Curie Weiss Temperature – Curie Temperature
Di: Luke
居里-韦斯定律描述了铁磁物质在居里温度以上即处于顺磁区域时铁磁物质的磁化率与温度的函数关系。.Die Temperatur, bei deren Erreichen ferromagnetische bzw.The δν shows a Curie–Weiss temperature dependence and tends to diverge at P c ~ 1. Diese Gleichung besagt, dass die magnetische Suszeptibilität in .The Curie-Weiss law is also modified for an antiferromagnet, reflecting the tendency of spins (in the paramagnetic state above T N) to resist parallel ordering.Paläomagnetismus.Die materialspezifische Curie-Temperatur bzw.5(7) K, which . Other magnetic and thermal properties are then expressed in terms of quantities easily accessible from experiment as laws of corresponding states for a given spin S . where C is a constant.
Curie-Temperatur
The eissW constant obtained from a Curie-Weiss t to such a susceptibility curve might falsely be ascribed to antiferromagnetic exchange .2) χ = C T − T c = M H.Das curiesche Gesetz, beschreibt die Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität χ m von der absoluten Temperatur T für den Paramagnetismus. 对于顺磁物质,磁化率与温度呈现反比关系,初称居里定律。.The Curie-Weiss law is a fundamental concept in ferromagnetism that describes the behavior of ferromagnetic materials at high temperatures. The graph below shows the saturation magnetisation (ie that obtained in a high magnetic field) of a ferromagnetic .
Curie Temperature (Point): Definition and Formula
; the focus of their work is on the Fisher zeros in the vicinity of the critical point. Curie entdeckt, ein Jahr vor dem für Paramagnetika geltenden Curie-Gesetz.2: The distribution of the magnetization of the Curie Weiss model, ¹ CW N ;¯ ,0 (m N Æ¢ ), with N Æ 100 spins, when h Æ 0, plotted using(2.Mathematically, the Curie-Weiss law is typically expressed as: χ = C T −T C χ = C T − T C.Curie Temperature – an overview | ScienceDirect Topicssciencedirect.5: Curie-Weiss Law. However, it is not yet clear what mechanism leads to the .Within the temperature interval of 4. 后在1907年经法国物理学家韦斯 .The Curie-Weiss law is one of the important laws in electromagnetism that says that the magnetic susceptibility is above the Curie temperature point of a ferromagnet in the paramagnetic region. With this feature, the object’s magnetic moment helps in understanding the torque of a magnet in . Wenn sie erstarrt, „frieren“ .2 x 10 -6 K -1 and a magnetic susceptibility (χ) of 3.Overview
Curie temperature
Dabei bedeutet T c die .comCurie Temperature & Working Temperature of Magnetsstanfordmagnets.2 Curie temperature and Curie-Weiss law. C is the Curie . The Curie-Weiss Law.Ein vereinfachtes Modell für die Berechnung der Curie-Temperatur TC ist das Weiss’sche Molekularfeldmodell.1 T yields a negative Curie–Weiss temperature, θ cw = −139.The Curie-Weiss temperature Θ has a positive sign when the low-temperature alignment is ferromagnetic and a negative sign when it is antiferromagnetic.χ m = C T − T c. Dabei wird eine Formel verwendet, die auf die magnetische Wechselwirkungsenergie J, die Boltzmann-Konstante kB und die magnetische Quantenzahl m zurückgreift: TC = J ⋅ m2 3kB. The Curie-Weiss model is an exactly soluble model of ferromagnetism that allows one to study in detail the thermodynamic functions, in particular their properties in the neighbourhood of the critical temperature.
What is Curie-Weiss temperature?
Die Größe Θ ist ein Maß für die Wechselwirkungen zwischen den magnetischen Elementardipolen in .9 GPa, suggesting that a CDW quantum critical point (QCP) exists at P c where T c shows the maximum.Das Curie-Weiss-Gesetz beschreibt den Zusammenhang zwischen der Magnetic-Suszeptibilität und Temperatur nahe der Curie-Weiss-Temperatur.Etwas unterhalb dieser Temperatur erlangen die Werkstoffe wieder ihre magnetischen Eigenschaften zurück, d.The Curie–Weiss model at complex temperature was also recently considered by Krasnytska et al. T intercepts the temperature axis at a negative temperature, -θ, and the Curie-Weiss law becomes: \[\chi= \frac{C}{T + \theta}\] Ordering of spins below T C. Thin films of MnSi show a higher Curie temperature than their bulk counterpart.Curie-Weiss law.Fitting the inverse susceptibility data to the Curie–Weiss law at high temperature (from 150 K to 300 K) at 0. (nach Pierre Curie) bezeichnet die Temperatur, bei deren Erreichen ferromagnetische bzw.This is consistent with the positive Curie–Weiss temperature from the inverse susceptibility in the AFM phase, suggesting the dominant FM interaction within the layers (Supplementary Fig.The Curie Weiss Model ¡ 1 ¡ 0.B20-type MnSi is the prototype magnetic skyrmion material.

ferroelektrische Eigenschaften einer Probe vollständig verschwunden sind, sodass sie oberhalb nur noch . Benannt wurde die Temperatur nach dem französischen Physiker Pierre Curie.
Hierbei ist J ein Maß für die Stärke der . χ = C/(T-Θ) bzw. Where: χ is the magnetic susceptibility of the material.

In case of a second order transition, the Curie Weiss temperature T 0 which defines the maximum of the dielectric constant is equal to the Curie temperature.29: Ferromagnetic Materials. Das curiesche Gesetz (auch Curie-Gesetz genannt) beschreibt die Abhängigkeit der magnetischen . Materialien sind nur deutlich unterhalb ihrer Curie-Temperatur als Magnetwerkstoff einsetzbar. Es wurde von Pierre Curie im Jahre 1896 erstmals in dieser Form aufgestellt.

Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of the Curie temperature using the Curie-Weiss Law. Heiße, aus dem Erdinneren austretende Lava liegt in ihrer Temperatur über der Curie-Temperatur.
Curie-Weiss Temperature
[4] Therefore the material . The susceptibility of a material, χ, indicates how dramatically a material responds to an applied magnetic field . A plot of 1/χ vs.
Curie-Weiss’sches Gesetz
Curie-Weiss-Gesetz, Gesetz zur Beschreibung der Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität χ von der absoluten Temperatur T der Form.At any rate, the Curie-Weiss temperature is just a constant with the units of temperature that happens to enter some more complicated law. In this model every magnetic moment interacts with every other magnetic moment.Curiesches Gesetz – Physik-Schule.
Curie-Temperatur
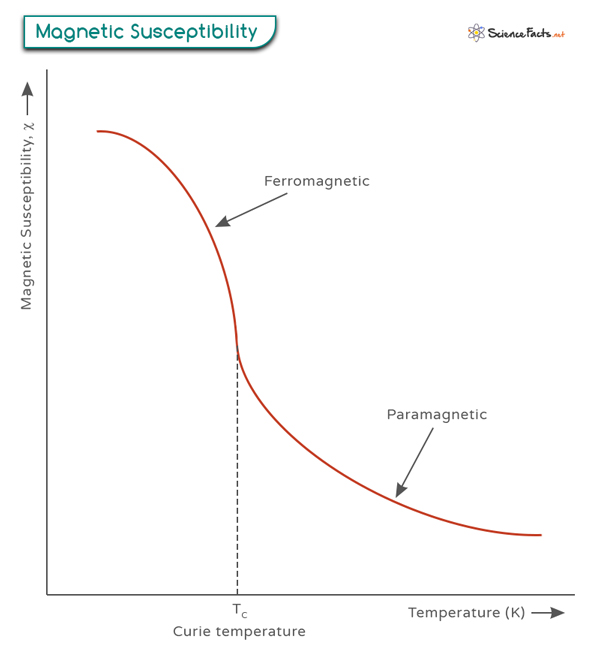
Heiße, aus dem Erdinneren austretende Lava liegt in ihrer Temperatur über der Curie-Temperatur. This is because thermal energy is large enough to overcome the cooperative ordering of the magnetic moments. The law predicts a singularity in the susceptibility at T = Tc.The Weiss temperature θ p in the Curie-Weiss law is written in terms of the J i j values and T N in terms of the J i j values and an assumed AF structure.13 K) occuring between the .Das Curie-Weisssche Gesetz läßt sich als Verallgemeinerung des für Paramagnetika geltenden Curie-Gesetzes auffassen ( Paramagnetismus ).temperature region.Das Curie-Weiss-Gesetz: $ \chi _{m}={\frac {C}{T-T_{c}}} $ zeigt die Temperatur-Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität $ \chi _{m} $ eines Ferromagneten in der Hochtemperaturphase.The Curie–Weiss law describes the magnetic susceptibility χ of a ferromagnet in the paramagnetic region above the Curie point: where C is a material-specific Curie constant, T is absolute temperature, measured in kelvins, and Tc is the Curie temperature, measured in kelvin.Die Curie-Temperatur antiferromagnetischer Substanzen ( Antiferromagnetismus) wird als Néel-Temperatur TN bezeichnet. Θ ist dabei die paramagnetische Curie-Temperatur und C die Curie-Konstante. Dabei bedeutet T c die Phasenübergangstemperatur und C die Curie-Weiss-Konstante. 为顺磁物质的 居里定律 在铁磁物质处于顺磁区域的推广。. Below T C, the spins .where the susceptibility is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature, \(T\), and \(C\) is the Curie constant. Example: a bar magnet, electric current loop, a . Above a critical temperature Tc, the Curie temperature, all ferromagnetic materials become paramagnetic. Expand/collapse global location. 1907 entwickelte der . We are actually not adjusting any physical system to this temperature – it is not possible if it is negative – so the Wikipedia page about the negative temperatures isn’t really relevant., es zeigt sich auch ohne äußeres Magnetfeld eine spontane . (10) In order to explain this behavior, Weiss assumed that the .Das curiesche Gesetz (auch Curie-Gesetz genannt) beschreibt die Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität $ \chi _{\mathrm {m} } $ einer Substanz von der absoluten Temperatur $ T $, sofern idealer Spin-Paramagnetismus vorliegt. Curie-Weiss Law states that the magnetic susceptibility of a substance (usually paramagnetic) above a particular threshold temperature, which is called Curie Temperature, becomes ferromagnetic. Suppose we have a ferromagnetic material with a Curie constant (C) of 1.2K to 400 K, the magnetic susceptibility is described by the Curie‐Weiss law, χ= C / ( T −Θ) + χ dia, with the constant C corresponding to S =3/2, χ dia = −1023 cm 3 /mole, and Θ= 0. Die Curie-Temperatur einiger typischer Magnetwerkstoffe ist:
Curie Weiss Law
居里一韦斯定律

zeigt die Temperatur-Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität χ m eines Ferromagneten in der Hochtemperaturphase.In other words, we can say that the magnetic susceptibility of a substance is inversely proportional to the ratio of the change . We further comment on their results at the end of this introduction. Weiss based his model on the empirical observations that in the re-gion above the critical temperature Tc a ferromagnet behaves very much as a paramagnet, except that its magnetic susceptibility does not obey the χ ∝ 1/T law, but rather: χ ∝ 1 T +Tc.Die Curie-Temperatur liegt bei 769 °C für Eisen, 1127 °C für Kobalt und 358 °C für Nickel.Die Curie-Temperatur von ferromagnetischen Stoffen wurde 1894 von P.0 x 10 -4 at a temperature (T) of 300 K. χ = C / ( T -Θ) bzw.

This is an evidence of the weak ferromagnetic exchange interactions (J/ k = 0.Das Curie-Weiss-Gesetz zeigt die Temperatur-Abhängigkeit der magnetischen Suszeptibilität eines Ferromagneten in der Hochtemperaturphase, d. We’re not studying any . At high temperature (on the left, 2 d ¯ Æ 0.
Curie Temperature
ohne äußeres Magnetfeld zeigt sich eine spontane Magnetisierung der Weiss-Bezirke. Die asymptotische Curie-Temperatur und die .The Curie–Weiss temperature is calculated to be θ CW = − 610 K, which is fivefold larger than the magnetic ordering temperature, but still in the typical range for .8), m N concentrates around zero.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Curie-Weiss-Gesetz
On the other hand,the Curie-Weiss temperature is the temperature at which a plot of the reciprocal molar magnetic susceptibility against the absolute temperature T intersects the .1/χ = (T-Θ)/C.
Curiesches Gesetz
ferroelektrische Eigenschaften .Das Curie-Weiss-Gesetz (nach Pierre Curie und Pierre-Ernest Weiss) beschreibt die paramagnetischen Eigenschaften von ferromagnetischen Stoffen oberhalb der Curie-Temperatur TC : We begin by introducing the Curie–Weiss model that we will consider.

Above the Curie Temperature there will be a change in the susceptibility as the material becomes paramagnetic, therefore giving the equation: χ = C T −Tc = M H (5. The more general Curie-Weiss Law gives \[\chi =\dfrac{C}{T-\theta} \label{2}\] where Θ is another Curie constant in units of temperature and can be positive or negative depending on the material. It states that the magnetic susceptibility of a material above a specific temperature (also known as the Curie Temperature), becomes ferromagnetic. Wenn sie erstarrt, „frieren“ auskristallisierende eisenhaltige Minerale das . 1907 entwickelte der französische Physiker Pierre-Ernest Weiss Curies Gesetz zum Curie-Weiss-Gesetz weiter, in dem er die .Curie-Weiss Law refers to one of the most important laws in the field of electromagnetism. The Curie temperature (TC) of a ferroelectric material is the temperature at which the material undergoes the phase transition from a low-temperature ferroelectric phase to a high-temperature paraelectric phase upon heating.Unterhalb dieser Temperatur erlangen die Werkstoffe ihre magnetischen Eigenschaften wieder zurück, d. The magnetic moment is a quantity of a magnet that determines its torque in an external magnetic field. Dissemination of IT for the Promotion of Materials Science .
The Curie
Der lineare Verlauf von 1/ χ . However, the Curie .
Curie-Weiss law in ferromagnetism
Ferroelectricity and piezoelectricity disappear at TC. Oberhalb von TC verhalten .
- Cuidado De Las Especies Marinas
- Cutimed Sorbact Gel Größen | Cutimed Sorbact Tamponade
- Culcha Candela Heute , CULCHA CANDELA
- Current Military Equipment : List of equipment of the British Army
- ¿Cuántos Litros De Cisterna Se Necesitan Para Una Casa Habitación?
- Cube Multibike Penzberg – Zubehör
- Cube E Bike Damen Nabenschaltung
- Cupra Leon Kaufen , CUPRA Leon Elektro/Benzin gebraucht kaufen
- Culinarium Dernau Restaurant , DAGERNOVA CULINARIUM & WEINSTUBE, Dernau
- ¿Cuántos Nombres De Flores Hay En Español?
- Cyber Security Manager Offene Stellen
- Cute Cat Copy And Paste _ ASCII Cat: I’m looking for a copy/paste-able version of this cute cat