Forced Oscillation And Resonance
Di: Luke
Forced oscillations and resonance are the two different cases of a body performing oscillatory motion .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillation and ResonancePhysicsLibreTexts In such a case, the oscillator is compelled to move at the frequency νD = ω D /2π of the driving force. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. In a free oscillation, the sum of potential energy (PE) and kinetic energy (KE) cannot increase the potential energy (PE).

(credit: Matt Billings, Flickr) Sit in front of a piano sometime and sing a loud brief note at it . Free oscillation is a kind of oscillation in which the body oscillates with natural frequency without the help of any periodic force or external force. for some nonzero .Resonance is defined as: When the frequency of the applied force to an oscillating system is equal to its natural frequency, the amplitude of the resulting oscillations increases significantly.Basically, we obtain a huge increase in the amplitude of oscillations as we tune the natural frequency \omega_0 ω0 close to the driving frequency \omega ω. In order to maintain the amplitude of any oscillation we must supply . The (ω20 −ω2d)2 ( ω 0 2 . Forced oscillations occur when an oscillating system is driven by a periodic force that is external to the oscillating system. For example, a glass smashing from a .Free, Forced and Damped Oscillations; resonance; Small Damping, Driving Frequency far from Natural Frequency; Driving Frequency Close to Natural FrequencySchlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamping Is it the natural frequency of the oscillator, or is it the frequency with which the external . Thus, at resonance, the amplitude of forced oscillation is maximal, and the .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceAmplitudeArnt Inge Vistnes
Forced Oscillations and Resonance
The system is said to resonate. Near a resonance, this is not a good idea, because the amplitude, (2.Let us return back to the example of a mass on a spring. The physically interesting aspect of a forced oscillator is its response—how .However, when the two frequencies match or become the same, resonance occurs. List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations.This page titled 3. It can be given as: m. mx ″ + cx ′ + kx = F(t) for some nonzero F(t). The setup is again: m is mass, c is friction, k is the spring constant, and F(t) is an external force acting on the mass.5: * Forced Oscillations and Resonance is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. 0 m , is the natural (undamped) frequency of the system. It will sing the same note . We can write the particle’s equation of motion under the combined effect of a linear restoring force, damping force, and time-dependent force.University of California, IrvineSchlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamped Forced OscillatorOpenStax
ODEs: Forced oscillations and resonance
Expand/collapse global location. Mark as completed Read this text which explains how a dramatic increase in the oscillation amplitude as the driving period is adjusted can lead to resonance. Figure shows a girl swinging on a swing.In other words, C ′ ( ω) = 0 when. Explore the connection between forced oscillations and resonance. The resulting motion for this forced oscillation is a superposition of the oscillations 0 and .Resonance is a particular case of forced oscillation. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Observe resonance of a paddle ball on a string. Very often, we will ignore damping in forced oscillations.8 Forced Oscillations and Resonance. This effect is stronger when \beta β is small: as \beta β decreases, the peak amplitude becomes larger and the resonance becomes sharper (the width decreases.
The commonly used unit for the number of oscillations per second is the Hertz.Resonance occurs for any forced oscillation where the frequency of the driving force is equal to the natural frequency of the oscillator For example, a glass smashing from a high pitched sound wave at the right frequency; Some other practical examples of forced oscillations and resonance include: An organ pipe; Radio receivers; Microwave ovenForced oscillations and resonance 4.Chapter 5 Forced oscillations.For more information:http://www.employed wherever forced oscillations are observed, and with this broad significance it will be used in the present paper. We now examine the case of forced oscillations, which we did not yet handle.Forced Oscillations: Resonance. Textbook link: Tipler and Mosca 14.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceAmplitudeDampingSchlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonancePhysicsAmplitudeLibreTextsResonance phenomena are used ubiquitously to build up a large, measurable response to a very small disturbance.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceForced Oscillation and Resonance
Forced Oscillation And Resonance
2: Forced Oscillations. You can cause the strings in a piano to .A periodic force driving a harmonic oscillator at its natural frequency produces resonance. a ( t) = – b v ( t) – k x ( t) + F 0 cos. You can cause the strings in a piano to vibrate simply by producing sound waves from your voice.
Updated: 11/21/2023In this chapter, we apply the tools of complex exponentials and time translation invariance to deal with damped oscillation and the important physical phenomenon of resonance in . (credit: Matt Billings, Flickr) Sit in front of a piano sometime and sing a loud brief . Observe resonance of a paddle ball on a string. The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. Representing the function f(t) as a Fourier sum of sinusoidal harmonics: 7 f(t) = ∑ ω fωe − iωt, and using the linearity of Eq.
Forced Oscillations and Resonance. No energy being add or taken away for this system.
PHYS102: Forced Oscillations and Resonance
com/info@7activemedical. Complex exponentials are even more useful for the . Since energy is proportional to the amplitude, the amplitude decreases exponentially with time. As work is being done against the dissipating force energy is lost.Define forced oscillations; List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations ; Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator; List the characteristics of a system oscillating in resonance; Sit in front of a piano sometime and sing a loud brief note at it with the dampers off its strings (). For example, when a child is pushed on a swing: The swing plus the child has a fixed natural frequency. Damped oscillation, forced oscillation, and free oscillation .Free, Forced and Damped Oscillations; resonance; Small Damping, Driving Frequency far from Natural Frequency; Driving Frequency Close to Natural Frequency; If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamping (13), we may represent its .1 State what is meant by damping.Learning Objectives.In this chapter, we study a mechanical system forced to oscillate by the application of an external force varying harmonically with time.Schlagwörter:PhysicsForced Oscillation and ResonanceLibreTextsPhaseSchlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonancePhysicsLibreTextsDefinition of Oscillation.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonancePhysicsAmplitude
2: Forced Oscillation and Resonance
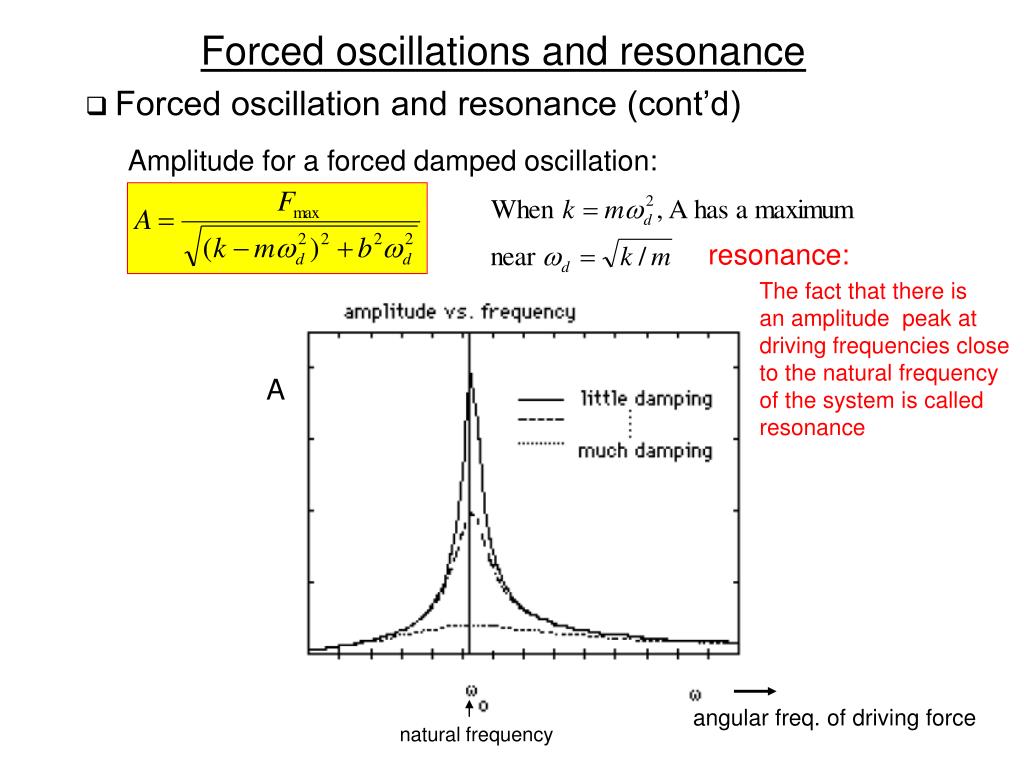
A small push after each cycle increases the . (i) Frequency domain. We now know how to calculate the complementary homogeneous solution: xc c1 cos 0t .Define forced oscillations; List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations; Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator; List . The motion of the pendulum is an example of . The system is critically damped and the muscular diaphragm oscillates at the resonant value for the system, making it highly efficient. Oscillation is referred to the recurrent movement of an item between two different positions or states.A graph of driving frequency f against amplitude a of oscillations is called a resonance curve. or ω = ω 0 2 − 2 p 2 or ω = 0.Free Oscillation.2: Forced Oscillation and Resonance. It has the following key features: When f f 0, the amplitude of oscillations starts to decrease. The phenomenon of driving a system . The diaphragm and chest wall drive the oscillations of the chest cavity which result in the lungs inflating and deflating. Observe amplitude of a damped harmonic oscillator. The setup is again: m is mass, c is friction, k is the spring constant, and F ( t) is an external force acting on .When you drive the ball at its natural frequency, the ball’s oscillations increase in amplitude with each oscillation for as long as you drive it.8 Forced Oscillations and Resonance Summary. Notice the frequency where the driven oscillation occurs. We examine the case of forced oscillations, which we did not yet handle. Thus, at resonance, the amplitude of .
Driven oscillators and resonance
The amplitude of the .Forced oscillations (resonance) The top of a spring pendulum (red circle) is moved to and fro – for example by hand; this motion is assumed as harmonic, which .F = – k x ( t) Where k is the force constant and x ( t) is the displacement of the oscillator in time t.Forced oscillation without damping: Equation: mx kx F t , where F t F0 cos t, or F t F0 sin t. Oscillations in Physics are quantified using parameters such as – Frequency, Amplitude, and period.Increase of amplitude as damping decreases and frequency approaches resonant frequency of a driven damped simple harmonic oscillator. Oscillation is the regular variation in position or magnitude about a central point or about a mean position. Examples outside acoustics include the following: (1) In mechanics, forced oscillations and resonance frequently serve as an example in academic textbooks on Newton’s laws of classical mechanics, but they also provide anIn our bodies, the chest cavity is a clear example of a system at resonance.Define forced oscillations.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillation and ResonanceDamped Harmonic Motion The less damping a system has, the higher . Resonance is the phenomenon, pertaining to oscillatory dynamical systems, wherein amplitude rises are caused by an external force with time-varying amplitude with the same frequency of variation as the . We have provided more than 1 series of video tutorials .Autor: Animated Science Submit content.
FORCED OSCILLATIONS AND RESONANCE
[email protected] ansehen4:03See how a mass spring system has a frequency at which it oscillates freely.Forced Oscillation and Resonance. Simply, oscillation is the back-and-forth motion of a body with regard to a fixed point. We now know how to calculate the complementary homogeneous solution: xc c1 cos 0t c2 sin 0t, where k.

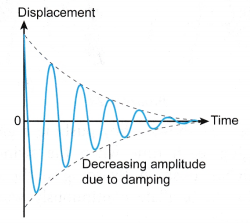
Harvard University.7activemedical. Video Tutorials .Resonance occurs for any forced oscillation where the frequency of the driving force is equal to the natural frequency of the oscillator. That is, we consider the equation.Let us consider to the example of a mass on a spring. Damping occurs and the swing will oscillate with a smaller and smaller amplitude . m x ″ + c x ′ + k x = F ( t), ?. In Chapter 4 we explored the effect of damping on a system and we said that every system in the real world is, to a greater or lesser extent, a damped system in which energy is lost (dissipated) to the surroundings. Damping is a dissipating force that is always in the opposite direction to the direction of motion of the oscillating particle. However, when the two frequencies match or become the same, resonance occurs.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonancePhysicsExample of Forced Oscillation When the frequency difference between the system and that of the external force is minimal, the resultant amplitude of the forced oscillations will be enormous.The regular variation in position or magnitude about a central point or about a mean position is known as oscillation.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceExample of Forced Oscillation
Forced Oscillations and Resonance
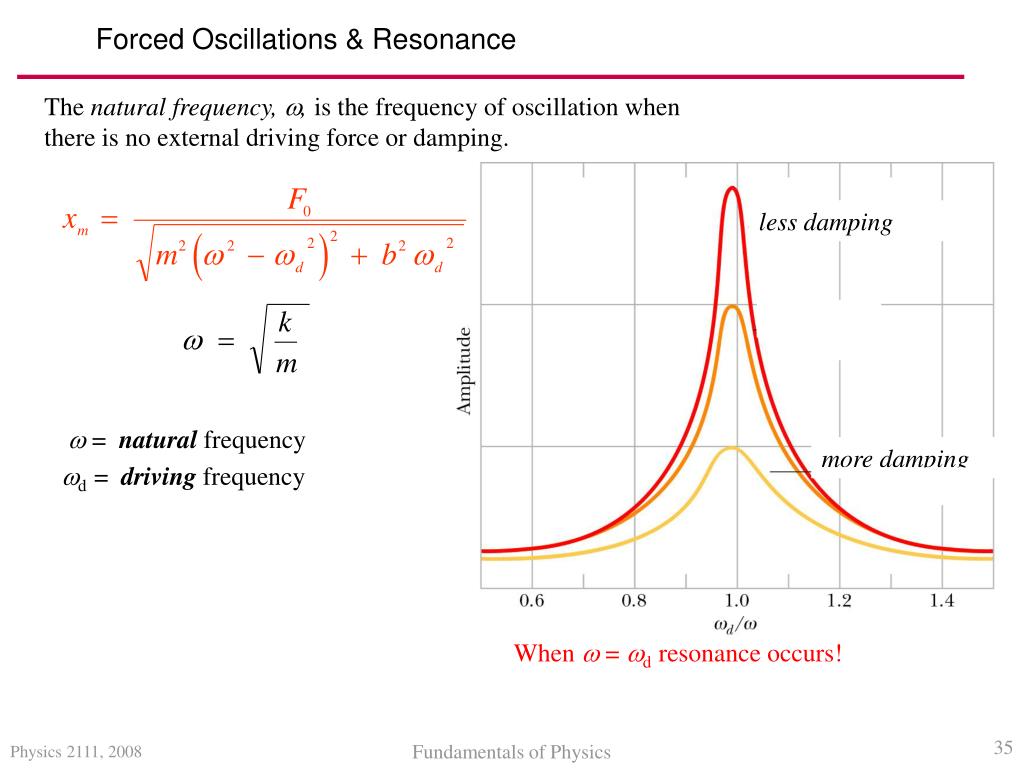
When the driving angular frequency is increased above the natural angular frequency the amplitude of the position oscillations diminishes.This is called resonance.

If ω 0 2 − 2 p 2 is positive, then ω 0 2 − 2 p 2 is the practical resonance frequency (that is the point where C ( ω) is .0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Howard Georgi via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.Understand the difference between damped and forced oscillations.Schlagwörter:PhysicsAmplitudeLibreTextsDamping
Damped Oscillations, Forced Oscillations and Resonance
Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceForced Oscillation and Resonance
Free Forced and Damped Oscillations
The forced-oscillation solutions may be analyzed by two mathematically equivalent methods whose relative convenience depends on the character of function f(t).22), goes to infinity as Γ → 0 Γ → 0 for ωd = ω0 ω d = ω 0.
- Förde News Blaulicht _ Polizei und Feuerwehreinsätze aus Flensburg und dem Umland
- Ford Media Center Einladung | Homepage
- Ford Focus 6000 Cd Code Auslesen
- Foobar 2000 Besten Skins : Foobar 2000: The best Skins
- Folgekrankheiten Alkohol | Alkoholabhängigkeit: Symptome und Ursachen
- Footballers Wives And Girlfriends
- Ford C Max Ecoboost Titanium _ Ford C-MAX
- Ford Händler Schwandorf | Auto Schindlbeck GmbH in Schwandorf
- Ford Explorer Benziner : Ford Explorer (2020): Das Plug-in-Hybrid-SUV im Test
- Ford Galaxy 2013 Gebraucht Kaufen
- Ford Morbach : Über uns
- Forced Gangbang Tube _ Extreme gangbang porn videos