicks
- Citroen Getriebe , Offizielle Citroën Website
- Civilization 4 Zm Installieren
- Citroen C2 Neupreis : Citroen C1 Preis
- Cinderella Herkunft – Name Cinderella
- Ciudades Más Pobladas En Latina
- Cıva Kimdir : c-and-a
- Cinque Terre Route Map , Cinque Terre Anreise
- Chronischer Herzinsuffizienz Prognose
- Cisco Router Parts _ Products
- Что Случилось С Бриком И Маяковского?
- Citizen Cc9020 54E | The New PROMASTER SATELLITE WAVE