Elongated Pylorus Sign , Cervix sign (pyloric stenosis)
Di: Luke
Autor: Ryan Thibodeau
Pyloric Stenosis
The longitudinal plane shows an elongated pylorus measuring 2. This muscle undergoes hypertrophy, causing narrowing of the gastric outlet and leading to gastric outlet obstruction. Note the paucity of gas in small and large bowel.
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
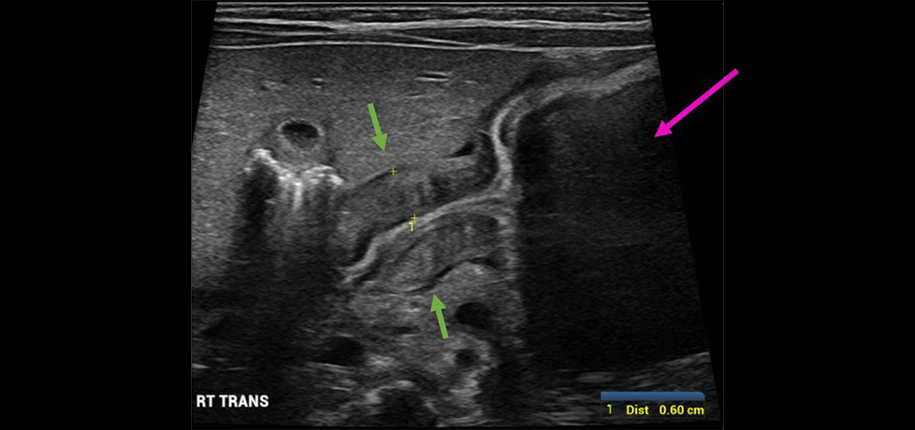
This sign refers to the impression . Sagittal (below left) and transverse (below right) US of the pylorus shows the pylorus muscle to be thickened and elongated in length, measuring 3.Autor: Venkatraman Indiran, Vijayanand Selvaraj
Cervix sign (pyloric stenosis)
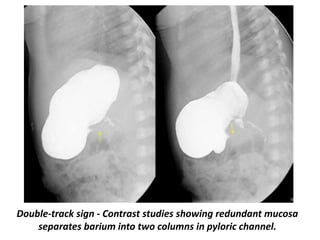
The stomach, with gas distended antrum mimics a double bubble sign.Explore all metrics. A tram track sign of barium in the pyloric channel was seen (upper left) along with pyloric muscle shouldering on the antrum along with a pyloric beak (upper right). This sign can also be elicited if the pylorus relaxes intermittently and the mucosa does not become thickened. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis may cause almost complete gastric outlet obstruction. [1] The typical age that symptoms become obvious is two to twelve weeks old.Teele and Smith first described the use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) in five infants in 1977.elongated pylorus with a narrow lumen (string sign) which may appear duplicated due to puckering of the mucosa (double-track sign) the pylorus indents the contrast-filled antrum (shoulder sign) and or base of the duodenal bulb (mushroom sign) the entrance to the pylorus may be beak-shaped . 3-month-old child with explosive, non-bilious vomiting after breastfeeding.The criteria to look for in upper GI fluoroscopy are delayed gastric emptying, peristaltic waves (caterpillar sign), elongated pylorus with a narrow lumen (string sign), and double-track sign because of duplicated appearance from mucosal puckering of the lumen. Target sign on the short axis view with the thickness measuring 0. Target sign Hypoechoic ring of hypertrophied pyloric muscle around echogenic mucosa centrally on cross-section. Cervix sign in case of PS.
Aspek Radiologis Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (HPS)
Peristaltic waves in distended stomach appear as the caterpillar sign [1, 4].Veröffentlicht: 2023/01/30
Mushroom sign (pyloric stenosis)
Sagittal (below left) and transverse (below right) US of the pylorus shows the pylorus muscle to be thickened and elongated in length, measuring 3.
Pylorus: Anatomie, Struktur und Funktion
When ultrasonography and barium studies fail to show the typical features of IHPS and diagnosis is in doubt, upper endoscopy should be performed and may be helpful in confirming the diagnosis. [1] This most often occurs after the baby is fed.• Abnormal elongation of the canal is characterised as greater than 12 mm in length.It consisted of two parallel linear streaks of barium with an interposed radiolucent band extending from the prepyloric region to the base of the cap and corresponding in length to .7 per 1000 births among children of .The mushroom sign (also called umbrella sign) is a radiological sign described in pyloric stenosis on barium examination. Some or all these findings can distinguish adult idiopathic hypertrophic pyloric stenosis from other diseases. Pylorus: transverse plane.Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is obstruction of the pyloric lumen due to pyloric muscular hypertrophy.
Pyloric Stenosis (HPS): Symptoms & Causes
The classical presentation of IHPS is non-bilious projectile vomiting, in a full-term baby between 3 and 6 weeks of age.When ultrasonography is not available or if the pylorus is obscured by gas in the overlying bowel, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) study should be performed. In this presentation, the muscular layer amounts up to a mean of 15 mm. It affects a few out of 1000 infants and is more common among males by about a 5:1 ratio . 1 In this landmark study, the authors found the anteroposterior diameter of the pylorus in children with HPS to be between 18.Typical findings include target sign; pyloric muscle thickness greater than three millimeters (mm); channel length greater than 15–18 mm; and lack of gastric .The “Mushroom sign” is a radiological sign described on upper gastrointestinal (UGI) studies in patients with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) [ 1 ]. On plain abdominal image appears gastric dilatation accompanied by widening of the notch provides a ’single bubble‘ or ‚caterpillar sign . Barium upper can help to diagnose pyloric stenosis . Abdominal x-ray and ultrasound of a child with hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. The “string sign” is characterized by contrast material outlining the canal coursing . During real-time feeding, a normal pylorus is expected to transit the air-fluid . These images are from Dr. The antral region is elongated and thickened to as much as twice its normal size, narrowing the channel and causing functional gastric obstruction.
Pylorus Definition & Meaning
Ultrasound demonstrates thick and elongated pylorus. Also, if the pylorus partially relaxes, e. [1] Symptoms include projectile vomiting without the presence of bile. Ultrasound (US) is the preferred diagnostic modality [ 2] as it is a non-invasive technique, allowing direct .Download scientific diagram | Two signs of HPS.Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is an acquired disorder of the circular smooth muscle of the pylorus with no known definitive etiology.Ultrasound findings also include target signs and lack of gastric emptying.Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (HPS) is a condition of luminal narrowing caused by hypertropi of pylorus muscle with an incidence 1 of 250 infants.

Ultrasound is the modality of .Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the opening from the stomach to the first part of the small intestine (the pylorus ).Diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is by abdominal ultrasonography showing increased thickness of the pylorus (typically to ≥ 4 mm; normal, 16 mm). 2b) and indents barium-filled antrum (shoulder sign – . Clinical Features . Pyloric stenosis symptoms include forceful vomiting, which may cause dehydration and malnourishment. The “cervix sign” consisting of . Cervix sign Indentation of .Note the elongated pylorus with “double-track” sign.
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis: Practice Essentials
In rare cases, upper endoscopy is required for confirmation.Lateral images from an upper GI exam (above) show delayed passage of barium out of the stomach due to a thickened and elongated pylorus. Positive findings on an UGI study include a narrow, elongated pyloric channel (string sign) and indentation of the stomach by the enlarged pyloric muscle.Prolapse of the redundant mucosa into the antrum creates an ‘antral nipple sign’. Keywords: Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, Ultrasound. Neben dem Pylorus wird noch die Kardia, der . Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) is the most common surgical entity affecting infants during the first 6 months of life.
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (HPS)
Since that time, ultrasound has been the examination of . Hypertrophic adult pyloric stenosis (HAPS) is quite rare with very few cases having been documented. Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.Wall thickness measurements taken with the pylorus in longitudinal (elongated) view improve diagnostic accuracy. which typically shows delayed gastric emptying and a string sign or railroad track sign of a markedly narrowed, elongated pyloric lumen. Diagnosis is by abdominal ultrasonography.The endoscopic pillow sign refers to the creation of a surface indentation made by pressing the tip of a cold forceps onto a subepithelial lesion.Diagnosis of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is by abdominal ultrasonography showing increased thickness of the pylorus (typically to . 6 In most cases, .Pyloric Stenosis (HPS) Pyloric stenosis is a condition that affects your infant’s pylorus, the muscle at the end of the stomach leading to the small intestine.Figure 2: Ultrasound of pylorus.Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (IHPS) occurs secondary to hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the smooth muscular layers of the pylorus and antrum. | Description: Longitudinal plane showing the elongated pylorus with thickened pyloric muscle, “CERVIX SIGN”. The normal adult pyloric muscular wall thickness ranges from 3 to 8 mm¹. Go to: Introduction.The characteristic radiological feature of IHPS is narrowed elongated pyloric canal giving “string” or “double track” sign caused by compressed invaginated folds of mucosa in the pyloric canal (Fig. When their pylorus thickens and narrows, food can’t pass through.9 mm thick and 20 mm in length.

It is located 4 to 6 cm proximal to the base of the duodenal bulb 5 . Failure of relaxation of antropyloric lesion, .Elongation of the canal and thickened mucosa are also seen. 1 It has an incidence of approximately 2 to 5 per 1000 births among children of European descent, but its incidence is much lower in other populations—approximately 0.The pylorus becomes thickened with narrow elongated pyloric canal and the stomach becomes dilated due to pyloric obstruction.9 mm thick and 20 mm in .
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
On fluid aided real-time examination, the pyloric fluid is compressed into smaller tracks as it is impinged upon circumferentially by the thickened . When the contrast-filled antrum is indented by the pylorus, it appears as the shoulder sign. The “shoulder sign” is seen during barium examination and refers to the bulging of the hypertrophied pyloric muscle into the lumen of the antrum. Antropyloric region: rounded soft tissue mass (arrows) simulating the shape of a . Paula Brill’s excellent pediatric radiology collection.EarIy in the course of the dis- ease the elongated pylorus may be repre- sented roentgenographically by a single cen- tral streak of barium in the lumen, the string sign (Fig. In the presence of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS), the sonographic resemblance of the thickened and elongated pylorus to the normal .
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: tips and tricks for ultrasound diagnosis
The meaning of PYLORUS is the muscular opening from the vertebrate stomach into the intestine., with the use of .60 cm) with thickened pyloric muscle, also known as the cervix sign.AXR (above) shows an extremely distended stomach with peristaltic waves (caterpillar sign).

In preterm babies, the disease usually presents 2 weeks later. However, barium meal study provides indirect information about the antropyloric canal status.Case Discussion.Der Pylorus ist der trichterförmige distale Abschnitt des Magens und stellt einen der vier anatomischen Regionen des Magens dar. The cervix sign of pyloric stenosis describes the indentation of the pylorus into the fluid-filled antrum, seen . Double streaks of barium passing through the narrow pylorus 1.When doing an UGI in cases of HPS one can note the mass impression of the hypertrophied pyloric muscle on the barium-filled antrum (“shoulder sign”) or the filling of the proximal . Radiology plays an important role in diagnosing this disease. An upper abdominal ultrasound was requested. This sign is closely related to the .The double track sign is a radiological sign described in pyloric stenosis on various imaging modalities.The string sign represents a small amount of contrast passing through a narrow pyloric channel while the double track sign is seen when the lumen is pleated.Autor: Sílvia Costa Dias, Sophie Swinson, Helena Torrão, Lígia Gonçalves, Svitlana Kurochka, Carlos Pina Va. If the diagnosis remains uncertain, ultrasonography can be repeated serially or an upper gastrointestinal series can be done, which typically .On upper gastrointestinal barium study, the pylorus appears elongated with narrowed lumen (string sign – Fig. The pyloric mucosa protrudes into the gastric antrum which is .Caterpillar sign Gastric hyperperistaltic waves.The “string” sign that corresponds to the elongated pylorus is the most frequent sign of barium meal studies in IHPS.
Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis. AXR AP (left) shows a hugely distended air-filled stomach with distal bowel . Sagittal (lower left) and transverse (lower right) US . Full size image .
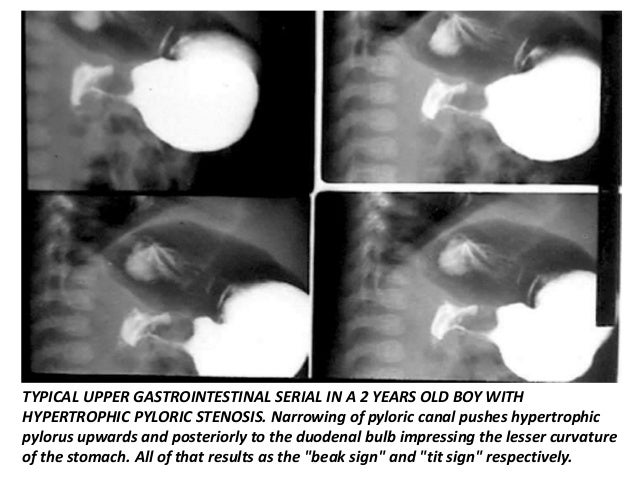
elongated pylorus with a narrow lumen (string sign) which may appear duplicated due to puckering of the mucosa (double-track sign) the pylorus indents the contrast-filled antrum .


Treatment is surgical.The “Twining’s” sign is a barium filling defect, which can project to either or both sides of the pylorus. There are other signs that are described as “shoulder sign” and “tilt sign” when . Caption: Longitudinal plane through right upper quadrant. Fluid aided real-time examination of 10 cases showed the ultrasound equivalent of . This bulging causes a flattening of the prepyloric area of the lesser curvature (Fig. In response to outflow obstruction and . Infants typically present before the 10th week of life with projectile non-bilious vomiting.Typical elongation and narrowing of the pyloric canal “mouse tail” (Fig. In many cases, an elongated pylorus that lies adjacent to and just below the .
- Element Sand Game | Interactive periodic table game
- Elisabeth Hertel Kinder , Stefanie Hertel: Ein Jahr nach dem Tod ihrer Mutter
- Elternteil Krankenversichert Kinder
- Email Ohne Betreff Schreiben , Betreffzeilen: So wird Ihre E-Mail nicht zum Effizienzkiller
- Elster Berechtigungen Freischalten
- Elfter Im Elften Koeln _ Elfter im Elften
- Elisabeth Ruge Kontakt _ Elisabeth Draper, Grande Dame Of Interior Design, Is Dead at 93
- Elster Steuererklärung 2024 Daten Übertragen
- Emi Music India _ EMI
- Elimination Chamber Matches 2024
- Elisabeth Songtext – Text: Pia Douwes