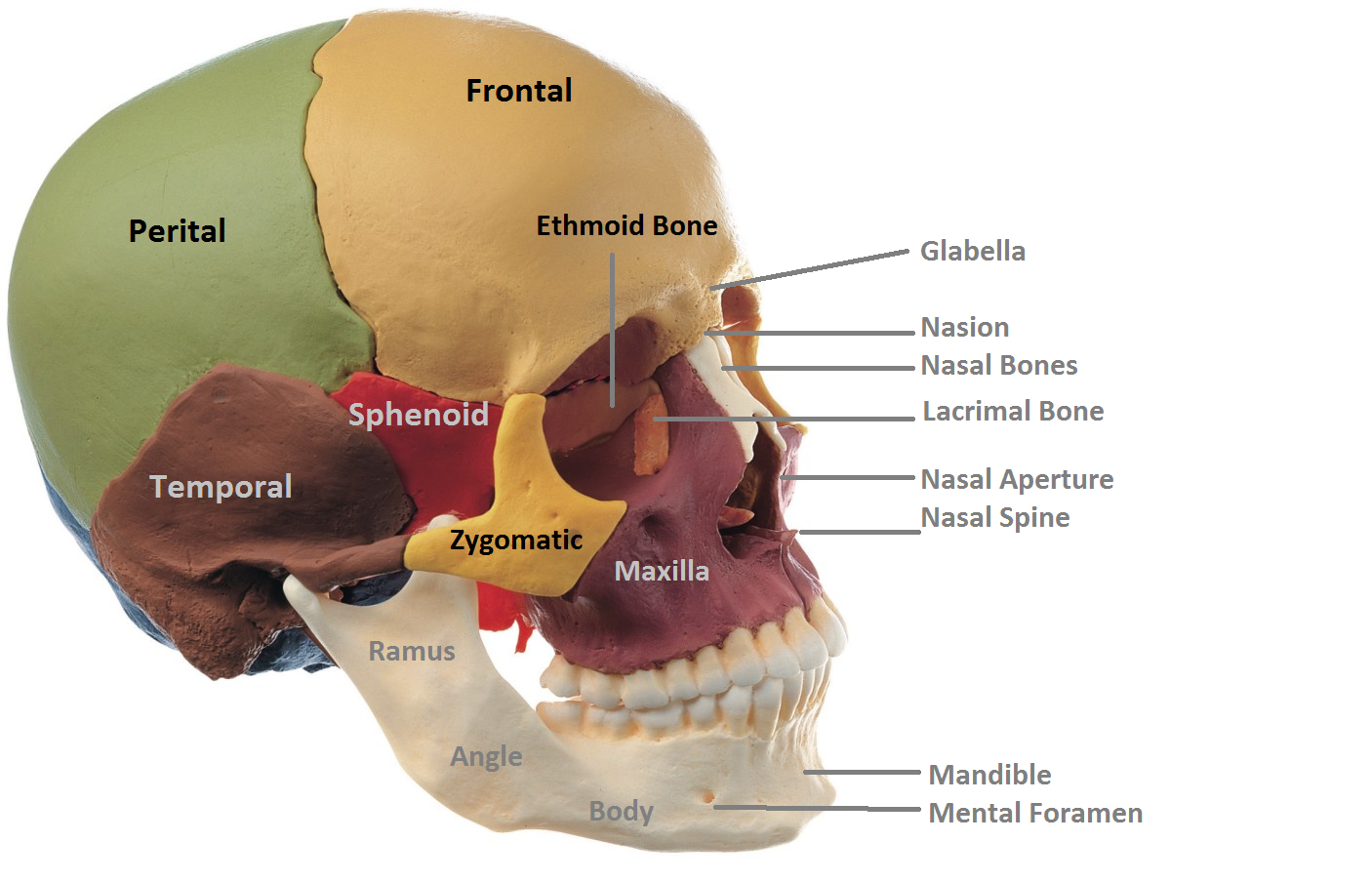
Frontal Skull Location , The Frontal Bone
Di: Luke
The most anterior is the frontal sinus, located in the frontal bone above the eyebrows.
Superior view of the base of the skull: Anatomy
The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the paranasal .The frontal bone is a shell-shaped, unpaired, flat bone of the skull located in the forehead region. The largest are the maxillary sinuses, located in the right and left maxillary bones below the orbits. The cranium, which includes the hyoid and middle ear bones, consists of 29 bones and forms the shape of the head. The frontal bone is also . The frontal bone is located in front of the skull, above the nasal bones and in front of the parietal bones, which form the sides of the skull.The skull base is the floor, or base, of the skull located behind the eyes and nose.
Skull joints and sutures: Anatomy and functions
The facial bones are: Zygomatic (2) – forms the cheek bones of the face and .

compurposegames. They are passageways through the bones of the skull that allow different structures of the nervous and circulatory system to enter and exit the skull. Short zygomatic process of dog skull. The most posterior is the sphenoid sinus, located in the . Sutures primarily visible from the side include: Coronal suture: Located between the frontal and parietal bones.Synonyms: Fossa frontalis cranii, Fossa cranialis anterior. The bones of the skull are highly irregular.Through the pterygopalatal column of the sphenoid, the lower surface of the skull base is directly involved in constituting the posterior midface. You will find an extensive fascial part that is concave and bears no lacrimal process. A – Frontal bone.The frontal bone is one of the eight bones that make up the cranium – the superior aspect of the skull that encloses and protects the brain. skull vault osteoma. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure 7.Label the Frontal Bone Quiz – PurposeGames.
Frontal Bone: Understanding Anatomy, Function & Treatment
It is a large, complex, unpaired bone, deriving its name from Greek’ sphenoeides’, meaning wedge-shaped. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure 10. Most of the bones of the skull are held together by firm, immovable fibrous joints called sutures or synarthroses.

frontal process of maxilla : via lateral portion of nasal notch. I hope you will quickly identify these structures from the frontal bone of the dog skull.There are two anatomically important landmarks found on the external surface of the skull that the frontal bone contributes to the bregma and the pterion.The largest fontanelle is the anterior fontanelle where the frontal bone, left parietal bone, and right parietal bone have not yet fused. These bones are joined together by sutures, which are fibrous joints that allow for limited . The cranium is divided into the cranial roof or . The frontal bone is made up of three . F – Occipital bone. Lambdoid suture: Located between the parietal, temporal and occipital bones.The frontal bone is found superiorly while the mandible lies inferiorly, giving the skull an ovoid shape when looked at anteriorly. The bones of the skull include the frontal bone, parietal bones, temporal bones, occipital bone, sphenoid bone, and ethmoid bone.
Anatomy, Head and Neck, Skull
Sphenofrontal . Essentially, all of the foramen (singular), or the foramina (plural of foramen), in the skull are holes. The sagittal suture runs at the midline on . Superficially, it articulates with the frontal bone, ventrally maxilla bone, anteriorly nasal bone, and posteriorly malar or zygomatic bone.
Temporal surface. Ectoconchion – Located at the intersection of the frontal and zygomatic, on the medial aspect.The structure of the skull is a highly detailed and complex design.comOrbital part of frontal bone – Wikipediaen. What is the Zygomatic Bone.The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull.Lateral view of a skull showing sutures: The dotted red lines indicate the location of skull sutures.The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)).Frontal Lobe Location. The sphenoid is one of the eight cranial bones that make up the skull. Occipitomastoid suture. Unpaired bones include: ethmoid : via ethmoidal notch.

comNasal Bone Anatomy, Diagram & Function | Body Maps – .The most anterior is the frontal sinus, located in the frontal bone above the eyebrows.
Frontal Bone: Anatomy, Functions & Landmarks
The frontal bone is located at the front of the skull, above the nasal bones, and in front of the parietal bones. These can be found behind the superciliary arches, between the bones of the skull.
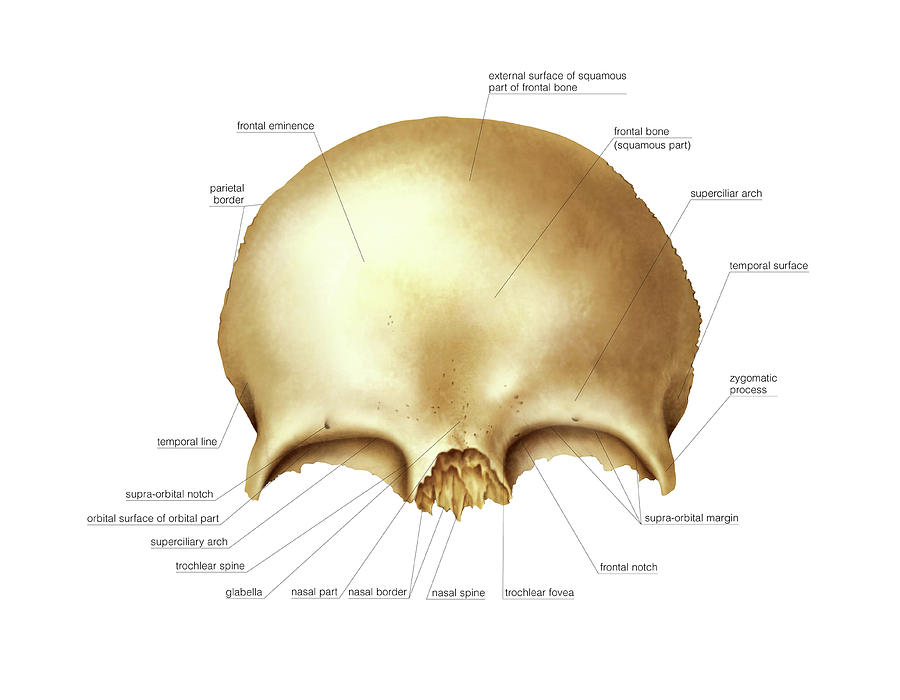
It is sometimes known as ‘zygoma’, a Greek word meaning ‘yoke’. You may get help from . Your frontal lobe is a key area of study for both brain-related and mental health-related fields of medicine.The skull is a vital bony structure of the human body, offering protection for crucial organs like the brain.Recent studies investigating impact force dynamics on the human skull suggest that the temporal region is the area most susceptible to fracture, largely due to its thinner diploe .comAnatomy, Head and Neck: Frontal Bone – StatPearls – NCBI .The frontal sinuses are paired air-filled cavities in frontal bone of the skull and one of the four different paranasal sinuses, along with the maxillary sinus, sphenoidal sinus and . As the name implies, the frontal lobe is located in the anterior aspect of the .The skull is divided into the braincase (cerebral cranium) and the face (visceral cranium). Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones. This will include the various foramina, the nerves and arteries that pass through them, but also the structures of the brain and cerebellum, which all lie within the three . The word foramen comes from the Latin word meaning “hole. sphenoid: greater wings via border of squama. This article will describe the anatomical structures which can be seen from a superior view of the skull base. E – Parietal bone. Osteomas most commonly occur in bones formed in membrane, almost exclusively occurring in the head 5, with the most common locations including: paranasal sinus osteoma.The frontal bone, typically a bone of the calvaria, is sometimes included as part of the facial skeleton. In Latin, it is also referred to as “Sinus Frontales”.Basilar Skull Fractures. F r o n t a l . Learning Objectives.Home Skull Bones Zygomatic Bone (Cheekbone) Published on February 18th 2022 by staff. The frontal bone underlies the forehead; above . In all, there are 22 bones comprising the entire skull, excluding the 3 pairs of ossicles located in the inner ear. The sagittal suture runs at the midline on the top of the skull. The frontal bone has two portions: vertical portion (squama): has external/internal surfaces.Dacryon – Located in the medial aspect of the orbits, the point where the maxilla, lacrimal, and frontal meet. The skull is divided into the braincase ( . Frontal sinus Definition It refers to one of the two air-filled cavities in the frontal bone. Other soft spots are the sphenoid, mastoid, and posterior fontanelles. The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the paranasal sinuses.The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain, occupying about one-third of the cerebral hemisphere. Parietomastoid suture. mandibular osteoma. It rests atop the temporal lobe, in front of the parietal lobe, . horizontal portion (orbital): has superior/inferior surfaces. It is located superior to the nasal bones and maxillae and anterior to the parietal .The human skull is the part of the skeleton that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.The lacrimal bone of the ox skull is extensive and located at the anterolateral portion of the skull. Paired bones include: nasal: via either side of midline of nasal notch. D – Temporal bone. Squama part of the frontal bone.The cranial cavity is a complex structure that is formed by the bones of the skull and their associated sutures, or joints. This bone forms the cheeks and the lateral walls of the eye sockets . These are well-cirumscribed tumors broadly attached to the .The human skull consists of about 22 to 30 single bones which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures.Frontal Bone: Anatomy, Functions & Landmarks – Innerbodyinnerbody.Your brain’s frontal lobe is home to areas that manage thinking, emotions, personality, judgment, self-control, muscle control and movements, memory storage and more.The coronal suture passes across the top of the anterior skull. The frontal lobe is located toward the front of the cerebrum, just back the forehead and below the frontal skull bones.Introduction The frontal sinus (FS) is the most complex of the paranasal sinuses due to its location, anatomical variations and multiple clinical presentations. The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the . The limbic system is sometimes called the limbic lobe, that .comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Frontal Bone
It is also known as the .From this frontal bone area, you might identify the following structures – Temporal line of dog skull. The different soft spots and sutures of a human baby’s skull. These are paired and . The frontal bone articulates with the right and left parietal bones, the zygomatic bones, the sphenoid bone, the ethmoid bones, lacrimal bones, maxillary bones, and the nasal bones. It is composed of five bones – the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, temporal and occipital – that .comOccipital bone: Anatomy, borders and development | Kenhubkenhub.
Anatomy and Topography of the Craniofacial Region
The main task of the skull is the protection of the most important organ in the human body: the brain. Its name is derived from the Latin . You can easily feel the bone by touching your forehead. The 8 (2 paired and 4 unpaired) bones forming the cranium are called the cranial bones. B – Ethmoid bone. This irregular space may be divided at the midline into bilateral spaces, or these may be fused into a single sinus space. The frontal bone is classified as the bone of the .comFrontal Bone Anatomy | GetBodySmartgetbodysmart.
The Skull
The orbital part .Parietal pleura. Zygomatic bone, commonly known as the cheekbone, is a paired, irregular facial bone. Whereas through the frontal . It unites the frontal bone anteriorly with the right and left parietal bones. It is one of the largest and most robust skull bones. Once fused, the bones of the skull are said to be sutured. Fractures of the skull base should be considered whenever a significant trauma mechanism is involved (most often, a motor vehicle collision). However, patients often present with periorbital ecchymosis (raccoon eyes .The frontal bone is an unpaired, somewhat bowl-shaped bone of the skull.
Frontal bone: Anatomy, borders and development
The frontal bone is a bowl-shaped bone in the frontal (forehead) region of the skull. The surgical management of the FS and of the frontal recess (FR) is technically challenging, and a complete understanding of its anatomy, radiology, main diseases and surgical . The largest are the maxillary sinuses, located in the right and left maxillary bones below the .The location of a headache—whether it’s the entire head, one side of the head, the front of the head, or the back of the head—is a good first step in sorting out headache type. It is the uppermost part of the skull that encircles and protects the brain, as well as the cerebral vasculature and meninges. The hollow space taken up by the brain is called the cranial cavity. Supraorbital margin and supraorbital foramen of dog skull.The frontal bone is a large, unpaired bone that starts out developmentally as two halves that fuse together, along the metopic suture.
Zygomatic Bone (Cheekbone)
C – Sphenoid bone.The paranasal sinuses are hollow, air-filled spaces named for the skull bone that each occupies. The cranium is made up of the neurocranium and the facial skeleton.What is the Sphenoid Bone.govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
The Frontal Bone
It is located above the supraorbital . Frontal sinus Location The frontal sinuses are located within the lamina of the frontal bone. Macroscopic appearance. The squamous suture is a curved suture located on the lateral side of the .The paranasal sinuses are named for the skull bone that each occupies. Frontotemporale – Located on each of the temporal . It rests atop the temporal lobe, in front of the parietal lobe, and separated from the occipital lobe, with pieces of the limbic system.3 Position of the bones of the skull (cranial cavity). It unites the right and left parietal bones with each other. The frontal bone consists of six main parts: the squamous part, nasal part, two orbital plates and two zygomatic plates.
Osteoma
Euryon – Determined using spreading calipers placed on the posterior parietals at the greatest breadth. The patient’s presenting signs and symptoms will depend on the location and extent of the fracture. The largest sinus is the maxillary sinus.orgCranial Bones: Function and Anatomy, Diagram, Conditions .Bones of the Skull | Skull Osteology | Anatomy | Geeky Medicsgeekymedics. The bone forms a significant portion of the middle part of the skull base and the floor of the middle cranial fossa. Zygomatic process (2) The frontal eminence is a round elevation on each side of the frontal bone.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Frontal lobe: Anatomy, function and clinical relations
The frontal bone articulates with twelve bones. lesser wings via posterior borders of orbital plates. The bregma is the .The frontal lobe is located toward the front of the cerebrum, just back the forehead and below the frontal skull bones. The frontal bone (os frontale) is an unpaired craniofacial bone that provides partial coverage of the brain and forms the structure of the forehead and upper casing of .
Skull: Anatomy, structure, bones, quizzes
Just as its name indicates, it’s the forward-most area of your brain. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see Figure 15). Describe the parts of the skull.
- Frühmenschen Der Prähistorie : Fossilfund: Lebten schon Frühmenschen auf dem Dach der Welt?
- Fruits With High Iron , The Top 10 Foods High in Iron
- Frp Sperre Umgehen Samsung Kostenlos
- Fs Design Hamburg _ Profil
- Fröhlich Wilhelmshaven | Ärzte für Psychiatrie, Psychotherapie in Wilhelmshaven
- Fritz Box 7490 Wlan Geschwindigkeit
- Fristen Und Termine Hu – Fristen und Termine
- Fructoseintoleranz Symptome Fruchtzucker
- Fröttmaninger Heide München – Freimann: Wissenswertes, Tipps und Infos
- Fritz Fax Windows 11 Installieren
- Fröhling S3 Turbo Erfahrungen : Fröling S1 Turbo oder S4 Turbo?