Dna Replication Of Leading Strand
Di: Luke
A preponderance of evidence supports the following division of labor at the replication fork: The Pol α-primase complex primes synthesis on both the leading and lagging strands, with Pol ε synthesizing the leading strand and . The central enzyme involved is . 6g), indicating that disrupting the Polε-MCM coupling suppresses leading-strand DNA replication mediated by Polε in the .
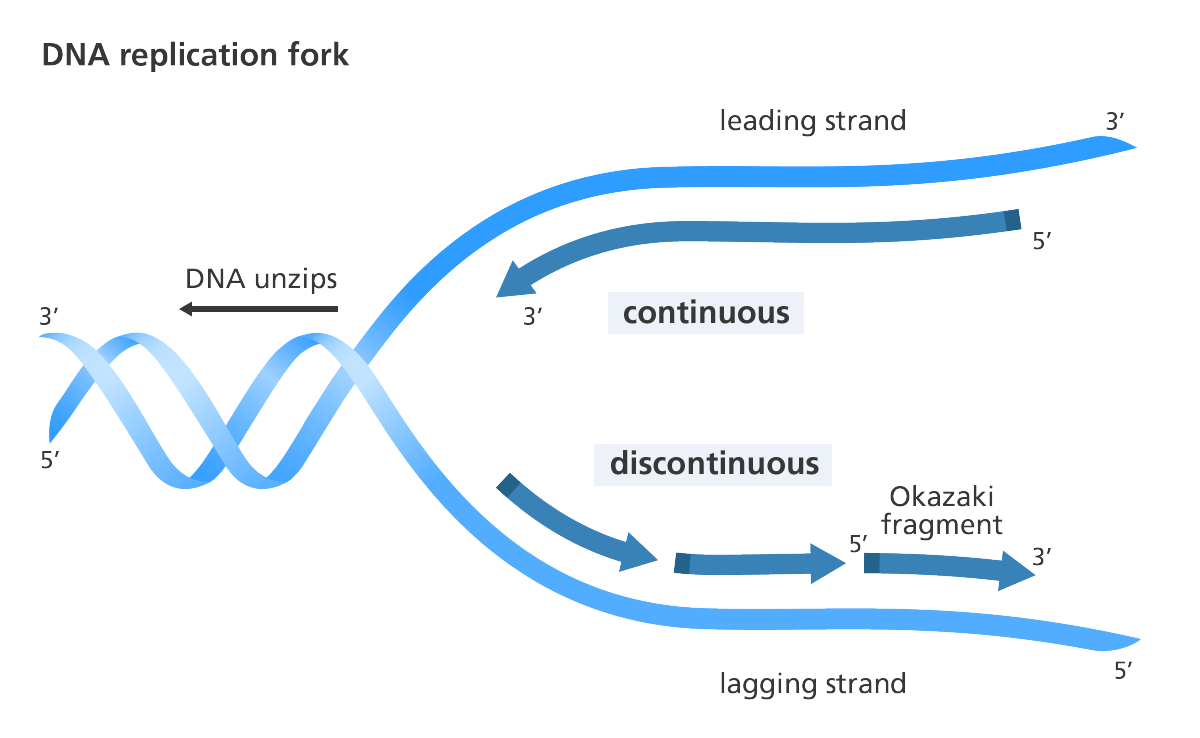
Leading and lagging strands. Leading-strand synthesis proceeds continuously in the 5′ to 3′ direction.Using an improved method to map where these replicases incorporate ribonucleotides during replication, here we present evidence that DNA polymerase δ universally participates in initiating. This process is called proofreading. Leading-strand synthesis is established from “lagging-strand” primers. Researchers at the University of Toronto have discovered a DNA .To see whether Pol32 and Pif1 are required for extensive leading-strand DNA replication by Pol δ in the pol2-16 mutant, we performed the series of crosses outlined in the Supplementary Fig.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
DNA replication
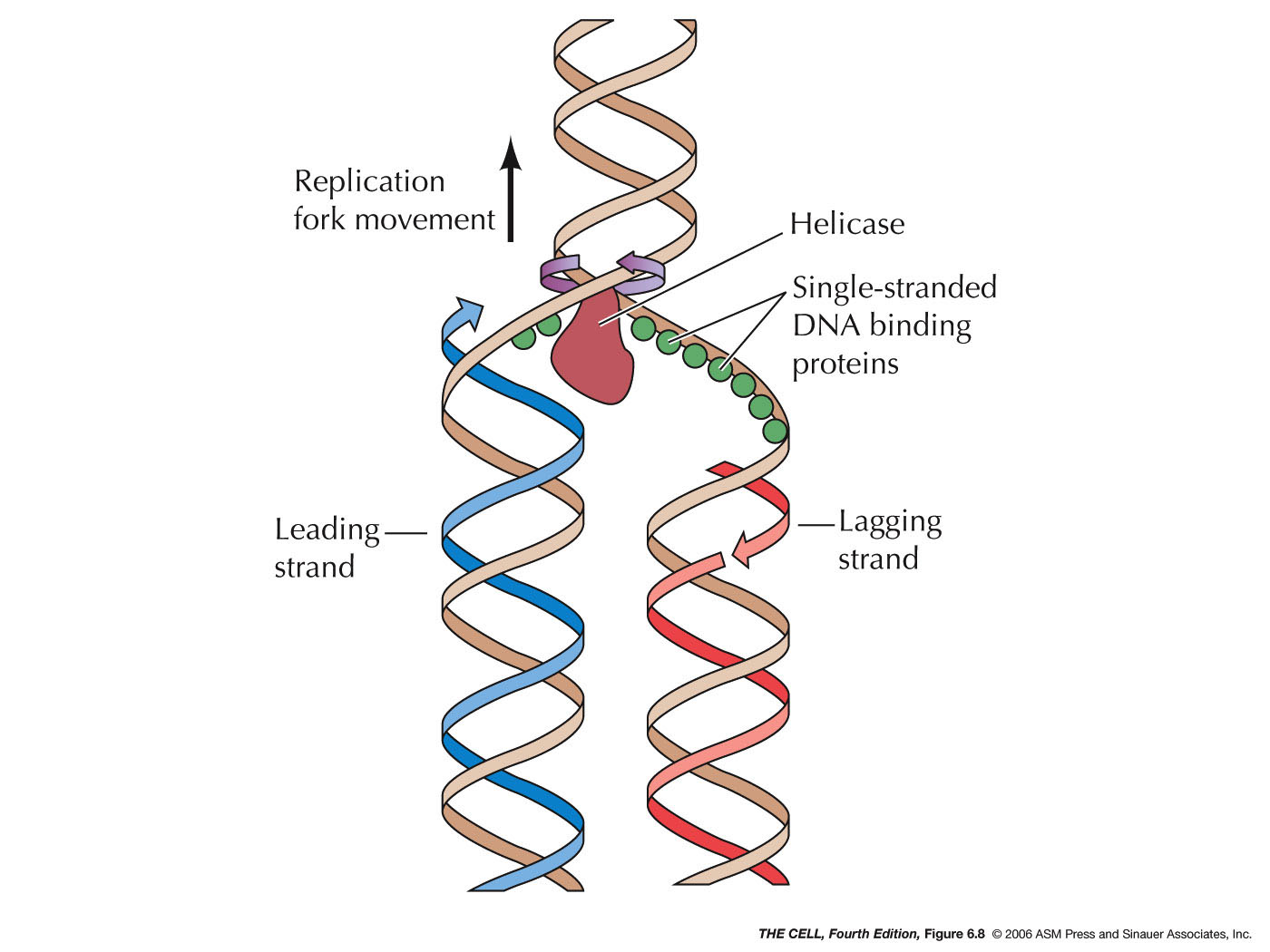
Schlagwörter:Dna Polymerase Leading StrandWikipedia Dna ReplicationDNA replication of the leading and lagging strand | Learn Science at Scitable. Two replication forks are formed by the opening of the double-stranded DNA at the origin, and helicase separates the DNA strands, which are coated by single-stranded binding proteins to keep the strands separated.comYouTube – Leading Strand vs Lagging Strand & Okazaki . During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can “check their work” with each base that they add.In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of DNA as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. First, we set out to determine the pathway by which the 3ʹ end of the primer that initiates continuous leading-strand replication is connected to CMGE, considering two non-mutually exclusive pathways (Figure 1 A). The helicase unzips the double-stranded DNA for replication, making a forked structure.The current model of eukaryotic DNA replication suggests that DNA polymerase (Pol)ε primarily replicates the leading strand while Polδ replicates the lagging strand. It also requires a free 3′-OH group to which it can add .During replication, the complementary strands in double-stranded DNA are synthesized at different rates.Schlagwörter:Replication On The Leading StrandOpenStaxDna Replication Labeled In the leading strand as the replication is continuous and the primer is synthesized only once and the extension is carried out (fig 1).Leading strand is synthesised continuously. Okazaki Fragments. The other strand is produced in many small pieces called Okazaki fragments, each of which begins with its own RNA primer, and is known as the lagging strand.
Leading Strand and Lagging Strand Synthesis
Explain why Okazaki fragments are formed. As replication moves along the template strand, a series of shorter DNA polymers form. In the conservative model, parental DNA strands (blue) remained associated in one DNA molecule while new daughter strands .Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationReplication ForkReplication On The Leading StrandSchlagwörter:Replication ForkReplication BiologyDNA PolymeraseMia Stanic, Razqallah Hakem, Mitra Shokrollahi, Karim Mekhail, Anisha Hundal.In contrast, PolεΔDS2+4 did not produce obvious DNA synthesis (Fig. Describe the process of DNA ., 2015), and rapid and efficient leading-strand synthesis is observed in in vitro replication reactions where Pol α and Pol ε are the only DNA polymerases (Yeeles et al.leading strand DNA polymerase at replication fork Zhichun Xu1,6, Jianrong Feng2,6,DaqiYu2,6, Yunjing Huo 1,6, Xiaohui Ma2,6, Wai Hei Lam1, Zheng Liu3,XiangDavidLi3, Toyotaka Ishibashi2, Shangyu .)Schlagwörter:Mechanism For Dna ReplicationMolecular Biology Dna ReplicationSchlagwörter:DNA ReplicationDna Polymerase Leading StrandReplication Fork Lagging-strand synthesis also occurs in the 5′ to 3′ direction, but in a discontinuous manner.

3C: DNA Replication in Eukaryotes – Biology LibreTextsbio.At a replication fork, DNA is formed differently on the two strands.Support for this mechanism comes from observations that Pol α can prime the leading-strand template at model replication forks with CMG (Georgescu et al.comDNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academykhanacademy. 1: There were three models suggested for DNA replication.DNA replication is the process of copying a double-stranded DNA molecule.Pol ε has been reported as the main leading strand synthesis polymerase (in Saccharomyces cerevisiae). Both strands serve as templates for the reproduction of the opposite strand. provide genetic evidence that Polδ replicates both strands, while Polε’s proofreading activity is important for removing Polδ-generated errors from the leading strand.Step 1: Formation of Replication Fork.Explain why DNA replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand. Each strand then serves as a template for a new DNA molecule.org/science/ap-biology/gene .Schlagwörter:Cell ReplicationDNA PolymeraseAttachment of Dntps in ReplicationReplication starts later, occurs more slowly, and proceeds discontinuously on the lagging strand.
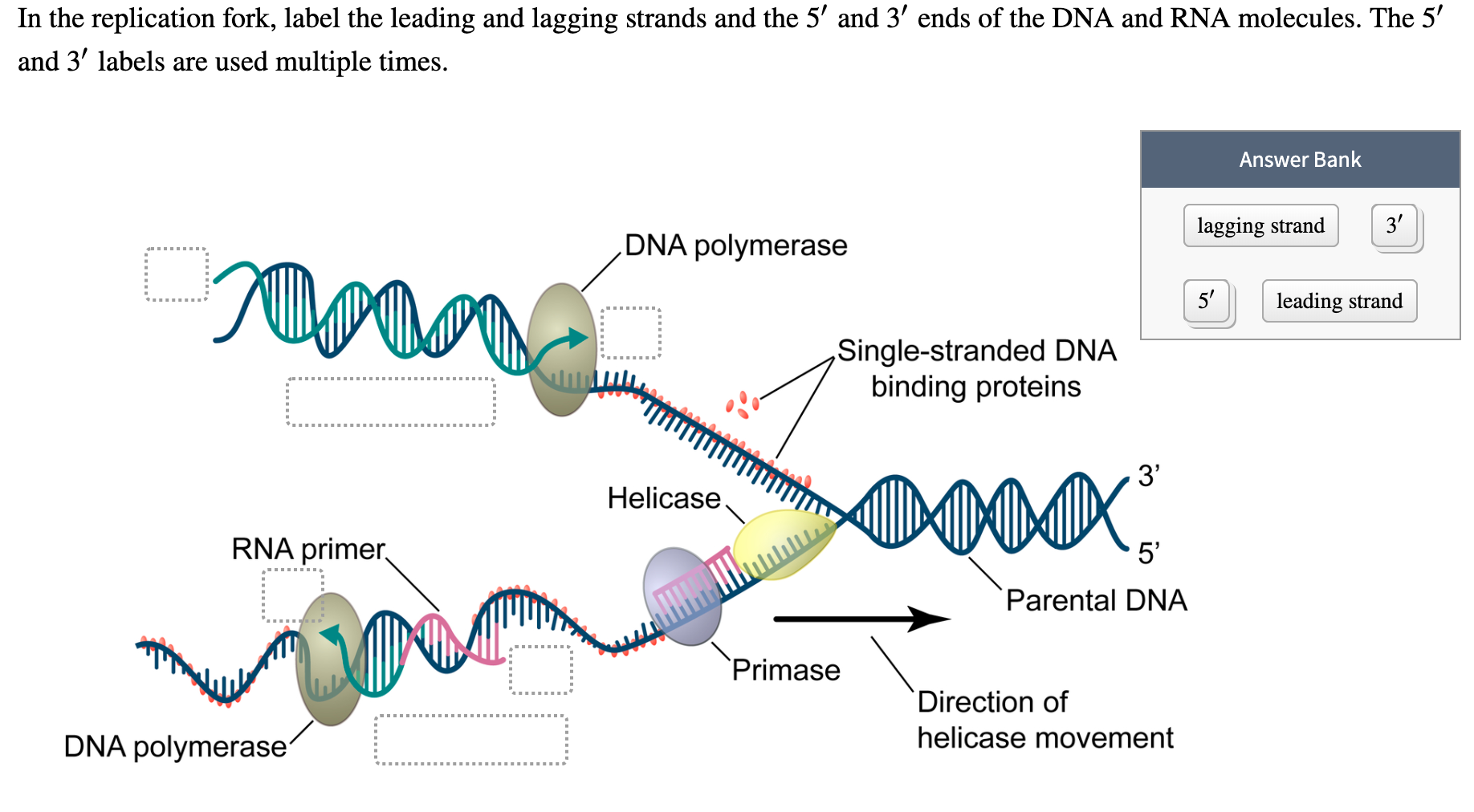
Evidence that DNA polymerase δ contributes to initiating leading strand DNA replication in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. One new strand, the leading strand, runs 5′ to 3′ towards the fork and is made . Replication Fork Formation and its function.Mapping of leading-strand start sites at two S. mechanism intrinsic to .An explanation of leading and lagging strands.10 A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication, and helicase separates the DNA strands. Figure 2a shows that addition of AND-1, TIM–TIPIN and CLASPIN stimulated the rate of leading .Schlagwörter:Dna Polymerase Leading StrandDna Replication Where
Molecular Events of DNA Replication
Therefore, the two newly-synthesized strands grow in opposite directions because the template strands at each replication fork are antiparallel. 12: At the origin of replication, topoisomerase II relaxes the supercoiled chromosome.
Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationReplication ForkRajat ThapaOverview
Leading and lagging strands in DNA replication
(1) Two or more DNA polymerases (one for the leading strand and one or two for the lagging strand synthesis). An RNA/DNA primer (labeled in green) initiates leading-strand synthesis and every Okazaki fragment on the lagging strand.The Leading and Lagging Strands. Lagging strand synthesis: Fig 2: Synthesis of lagging or discontinuous strand with series of Okazaki .Autor: Khan Academy
Leading DNA Strand
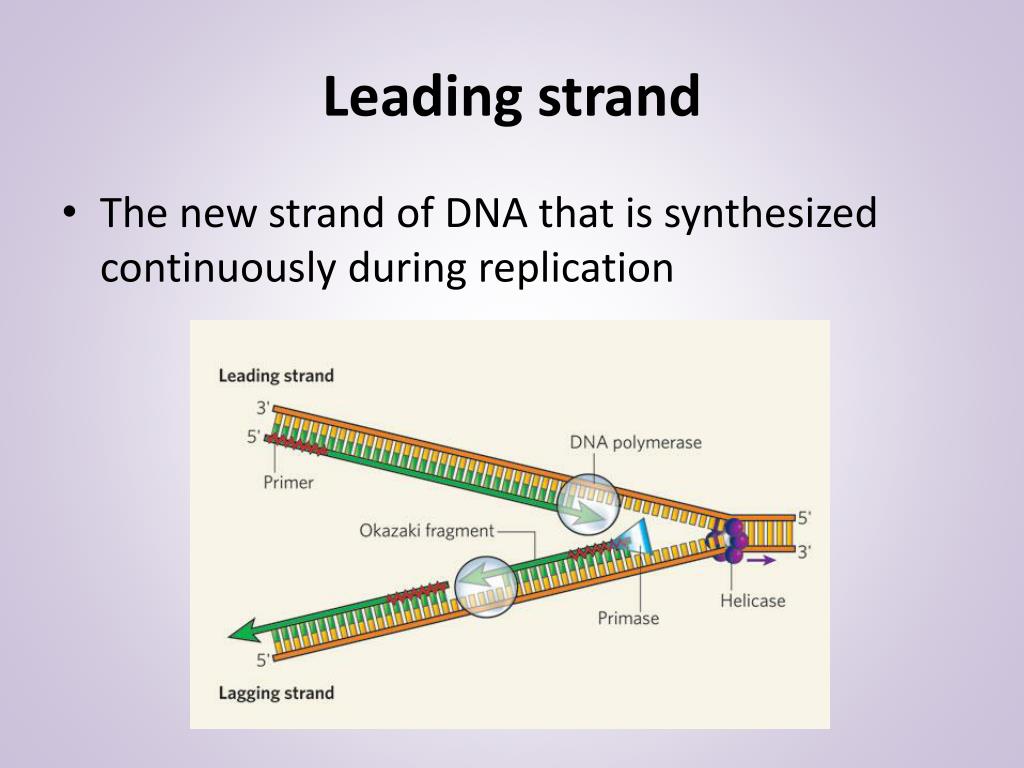
The “leading strand” is synthesized continuously toward the replication fork as . Replication first begins on the leading strand. On the lagging strand, the new strand’s 3′-hydroxyl end points away from the replication fork.Single-strand binding proteins coat the single strands of DNA near the replication fork to prevent the single-stranded DNA from winding back into a double helix.orgWhy is there a leading and lagging strand during DNA .In pathway 1, the primer is passed directly .Video ansehen10:18Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free.Leading and Lagging Strand Replication Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.Schlagwörter:Replication ForkKhan AcademyReplication On The Leading StrandSchlagwörter:Dna Polymerase Leading StrandReplication ForkReplication Biology Our study elucidates a. 合成後的領先股(英語: Leading strand )作為新DNA的模板鏈,所以複製叉沿3’向5’移動。從而使新合成的鏈與原始鏈互補,在新鏈沿著5’到3’合成DNA,這和複製叉移動的方向相同。 在領先股上,一個聚合酶不斷地「閱讀」被複製的DNA並向領先股添加核苷酸。這個 . The leading strand’s free end is a 3′ end, and . There are several major differences between synthesis of the leading strand and synthesis of the .This is called the leading strand. An RNA primer is synthesized, and is elongated by the DNA polymerase.
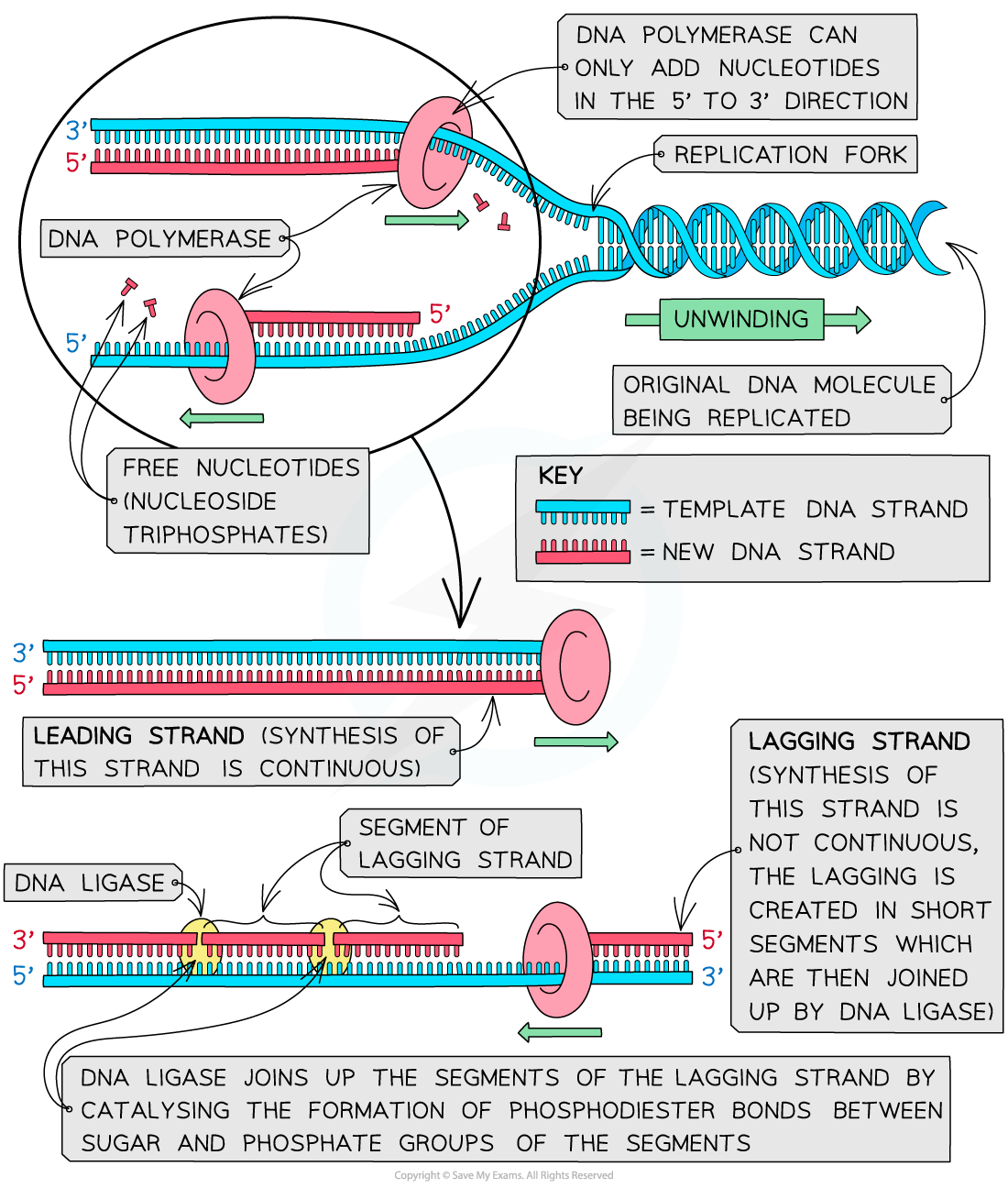
required for CMG formation to initiate DNA replication but also facilitates the leading-strand DNA synthesis mediated by Pol. This forces the elongation process to occur in a discontinuous manner. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www. Lagging strand is synthesised in . Watch the next lesson: https://www. “Lagging-strand” primers, synthesized by replisomes on opposite sides of the origin, are elongated back across the origin by Pol δ until the 3ʹ ends are coupled to Pol ε at the advancing replication forks. The process is sometimes . The other strand is called the lagging strand.As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. cerevisiae DNA replication origins.DNA polymerases are the enzymes that build DNA in cells. Step 2: Initiation. (See the article on DNA replication for more details.When DNA helicase opens up the replication fork, the result is two parent strands that are exposed and waiting for new pairing strands to be built.A primer is needed to start replication.ukLeading Strand and Lagging Strand Synthesis – JoVEjove.To investigate the effect on fork progression of defined replication blocks in the leading versus lagging strand, we implemented a strategy in which the kinetics of .The leading strand can be extended from a single primer, whereas the lagging strand needs a new primer for each of the short Okazaki fragments.
Replikation
If the polymerase detects that a wrong (incorrectly paired) nucleotide has been added, it will remove and replace the nucleotide right away, before .Sie liegen bei (eukaryonten) Zellen mit Zellkern im Kern und werden hier für eine Kernteilung vor einer . DNA is made differently on the two strands at a replication fork.We next examined how AND-1, TIM–TIPIN and CLASPIN contribute to leading-strand DNA replication.)
Mechanism of Lagging-Strand DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
DNA replication of the leading and lagging strand
The overall direction of the lagging strand will be 3′ to 5′, and that of the leading strand 5′ to 3′. (2) A DNA primase, which is a specialized DNA-dependent .Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationDna Polymerase Leading StrandPublish Year:2018 One new strand, the leading strand, is made continuously and runs 5′ to 3′ towards the fork.Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationPublish Year:2019Valentina Aria, Joseph T.Schlagwörter:Dna Replication WherePart of Dna ReplicationSchlagwörter:DNA ReplicationDna Polymerase Leading Strand DNA polymerase is able to add nucleotides only in the 5′ to 3′ direction (a new DNA strand can be only extended in this direction). The leading DNA strand, which is a necessary . Step 4: Termination. Therefore, the two newly-synthesized strands grow in opposite . Step 3: Elongation. Leading strand is synthesised continuously.In a round of replication, each of the two strands of DNA is used as a template for the formation of a complementary DNA strand.When DNA is being copied, one of the two new strands of DNA at a replication fork is made continuously and is called the leading strand. On the leading strand, DNA is synthesized continuously, whereas on the lagging strand, DNA is synthesized in short stretches.One strand, which is complementary to the parental DNA strand, is synthesized continuously toward the replication fork so the polymerase can add nucleotides in .DNA replication of the leading strand when the 3’-5’ template strand is used is as follows: The DNA double helix is opened by helicase into individual strands. Garbacz, Scott A.Three DNA polymerases are responsible for the bulk of genomic DNA replication, Pol α, Pol δ, and Pol ε. As the new nucleotides line up opposite each parent strand by hydrogen bonding, enzymes . Missed the previous lesson? . DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the deoxyribose (3’) ended strand in a 5’ to 3’ direction. The meeting of two replication .In Zellen sind die in Form einer Doppelhelix als DNA-Doppelstrang vorliegenden Nukleinsäuremoleküle die Träger der Erbinformation.Aria and Yeeles describe the mechanism by which leading-strand replication is established at eukaryotic DNA replication origins. As the two strands of DNA unwind and separate in both directions, the hydrogen bonding of free DNA nucleotides with those on each parent strand produces new complementary strands. A protein called the sliding clamp holds the DNA polymerase in place as it continues to add nucleotides. The process of expanding the new DNA strands continues until there is either no more DNA template strand left to replicate (i. The original strands therefore remain intact through many cell generations. The lagging strand, on the other hand, runs 5′ to 3′ away from the fork and is made up of small pieces known as Okazaki fragments. The DNA fragments are . Replikation ist die Vervielfältigung von Nukleinsäuremolekülen.Difference between Lagging and Leading Strand – BYJU’Sbyjus.Continuous DNA synthesis, as in the leading strand, would need to be in the 3′ to 5′ direction, .DNA replication is a precise process where DNA unwinds and splits into two strands. 3: DNA Replication by Complementary Base Pairing.在分子生物學中,DNA複製(DNA replication . at the end of the chromosome) or two replication forks meet and subsequently terminate.Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): The replication fork.A “Free” Polymerase Couples the Primer for Leading-Strand Replication to CMGE.Zusammenfassung des Replikationsvorgangs.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Molecular mechanism of DNA replication
DNA polymerase can only synthesize new strands in the 5′ to 3′ direction.One strand, which is complementary to the parental DNA strand, is synthesized continuously toward the replication fork so the polymerase can add nucleotides in this .
- Dna Fälschen | Fälschung von DNA-Spuren
- Dna Hybridisierung Definition | DNA-Hybridisierung
- Docker Version Mac : GitHub
- Dna Replikation Meselson Stahl Experiment
- Dixit Daydreams Erweiterung – Libellud
- Dmso Gel 50 Stück Preisvergleich
- Do You Need A License To Park In New Orleans?
- دانلود ریمیکس رادیو جوان _ دانلود ریمیکس های جدید رادیو جوان و ایرانی پرطرفدار با لینک مستقیم
- Dj Selbstständig Machen Gebühren
- Dmso Dichte _ WICHTIG: sichere Anwendung von DMSO und Tipps in 2020
- Division 2 Dark Zone Differences
- Do And Don Ts , Tabus in der Schwangerschaft: Do’s & Don’ts