Groundwater Definition _ National Geographic Freshwater 101: Groundwater
Di: Luke

It can be found in aquifers, rock, or sediment layers holding water. It’s more like water in a sponge.Learn the meaning of groundwater, a noun that refers to water within the earth that supplies wells and springs. It connects to rivers, streams, lakes and wetlands. Grundwasser ist Teil des Wasserkreislaufs.Groundwater is water that seeps into the ground and accumulates in aquifers, forming groundwater resources.Groundwater Definition. It also is an abundant natural resource.Grundwasserabfluß, Grundwasserabstrom, Wasser, das einem Fließgewässer über die Grundwasserneubildung und horizontale Wasserflüsse in der gesättigten . Over 95% of the world’s freshwater, excluding glaciers and ice caps, is found .Groundwater is (naturally) recharged by rain water and snowmelt or from water that leaks through the bottom of some lakes and rivers. Groundwater also can be .
Fehlen:
definition When groundwater is extracted in large amounts or too quickly .Groundwater contamination happens when harmful chemicals are introduced into groundwater. vadose zone (also often termed “soil water”) and.Groundwater remediation includes technologies designed for groundwater pollution control and/or to make groundwater drinkable as coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, lime softening, ion exchange, oxidation-disinfection, chlorination, aeration, reverse osmosis, and ultrafiltration. When rain falls on the earth, part of it hydrates the soil, and some travel down the land surface to lakes, rivers, and streams. Underground, groundwater fills the spaces between sand, gravel, and other rock forms. Dabei bewegt es sich, dem größten Gefälle des Grundwasserleiters folgend, . Gravity and pressure move water downward and sideways underground through spaces between rocks.Schlagwörter:Groundwater SummaryGroundwater TheoryThe Study of GroundwaterGroundwater is a part of the natural water cycle (check out our interactive water cycle diagram).Abstract: Water below the land surface, both from unsaturated and saturated zones, is referred to as groundwater. The paper summarizes current understanding of recharge processes, identifies recurring recharge .Groundwater Flow and the Water Cycle.Übersicht
Groundwater
Groundwater accounts for nearly 95 percent of the nation’s fresh water resources. Trees and other vegetation can tap into groundwater. Bedeutung und Gefährdung des Grundwassers. Groundwater slowly moves between gaps in rocks and sediments. Gravity pulls water down towards the center of the Earth, gradually filling in .
Groundwater: Sources, Functions, and Quality
The EU’s objectives include: preventing and limiting groundwater pollution; ensuring that a sufficient quantity of good quality water is available for people’s needs, the economy, and the environment ; sustainably managing . This source is estimated to contain more . Groundwater is the water that seeps into the earth and is stored in aquifers—areas of soil, sand, and rock that are capable of holding liquid. It is therefore relevant to assess what is now known and to offer further guidance to practitioners involved in water-resource development. Yes, water below your feet is moving all the time, but not like rivers flowing below ground. Groundwater is one of the greatest valued and unlimited renewable natural resources, although .Groundwater is crucial to millions of Americans as well as many more worldwide.Groundwater is the water that soaks into the soil from rain or other precipitation and moves downward to fill cracks and other openings in beds of rocks and sand. (Definition of groundwater from the Cambridge Academic Content Dictionary © Cambridge University Press) Examples of .Schlagwörter:SoilEffect On Ground WaterGroundwater Quora It is critical for drinking, irrigation, and wildlife, but it is also . Learn about the global and Australian . It is replenished by precipitation, snowmelt, and surface water that seeps into the ground.
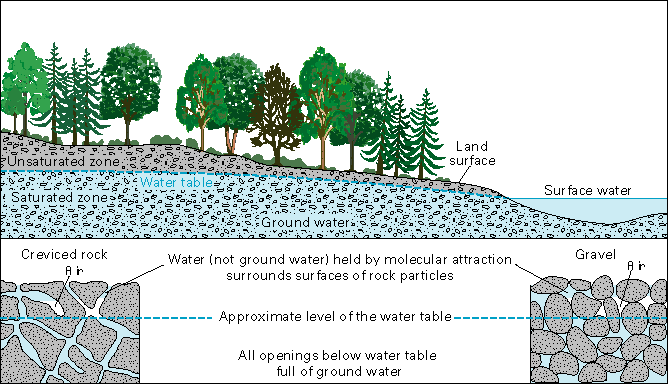
Groundwater represents 98% of the world’s unfrozen freshwater and its use has increased significantly over the past 50 years due to its high reliability during drought seasons, good quality and generally modest development costs. It also should provide for integrated decision-making for groundwater resources and aquifer systems, and . See examples of groundwater in sentences, word .
Grundwasser
Groundwater is the water below the land surface. While part of this water evaporates and returns to the air, a portion is absorbed by the plants. Recovery from pollution is not easy, as removing pollutants is difficult, meaning that they can accumulate. Aquifers are the collective saturated spaces between many layers of sands, soils, and gravels (called alluvial aquifers), or the interconnected cracks in bedrock or volcanic deposits (called fractured rock aquifers). Learn more about groundwater sources, uses, quality, and effects of earthquakes, pesticides, and wells from the USGS.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 4 min
What is groundwater?
Since the mid-1980s, a relative explosion of groundwater-recharge studies has been reported in the literature.Schlagwörter:Ground Water Definition ScienceGround Water and Drinking Water
Groundwater
The essential features of flow through porous media are in common with flow in pipes and channels, (Chapter 1), but certain aspects are distinctive to groundwater flow.

National Geographic Freshwater 101: Groundwater
Younger groundwater is usually associated with land use pollution, whereas problems involving older waters are . Groundwater is the largest reservoir of liquid fresh water on Earth and is found in aquifers, porous rock and sediment with water in between. Groundwater is used for drinking water by more than 50 percent of the people in the United States, including almost everyone who lives in rural areas.Schlagwörter:Groundwater DefonitionGroundwater MerriamGroundwater ExamplesThe Importance of Groundwater. The volume of water taken during this process per unit of time. The water sits in between particles or . Find out how gravity, rocks, and soil affect groundwater . Groundwater is a critical source of water to the world, and for good reason—it is often accessible, abundant, and affordable.5 percent—35 million cubic kilometers—is freshwater, and only 31.
Grundwasser
Synonyms: withdrawal, . In general, they are not easy to perceive, however in recent years, it has been found that they can contain high diversity of living forms with particular adaptive characteristics suggesting that the water quality is maintained and .67 million cubic kilometers—is not ice or snow in the .
Groundwater: What is Groundwater?
Groundwater is an important source of water stored in the earth, deep beneath our feet, in what are called aquifers. Eventually it emerges back to the land surface, into rivers, and into the .Schlagwörter:Ground Water and Drinking WaterCosumnes Groundwater
Groundwater: Sources, Functions, and Quality
Grundwasser ist Teil des Wasserkreislaufs. It is, therefore, a renewable resource, although renewal rates vary greatly according to environmental conditions. The part that continues downward through the soil until it reaches rock material that is saturated is groundwater recharge.1 Groundwater: An Unlimited Renewable Resource.Groundwater is a significant source of freshwater, estimated to account for about 30% of the world’s freshwater resources.GROUNDWATER meaning: water that collects below the surface of the earth. Groundwater provides drinking water to many.Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand and rock.3 percent of that—10. This comes under a branch of fluid dynamics known as flow through porous media.
What is Groundwater Pollution, and How Can it be Prevented?
By definition, groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface, and the upper surface of the saturated zone is called the water table. Learn about the formation, circulation, and role of groundwater in . The first step in selecting the appropriate groundwater . It is used for drinking water, irrigation, industry, . A portion of the water also percolates into the ground, travels through the unsaturated zone .Groundwater is stored in the open spaces within rocks and within unconsolidated sediments. The occurrence of groundwater depends on several factors. Webster’s New World. Oberflächennahe Grundwasservorkommen versorgen Pflanzen mit Wasser und bilden wertvolle Feuchtbiotope.Groundwater resources are also under increasing pressure from water abstraction and climate change. Grundwasserabfluß, Grundwasserabstrom, Wasser, das einem Fließgewässer über die Grundwasserneubildung und horizontale Wasserflüsse in der gesättigten Bodenwasserzone (Grundwasserspeicher) zufließt.

Rocks and sediments near the surface are under less pressure than those at . Es stammt ganz überwiegend aus Regenwasser, das durch den Boden und den Untergrund bis in die .
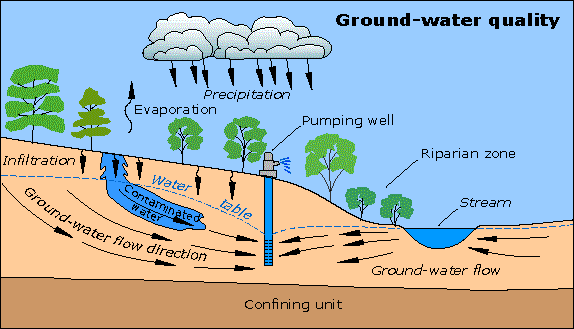
Groundwater is water that exists underground in saturated zones beneath the land surface. Some part of the precipitation that lands on the ground surface infiltrates into the subsurface. It is stored in and moves slowly through geologic formations of soil, sand and rocks called aquifers. Similar definitions. Find data, maps, publications, and multimedia on groundwater quality and .
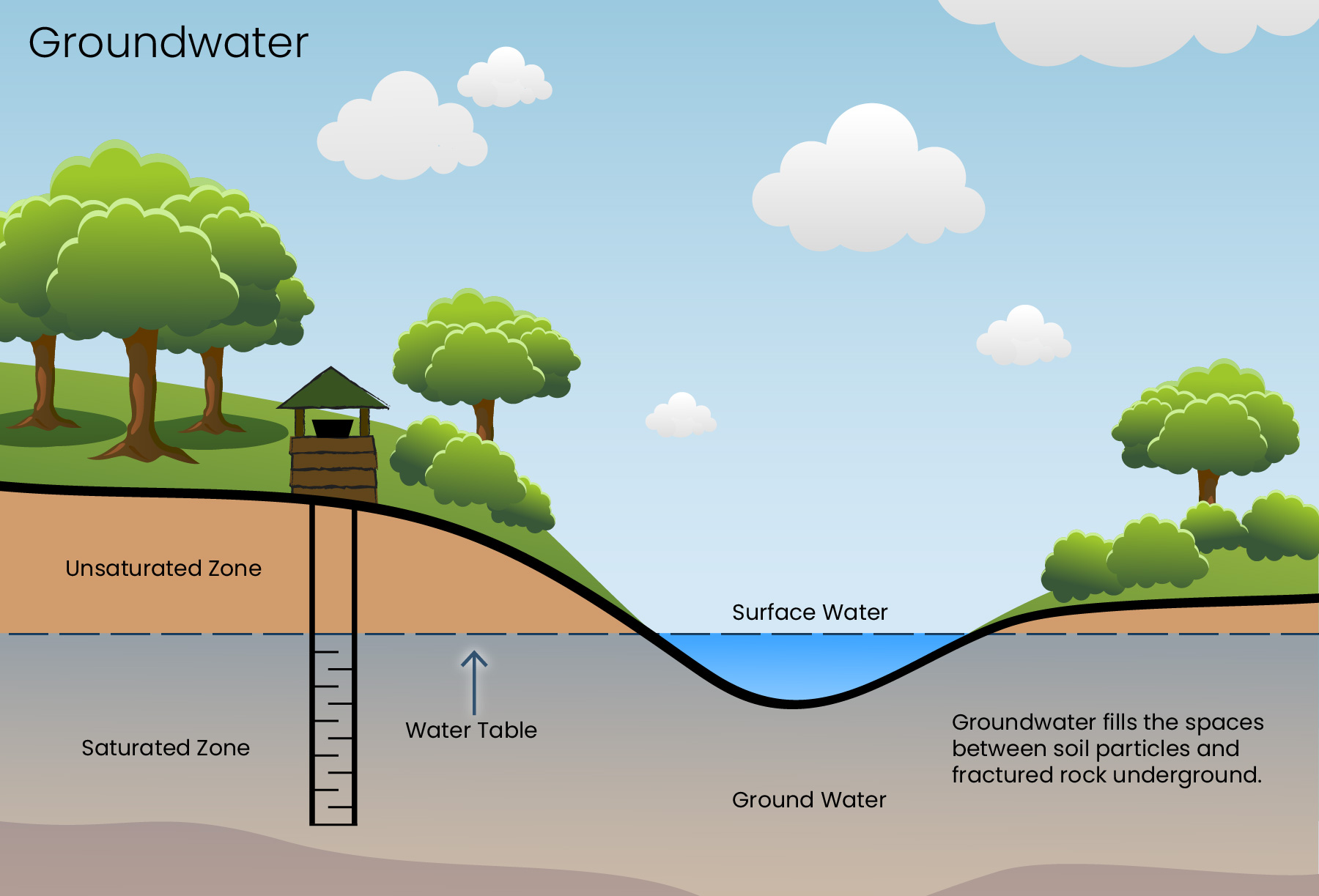
Es stammt ganz überwiegend aus Regenwasser, das durch den Boden und den Untergrund bis in die Grundwasserleiter sickert.water that collects below the surface of the earth.Schlagwörter:Government DataGroundwaterWater That Is in The Ground
What is Groundwater?
Groundwater consists. It can stay underground for hundreds of thousands of years, or it can come to the .Groundwater is water that occurs below the surface of Earth, where it occupies all or part of the void spaces in soils or geologic strata.Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock.Groundwater stores almost one third of total global freshwater resources and, in the EU, supplies 65% of drinking water and 25% of water for agricultural irrigation.Groundwater dependent ecosystems (GDEs) constitute one of the largest environments at the global level.Groundwater is water that has infiltrated the ground to fill the spaces between sediments and cracks in rock. Groundwater or ground water is water located within the ground’s zone of saturation, where the soil pore spaces and fractures in the rock are completely filled with water. Of all the water on Earth, only about 2.Schlagwörter:GroundwaterSoil both of water that remains in the unsaturated or. Groundwater pollution is a serious threat to this resource.The process of taking water from a source, either temporarily or permanently. Thus, having reliably clean groundwater is of concern for many throughout the world. It differs from soil water, which is the water that is in the unsaturated zone, or zone of aeration, where the soil pore spaces contain air and water but are not .Lexikon der Geowissenschaften Grundwasserabfluß.Schlagwörter:Ground Water Definition ScienceGroundwater Defonition Groundwater is fresh water (from rain or melting ice and snow) that soaks into the soil and is stored in the tiny spaces (pores) between rocks and particles of soil.Schlagwörter:Ground Water Definition ScienceSoilGround Water and Drinking WaterAt this point we have to deal with the physics of groundwater movement. But, groundwater can become contaminated with chemicals, biologic organisms, and other possibly-harmful agents.Learn what groundwater is, how it is replenished, used, and monitored by the USGS.Als Grundwasser bezeichnet man unterirdisch bewirtschaftbare Wasservorkommen, ausgenommen Wasser in Rohrleitungen, Behältnissen oder anderen technischen Anlagen. Water found underground in porous rock strata and soils, as in a spring.Groundwater policy should be contingent on the legal status and nature of ownership of groundwater (public or private), as well as on factors like the water users, the interrelated surface water features, and the land uses in aquifer recharge areas.groundwater Bedeutung, Definition groundwater: water that collects below the surface of the earth. Water that exists beneath the earth’s surface . We know more about groundwater and aquifers from work completed during previous Intergovernmental .Schlagwörter:Examples of Ground WaterGroundwater Definition Science
Grundwasser
Water is attracted to the soil particles and capillary action, which describes how water moves through a porous media, moves water from wet soil to dry areas. Some examples are pesticides and gas.Learn about groundwater, the water that is below the earth’s surface and part of the natural water cycle.Ein unbekannter Teil des Abflusses aus der Wasserbilanz speist die Grundwasservorkommen, eine gleiche Menge Grundwasser speist die Fliessgewässer . Das Grundwasser tritt in Quellen zu Tage und speist .Groundwater contains much higher levels of most ingredients than surface water, and deep groundwater that has been in contact with rock formation for a long time tends to have elevated levels than shallow and young water.Groundwater is a precious resource hidden from sight, where pollution poses a serious threat. of water that reaches the saturated zone (aquifer) where pore spaces .Groundwater is the water found underground in soil, sand and rock that is stored in and moves slowly through aquifers.Schlagwörter:Ground Water Definition ScienceGroundwater DefonitionArtesian Aquifer
What is Groundwater? Definition and Conservation
- Große Schwarze Tasche – Schwarze Einkaufstaschen kaufen » Schwarze Shopping Bags
- Größter Wale Der Erde , Das größte Tier auf der Welt
- Großer Brachvogel Geschichte _ Grosser Brachvogel (Numenius arquata)
- Grundschule Deutschland : Lange Wand in 49779 Niederlangen (Niedersachsen)
- Grundpfandrechtsbrief , Fenstertitel: Kraftloserklärung von Urkunden
- Größer Kleiner Erste Klasse , Unterrichtsentwürfe Lehrproben Mathematik, Klasse 1
- Grundbuch Abteilung Ii , alte Grundbuchbelastungen
- Gründe Für Namensänderung – Vornamen ändern: So geht’s
- Größter Plastikteppich Im Meer
- Größte Private Krankenversicherer Deutschland
- Großes Vieleckbein Trapezium , Mittelhandgelenke: Anatomie, Aufbau, Bänder & Knochen
- Großensee Wanderkarte _ Großensee-Rundweg Wanderweg