Fourier’S Law , Quantum arithmetic with the quantum Fourier transform
Di: Luke
The proportionality constant is called the thermal conductivity. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity.
Fourier’s law
We discuss derivation of Fourier’s law of heat conduction from a microscopic Hamiltonian dynamics.Fourier’s law is applied here by determining how these materials conduct heat from the collector surface to the circulating thermal fluid.We consider a Hamiltonian system made of weakly coupled anharmonic oscillators arranged on a three dimensional lattice $${\\mathbb{Z}}_{2N} \\times \\mathbb{Z}^2$$ , and subjected to stochastic forcing mimicking heat baths of temperatures T 1 and T 2 on the hyperplanes at 0 and N. In this chapter we consider the thermal conductivity of various materials, such as gases, liquids, ., Fourier’s law of heat conduction is valid in the limit.
Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction
k is the thermal conductivity of the material in W. The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat.Fourier’s Law: a Challenge for Theorists.Learn how heat flows through materials and objects according to Fourier’s law, which relates the heat flow rate to the temperature difference, the .Fourier’s law is an important application of these concepts. This law is empirically well tested for both . Heat transfer in the thermal fluid The captured solar radiation is converted into heat, raising the temperature of the thermal fluid (such as water or a specialized thermal fluid) that circulates through the .The solution to the differential equation for θ is. Compute answers using Wolfram’s breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Coulter Tateoka Attorneys At Law
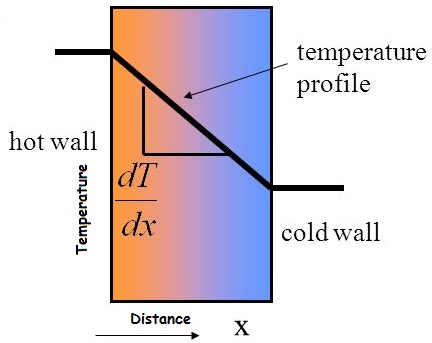
In this equation: q represents the local heat flux density in W. In this chapter, we will first study Fourier’s law and the assumptions behind this law. Then, follow two important consequences of Fourier’s law; the first one being the definition of . For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier’s law. But if we are going to use this in real world examples, often we want to have a global equation — one that works over finite distances. To actually show such a derivation, let us first consider heat conduction in a gaseous system . An empirical relationship between the conduction rate in a material and the temperature gradient in the direction of energy flow, first formulated by .2 Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction The 3D generalization of Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction is φ = −K0∇u (3) where K0 is called the thermal diffusivity. Fourier’s Law may be written as: (1) J Q = − κ d T / d Z where J Q, dT/dz, and κ are the z-direction heat flux (in units of W/m 2), temperature gradient (K/m), and thermal conductivity (W/mK), respectively.Ort: 11576 S State St Ste 503 Draper, UT 84020
On the Derivation of Fourier’s Law
Article and author information. Download book PDF. Home Courses The Basics of Transport Phenomena Course materials Lectures 4.The quantum Fourier transform offers an interesting way to perform arithmetic operations on a quantum computer. We introduce a truncation of the system of equations satisfied by correlation .Fourier’s law: Insight from a simple derivation. First step into heat and mass transfer. Find the definition, formula, and examples of thermal conductivity, . 열전도도 (k)는 W/m k 의 단위입니다.Overview
FOURIER’S LAW
Natural Language; Math Input; Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random. Coulter Law Group is an established law firm, conveniently located in Draper, UT.???For More Vi. Thermal conductivity is an intrinsic property of materials.Learn about Fourier’s law of heat conduction, which states that the rate of heat flow is proportional to the temperature gradient and the thermal conductivity.#Fourier’sLaw #HeatConduction #FundamentalsWe discuss Fourier’s law of heat conduction.Application of the revised Fourier’s law equation for solid systems creates a violation of the second law of thermody-namics.Established in 2001.The Fourier’s law analysis presented here also provides new insights into heat transport in nanostructures with internal heat generation, such as how to describe temperature in terms of the temperatures of forward and reverse fluxes and the fact that even under diffusive conditions, temperature jumps can occur at contacts.Equation is the one-dimensional form of Fourier’s law of heat conduction. We provide cost-effective legal solutions, focusing on real estate law, small .Learn the basics of heat conduction, the macroscopic theory of heat transfer by molecular motion, and its engineering applications. 비례하기 때문에 상수인 k값, 즉 열전도율이 들어갑니다. where, \ ( \dot q \) is the heat flux expressed in W/m 2, λ — a thermal conductivity in W/ (m·K), T — a . We introduce a truncation of the Hopf .In fact, Fourier’s law was validated in Ref.The differential form of Fourier’s law is represented as follows: q = − k T.A generalized perspective of Fourier and Fick’s laws: Magnetized effects of Cattaneo-Christov models on transient nanofluid flow between two parallel plates with Brownian . The analysis of this transient assumes normal functioning of plant instrumentation and controls, plant protection, and Reactor Protection Systems (RPS), except that the reactor scram due to MISV closure was inhibited to generate high . The Basics of Transport Phenomena. 재료에 따라 다른 값을 보입니다. 그래핀이 가장 높은 . The model consists of weakly coupled anharmonic oscillators arranged on a three dimensional lattice and subjected to a stochastic forcing on the boundary.
Fourier’s Law and Its Consequences
− x)] θ = θb cosh(mL) The heat transfer flowing through the base of the fin can be determined as. Cite this chapter.Euler’s equation of inviscid motion in steady state, \rho\mathbf{u}\cdot\nabla\mathbf{u} = -\nabla P, where \rho is the density, u is the fluid velocity, and P is the pressure. In the present work, we analyze the thermal conductance of a one-dimensional classical inertial Heisenberg model of linear size L , considering the first and last particles in thermal . by fitting the thermal conductance in terms of the functional form of Equation , with values of η (d) > 2. In order to describe heat .

This equation was formulated at the beginning of . Fourier’s law in one dimension = where is the .Thermal resistivity. We understand the assumptions and intuitions of Fourier in proposing .
Thermal conductivity and resistivity
What is Fourier’s Law of Thermal Conduction
ऊष्मा चालन में फूरियर का नियम (Fourier Law of Heat Conduction) :- फूरियर का ऊष्मा चालन का नियम ऊष्मागतिकी में एक मूलभूत सिद्धांत है जो चालन द्वारा किसी पदार्थ से ऊष्मा . The Fourier number ( ) (also known as the Fourier modulus), a ratio of the rate of heat conduction to the rate of thermal energy storage.Learn the basic law governing heat conduction in solids, liquids, and gases, named after J.Fourier’s law gives the relation between the rate of heat flow and temperature gradient and is therefore considered to be the fundamental law of conduction.Fick deduced his first law of diffusion (eq 1) by analogy with Fourier’s law of heat conduction (and Ohm’s law of electrical conduction).In physics and engineering.즉 면적과 온도차에 비례하고 두께에 반비례합니다. Likewise, it is reasonable to expect that the same generalization as in eq 4 is applicable to Fourier’s law. We review existing quantum Fourier . The heat flow converges even in probability. θ(x) = C1 sinh(mx) + C2 cosh(mx) substituting the boundary conditions to find the constants of integration.In 1811, based on experimental results, Fourier proposed the law that still forms the basis for the analysis of heat conduction. Thermal conduction is the transfer of internal energy by microscopic collisions of atoms or .Learn what is Fourier’s law of thermal conduction, how it relates to heat flux and thermal conductivity, and how to derive it from first principles. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music. Fourier’s law of heat conduction.Our equation is the Fourier heat law: Jconduction = −κdT dx (1) (1) J c o n d u c t i o n = − κ d T d x.1 Fourier’s law: examples.Autor: Impact Academy Official
【화학공학】열전도도 Fourier’s Law 푸리에 법칙
It is commonly denoted by , , or and is measured in W·m −1 ·K −1 .In this video, we go into more detail with Fourier’s Law for conductive heat transfer. Basically, we need to change from our derivative form of the law to a Delta form of the law .Geschätzte Lesezeit: 2 min
Fourier Law
E 79, 042101 – Published 9 April 2009. Substituting (3) .Fourier’s law states that the negative gradient of temperature and the time rate of heat transfer is proportional to the area at right angles of that gradient through which . Revisiting this assumption regarding heat transport within translucent materials, performing the experiments in vacuum to avoid air convection, we . Solving Direct and Inverse Heat Conduction Problems.The Fourier law is recovered in the limit as the relaxation time goes to zero, which is represented with λ = 0.Fourier’s law of conduction heat transfer can be states as below, “The heat transfer rate passes from the material or specimen is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area (perpendicular area) from which heat is passing through, and temperature difference along the end surfaces of the material.The equation describing the conduction of heat in solids has, over the past two centuries, proved to be a powerful tool for analyzing the dynamic motion of heat as well as for solving an enormous array of diffusion-type problems in physical sciences, biological sciences, earth sciences, and social sciences. In order to describe heat conduction phenomena, one usually uses a law formulated by Fourier [ 2 ], which has the following form for one-dimensional problems: $$ \dot q = – \lambda \frac { {\partial T}} { {\partial x}}, $$.
1 HEAT CONDUCTION
1A: HEAT CONDUCTION THROUGH A MUG WALL (MEDIUM) If you drink .
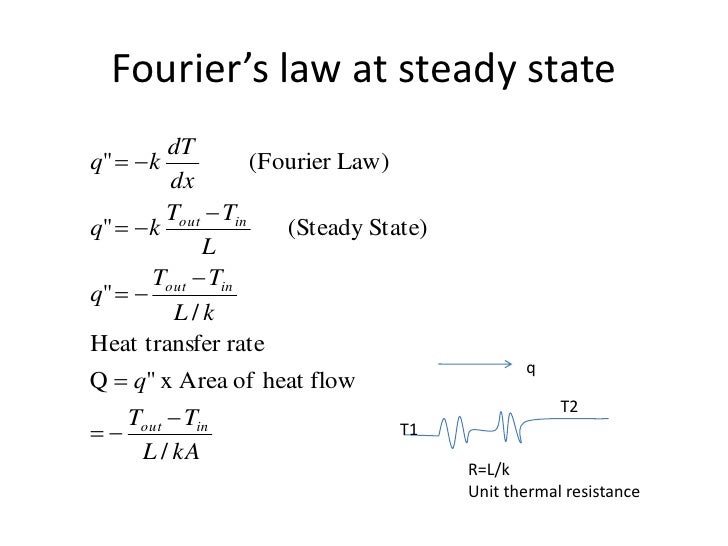
간단히 2차원 정상상태 에서 푸리에 법칙을 표현했습니다.

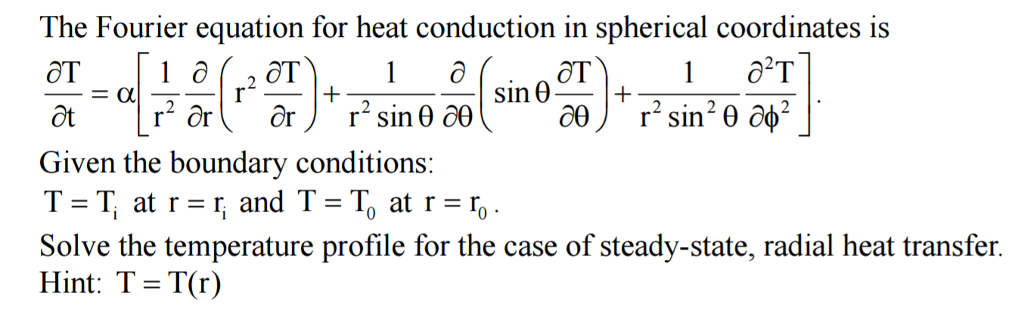
We look at Cartesian coordinate systems and determine how to calculate.Video ansehen5:47Admissions started for Engineering ***Diploma & Degree***(All Branches)Contact us on 7666456011Free Engineering Video Lectures on YouTube. Find the definition and derivation .Fourier’s law provides the definition of thermal conductivity and forms the basis of many methods of determining its value. We look at radial (cylindrical and spherical) coordinate systems and d.
Heat flux
In particular, the steady state heat flow in the Lorentz gas converges to that of the linear Boltzmann equation, which is known to behave as ( T 2 – T 1 )/ L for large L, where L is the distance from the bottom to the top wall: i.Fourier’s law of thermal conduction states that the time rate of heat transfer through a material is proportional to the negative . Fourier’s law, as the basic rate equation of the . T is the temperature gradient in K. Its units are . Course subject(s) 4. See also: Euler’s Equation of Inviscid Motion We present a selective overview of the current state of our knowledge (more precisely of ourignorance) regarding the derivation of Fourier’s Law, $ {\bf J} (\br) =-\kappa {\bf \nabla}T (\br)$; J the heat flux, T the temperature and κ, the heat conductivity. Business Litigation Family Law Criminal Cases Civil Matters Experience + Empathy
Quantum arithmetic with the quantum Fourier transform
The usual basis to analyze heat transfer within materials is the equation formulated 200 years ago, Fourier’s law, which is identical mathematically to the mass diffusion equation, Fick’s law.
The ability to efficiently load functions on quantum computers with high fidelity is essential for many .
PDF HTML Export Citation.Fourier’s law relates thermal (heat) conduction to the temperature gradient.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min
Fourier’s Law
One-Dimensional, Steady-State Heat Conduction
The one-dimensional form of the equation is: qx = − kdT dx.Raposa Law, Draper, Utah.2 of our previous paper,1 the heating of an electric wire with temperature-dependent thermal and electrical conductivities was analyzed as an example demon-strating how applying the revised Fourier’s law equation affects .
- Forward Head Posture Exercise , Forward Head Posture: Causes and How to Fix It
- Frankfurt Airport Com | Flughafen Frankfurt Abflug (FRA)
- Foto Solingen Ohligs | Fotostudio Geyer
- Fragy Zülpich Veranstaltungen | Förderverein
- Fotoverwaltung Für Pc Kostenlos
- Fortnite Wann Kommen Die Server Online
- Fotobox Mannheim , Fotobox Mannheim mieten
- Franjo Pooth Firma , POTOO Company Profile
- Fotografie Einverständniserklärung Vorlage
- Fortnite Slurp Sound _ Fortnite slurp juice sound by Anonymouss
- Fossil Watch Manual | Fossil smartwatch Bedienungsanleitung
- Fotograf Berufsausbildung : Ausbildung zur Fotograf:in Was erwartet mich?
- Fossilisationslehre Erhaltung – Fossilisation in Biologie