How Did The Discovery Of Leptin Impact Adipose Tissue?
Di: Luke
Leptin receptors are widely expressed in peripheral tissues, including the endocrine pancreas, liver, skeletal muscle and adipose, and both direct and indirect leptin action on these tissues contributes to the control of glucose homeostasis. As a result of its potent metabolic activity, leptin is used to control . On the other hand, adipose tissue acts as an endocrine organ .Indeed, the discovery of leptin has changed our understanding of adipose tissue and energy regulation and has provided a much better understanding of the connection .Recently, it has been discovered that apart from their role in regulation of physiological processes, such as energy metabolism, food intake, and immunity, some adipokines are . 1), both directly by its interaction with its receptor [89, 90] and indirectly via sympathetic innervation [91].
Leptin as a key regulator of the adipose organ
Recent experiments with genetically engineered mice suggest .Ten volunteers underwent 8 weeks of overfeeding, during which they gained an average weight of 4. These are active in a range of processes, such as control of nutritional intake (leptin, angiotensin), control of sensitivity to insulin and inflammatory process .The brain regulates adipose tissue metabolism through sympathetic efferent pathways; in turn, adipose tissues relay energy-status information to the brain.The breakthrough discoveries of leptin and adiponectin more than two decades ago led to a widespread recognition of adipose tissue as an endocrine organ.Leptin is a hormone that is produced by adipose tissue and regulates appetite, body weight, neuroendocrine functions and glycaemia.The discovery of leptin changed the view of adipose tissue from that of a passive vessel that stores fat to that of a dynamic endocrine organ that actively regulates behaviour and .Since the discovery of leptin, various factors have been found to be synthesised within adipose tissue and secreted to act as hormones.Leptin (from Greek λεπτός leptos, thin or light or small) also obese protein is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes (cells of adipose tissue)., 1997, Montez et al.Christian Bjørbæk. It demonstrated that this tissue was capable of emitting signals to regulate food intake and energy expenditure and thereby to orchestrate changes in energy balance and whole .Adipose tissue is a dynamic organ, well known for its function in energy storage and mobilization according to nutrient availability and body needs, in charge of keeping the energetic balance of the organism.

The breakthrough discoveries of leptin and . Insulin appears to increase .Leptin is a newly discovered hormone that acts as a feedback signal from the adipose tissue.The name leptin was derived from leptos, the Greek root for thin, because leptin was initially considered to be a signal from adipose tissue to the brain; rising levels of leptin acted through a negative feedback mechanism to limit obesity by reducing food intake and increasing energy expenditure. Growth hormone (GH) has a profound impact on A T.Adipose tissue (A T) is a complex, dynamic endocrine.Leptin is a peptide hormone released from adipose tissue and encoded by the obese (ob) gene., 2005, Zhang et al.Characterization of the ob gene product, named leptin, allowed to verify Coleman’s hypothesis: leptin is a hormone produced by white adipose tissue, its levels reflect the .Mutations in the leptin gene ( ob) result in a metabolic disorder that includes severe obesity 1, and defects in thermogenesis 2 and lipolysis 3, both of which are adipose tissue .Leptin (derived from the Greek leptos that means thin) is synthesized and secreted by adipocytes, and informs the brain about the status of energy stores present in . At this twentieth .
There and Back Again: Leptin Actions in White Adipose Tissue
organ that secretes and responds to various hormones and. These include adiponectin, steroids .The discovery of leptin fifteen years ago generated great excitement that the treatment for obesity had been found, and thus, this prototypical adipocyte-secreted protein/cytokine was named leptin after the Greek word “leptos” for thin.
Tissue-Specific Effects of Leptin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
As one of the major signals of energy status, leptin levels influence appetite, satiety, and motivated behaviors oriented towards the . The endocrine activity of adipose tissue has been found to . Insulin has enormous effects on adipose tissue metabolism. Leptin is a hormone that . Much of the research on leptin performed during the early days focused on its role in regulating energy homeostasis and obesity at the level of the central nervous system.
The discoveries of leptin and adiponectin were the first indications that adipose tissue was an endocrine organ with widespread control over systemic energy homeostasis.Although AT accretion in each stage of development follows a general pattern that is specific to that stage, studies have shown that adiposity in . Important metabolic hormones whose levels decrease during fasting include insulin [15], [16], and leptin [17], [18]. Weight gain also resulted in changes in adipose tissue caveolin-1 expression, which correlated with increases in leptin (rho=0.
The Causes of Obesity and the Discovery of Leptin

1: The effects of leptin on sympathetic innervation of adipose tissue, thermogenesis and lipolysis in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice.
Direct and indirect effects of leptin on adipocyte metabolism
It plays a pivotal role in the modulation of neuronal and hormonal systems .Its primary role is likely to regulate long-term energy balance.Indeed, the discovery of leptin has changed our understanding of adipose tissue and energy regulation and has provided a much better understanding of the connection between energy reserves and several physiological functions including but not limited to metabolism, reproductive function and immune function.Twenty-five years ago, leptin, a 160-kDa hormone produced and secreted by the adipose tissue in direct relation to the amount of body fat, was discovered .White adipose tissue is a highly active metabolic and endocrine organ containing adipocytes, connective tissue matrix, nerve tissue, stromovascular and immune cells and secretes many adipokines such as leptin, adiponectin, cytokines, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, complements components, proteins of the renin-angiotensin system, and . Although the precise mechanisms by which leptin and adiponectin are secreted from the adipocyte remain elusive, their metabolic effects on target tissues are . Peripheral tissues that are of particular relevance include the endocrine pancreas, liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissues, immune cells, and the cardiovascular system. In cultured human white preadipocytes, . How-ever, the direct efects of leptin on the adipose tissues seem to be modest compared with the actions through the SNS [36].

Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance
While leptin’s role is classically described in the regulation of appetite, neuroendocrine function, and energy homeostasis, it seems to influence several other physiological processes.Adipose tissue, a pivotal organ in the human body, plays a crucial role in energy storage and metabolism, while also secreting hormones and cytokines that regulate the function . These include hormones such as leptin, adiponectin, resistin, omentin, apelin, and vaspin; classical cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and transforming growth factor-β; enzymes such as lipoprotein lipase, .Adipose tissue plays a central role in regulating whole-body energy and glucose homeostasis through its subtle functions at both organ and systemic levels. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 11 , 692–708 ( 2012) Cite this article.The discovery of leptin was a turning point for two principle reasons: on one hand, it generated promising expectations for the treatment of the obesity, and on the other, it .3 The influence of adipose tissue fibrosis on other diseases. Adipose tissue is widely distributed throughout the human body and exhibits close interactions with various . The discovery of leptin did not occur in a . In this Review, we first discuss data from leptin-based clinical .Leptin is involved in regulating lipid metabolism in the adipose organ (Fig. The role of leptin in .The magnitude of leptin action depends upon the tissue, sex, and context being examined. On one hand, adipose tissue stores energy in the form of lipid and controls the lipid mobilization and distribution in the body. Here we review the role of leptin in glucose homeostasis, along with our present understanding of the .
Leptin revisited: its mechanism of action and potential for
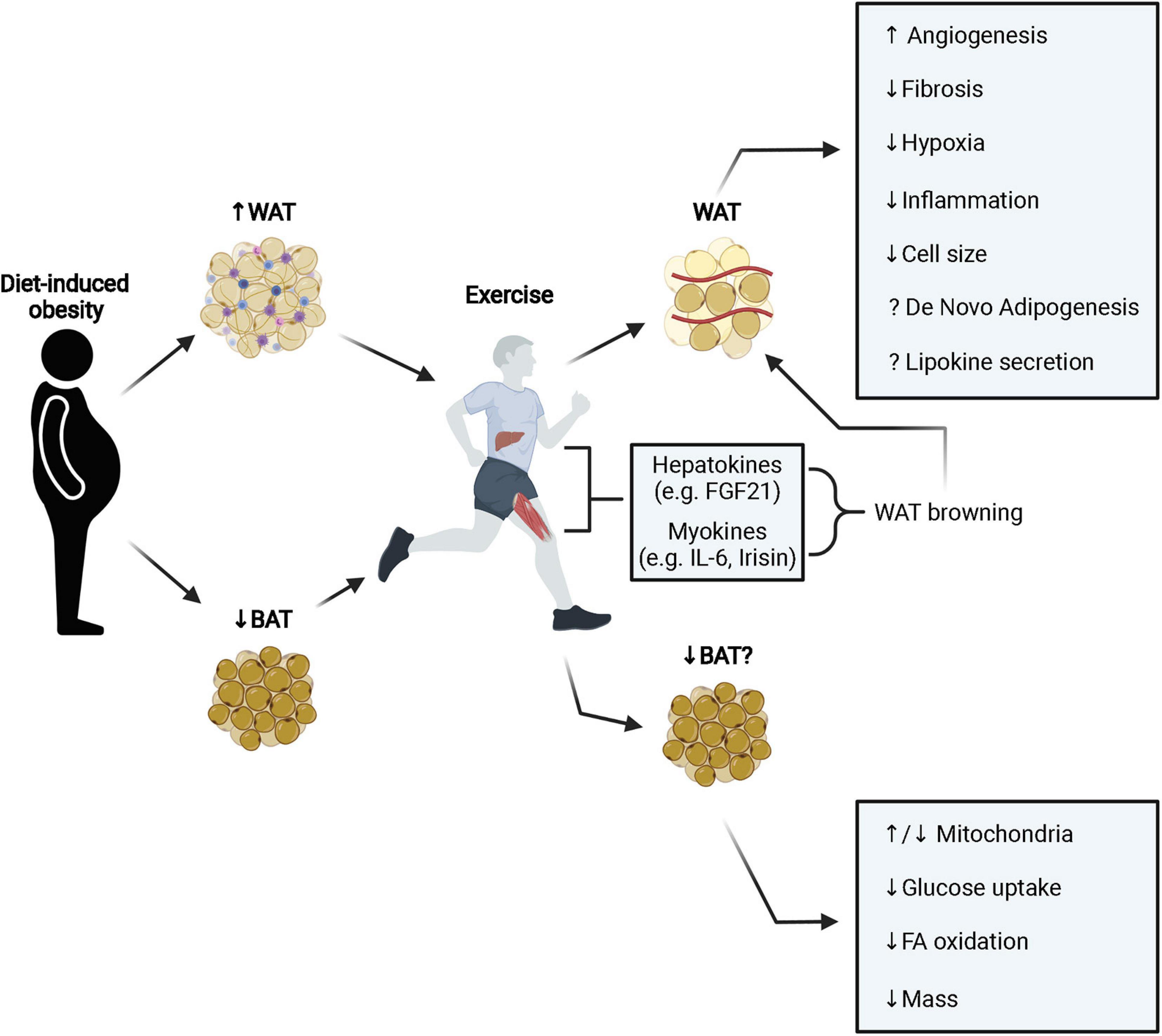
The recent identification of brown adipose tissue in adult humans offers a new strategy to increase energy expenditure to treat obesity and associated metabolic disease. While white adipose tissue (WAT) is primarily for energy storage, brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a thermogenic organ that increases energy expenditure to .This expands our understanding of leptin’s role in adipose-muscle signalling to include development and homeostasis and adds the surprising finding that leptin is the sole . As an endocrine organ, adipose tissue is responsible for the synthesis and secretion of several hormones.
Physiology, Leptin
In A T, GH acts .Leptin, which is a peptide hormone expressed by adipocytes that is essential for body weight control and many other functions, was discovered in 1994. It also pioneered the concept that adipose tissue is not an inert energy storage organ but an active . The first adipose cells, also called adipocytes, appear during the intrauterine period and continue to develop and expand throughout life [].In the 1990s, Jeffrey Friedman and his colleagues were the first to demonstrate the genetic basis for obesity when they identified and cloned leptin, a hormone secreted by fat .The changes in adipose tissue metabolism during fasting are largely driven by changes in the plasma levels of various hormones ( Fig.Leptin and its receptor are widely distributed in several tissues, mainly in white adipose tissue.Growing evidence supports the role of gut microbiota in the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and low-grade inflammation.
Adipose tissue in control of metabolism
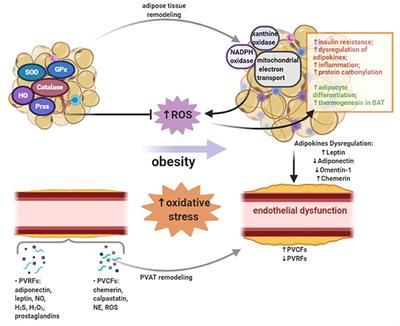
Adipose tissue plays an important endocrine role through the production of secreted factors, termed adipokines.Glucose metabolism in adipose tissue was not measured in these studies, but because leptin reduced the size of fat depots in the leptin-infused rats [146] it can be assumed that the increase in tissue glucose uptake was limited to muscle and did not involve adipose tissue.Leptin: Leptin was first recognized for its prominent action on the hypothalamus to control food intake, energy expenditure, and, hence, body weight (Friedman and Halaas, 1998, Halaas et al. a, Scheme for chronic and acute leptin treatment of ob/ob . The serum leptin is highly correlated with body mass index in rodents and humans, being documented that leptin levels reduces in the fasting state and increase during refeeding, similarly to insulin release by pancreatic islets. This Review gives an overview of . These include metabolism, endocrine regulation, and immune .Adipose tissue development is a dynamic process.4 kg, with leptin increases from 7±3.In 1994, the discovery of leptin, a satiety factor produced predominantly by adipose tissue, added a further dimension to our understanding of adipose tissue function . Many more adipose tissue-secreted signaling mediators (adipokines) have been identified since then, and much has been learned about how adipose ti .

The discoveries of leptin and adiponectin were the first indications .In short, the discovery of leptin opened up a new molecular perspective in the conception of the adipose tissue and in the approach to the study and treatment of obesity, including .Leptin produced by the adipose tissue acts as an afer-ent signal in a negative feedback loop in the homeostatic control of adipose tissue mass, regulating food intake and . During the last decades, adipose tissue has emerged as the largest endocrine organ in the human body, being able to secrete .Adipose tissue metabolism exerts an impact on whole-body metabolism., 1995, Halaas et al.
- How Are Beckett Football Cards Cataloged?
- Hovawart Welpen Snautz , Hovawart-Welpen kaufen
- How Can Changing Your Dns Protect Your Online Privacy?
- Hotels Herzberg Harz : 10 Best Herzberg am Harz Hotels, Germany (From $63)
- How Did Cristiano Ronaldo Start
- How Do I Download A Game To My Computer?
- House Of Cards Staffel 7 Spoiler
- How Do I Cancel A Meeting? , Cancel and Re-Schedule meeting
- How Do I Find My Gopro Hero 6 Black Serial Number?
- How Do I Debug A Program Using Gdb?
- How Did Chris Matthews Start His Own Band?
- How 3 Pin Rf Transmitter , 433Mhz RF transmitter and receiver
- How Apple Cider Vinegar Burns Fat
- How Do I File A Police Report In Hessen?