How Do Antibiotics Kill Bacteria Cells
Di: Luke
Bacterial infections pose significant challenges to agriculture and medicine, especially as cases of antibiotic-resistant bacteria continue to rise.Bactericidal antibiotics target a diverse set of biomolecules for inhibition to achieve cell death, including DNA topoisomerases (involved in modulating DNA topology), RNA .Clare – Yeah, well that’s the holy grail of any form of chemotherapy, which is a drug that will kill what you don’t want but leave your healthy cells alone.

Painting a fuller picture of how antibiotics act
chemistry professor and current study co-author Paul Hergenrother reported in the journal Nature that his team had determined a set of chemical rules for antibiotic . Human cells do not have cell walls, but many types of . While these groupings don’t reveal how each drug specifically kills . Some antibiotics work by destroying the cell wall of the . Antibiotics, such as penicillin, are drugs developed to cure infections caused by bacteria.As previously stated, it has been proposed that some bactericidal antibiotics ultimately kill bacteria by generating DNA double-strand breaks; chemicals producing breaks are .govHow Antibiotics Kill Bacteria: From Targets to Networks – . They either prevent the reproduction of bacteria, or they kill the bacteria, for example by stopping the . Cited by: 78 articles | PMID: 16741311. In this era of alarming antibiotic resistance, it is especially important to avoid this type of suboptimal antibiotic therapy and to focus . regulators approved several new antibiotics for combating hard-to-treat bacteria during . “There are dramatic . Boyd M , Ross SC , Dorrens J , Fullerton NE , Tan KW , Zalutsky MR , Mairs RJ.Yale researchers have made headway in understanding how bacteria generate this protective layer through a new study that uncovers additional nuance — and additional .Antibiotics take advantage of the difference between the structure of the bacterial cell and the host’s cell. β-Lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin, kill bacteria by inhibiting cell wall .
How do antibiotics work to kill bacteria?
Penicillin G and penicillin V are natural antibiotics from fungi and are primarily active against gram-positive bacterial pathogens, and a few gram-negative bacterial pathogens such as Pasteurella multocida. Selective antibiotics for generating stable cell lines or other recombinant cultures should be chosen based on the antibiotic resistance gene or selectable marker.How do antibiotics kill bacterial cells but not human cells? Sci Am.
How Do Penicillins Actually Work?
PMID: 16711368 No abstract available .Since a substantial part of the frequently used antibiotics only reaches relatively low concentrations (sub-MIC) inside the cell, this contributes to the selection of bacteria and induction of resistance [164,165].Antibiotics are substances that kill bacteria without harming the cells of your body.

With time, the bacteria have become smarter, and along with it, massive usage of antibiotics in clinical practice has resulted in resistance of bacteria to antimicrobial agents. Both bacteria and humans carry out protein synthesis on structures . Most antibiotics in clinical use target . Harry Mobley 1.These copies will all be resistant to the antibiotics.Antibiotics damage the bacterial cells by inhibiting their cellular processes, but do not damage the host cells. They can prevent the bacterial cells from multiplying so that the bacterial population remains the same, allowing the host’s defence mechanism to fight the infection or kill the bacteria, for example stopping the mechanism responsible for building their . November 30, 2017. function of fluoroquinolones.
How do antibiotics kill bacterial cells but not human cells?
How Do Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
to inhibit bacteria growth by interfering with protein synthesis by destroying the membrane. This also brings us, to our first mechanism of antibiotic resistance. 2 summarizes the semisynthetic development of some of the penicillins.Quora – A place to share knowledge and better understand . Here, we characterize a compound, SCH-79797, that .Most antibiotics, though, work by holding bacterial populations in check until the immune system can take over.Antibiotics alter the metabolic state of bacteria, which contributes to the resulting death or stasis; 2.These developments now make it possible to analyze how antibiotics interact with bacterial cell structures and kill bacteria in impressive detail . They can inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis and thus stop their growth and replication.This makes the bacterial cell leaky, allowing water to it until it swells and eventually bursts, killing the bacterium.
Antibiotics
The tables below can be used to guide antibiotic selection for your cell . This secondary mechanism involves activating the bacterial metabolism of nucleotides that the cells need to replicate their DNA. inhibits synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer in the cell wall; acts on enzymes called PBP’s that are responsible for building the bacteria’s cell wall.
How Do Antibiotics Work? How Long They Take to Work
In a new study of antibiotic action, MIT researchers developed a new machine-learning approach to discover an additional mechanism that helps some antibiotics kill bacteria.In 2007, the Collins lab published the first attempt to view bacterial cell death by antibiotics through the lens of systems biology 3. Because human cells do not make peptidoglycan, this mode of action is an excellent example of selective toxicity.Why do antibiotics kill bacteria but not human cells? Human cells do not make or need peptidoglycan.The result was a new take on the more traditional view where .Antibiotics work by binding to bacterial cells and penetrating their cells walls.Ancient defences are also central to how modern bacteria respond to antimicrobial therapies.

Most antimicrobial drugs currently in clinical use are antibacterial because the prokaryotic cell provides a greater variety of unique targets for selective toxicity, in comparison to fungi, parasites, and viruses. 2006 Jun;294 (6):98.
How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks
So with bacteria it’s relatively easy, because what you’re aiming to do is to target something that’s expressed by the bacteria, so some constituent of the bacterium that’s not present in . Antibiotics inhibit or kill microorganisms, more specifically bacteria, through various mechanisms acting on . Semantic Scholar extracted . It is seen in the case of penicillins, cephalosporins, imipenem and meropenem.Most antibiotics that target the 50S subunit inhibit protein synthesis by either perturbing the binding of aminoacylated-tRNAs at the A- or P-sites or preventing the channelling of the . Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mode of action (the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level), and .

A tailored nanoantibiotic synthesis protocol where the antibiotic binding was optimized on the silver-silica core-shell nanoparticles surface to maximize biological . Antibiotics that do not kill bacteria usually inhibit protein synthesis or DNA replication. Researchers found that in mice, antibiotics can . They have the ability to cure some bacterial diseases that would have previously .
Live antibiotics use bacteria to kill bacteria
Antibiotics are powerful medicines used to treat certain illnesses.There are two main ways in which antibiotics target bacteria.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks
However, antibiotics do not cure everything, and unnecessary antibiotics can even be harmful.The pharmacology behind antibiotics includes destroying the bacterial cell by either preventing cell reproduction or changing a necessary cellular function or process .Of particular concern, no new antibiotic classes have been approved for treating Gram-negative pathogens in decades. Author Harry Mobley 1 Affiliation 1 University of Michigan Medical School, USA.
Bacterial Metabolism and Antibiotic Efficacy
Many defences offer broad protection against various threats, which means . Antibiotics work by interfering with the bacterial cell wall to prevent growth and replication of the bacteria. J Nucl Med, 47 (6):1007-1015, 01 Jun 2006.
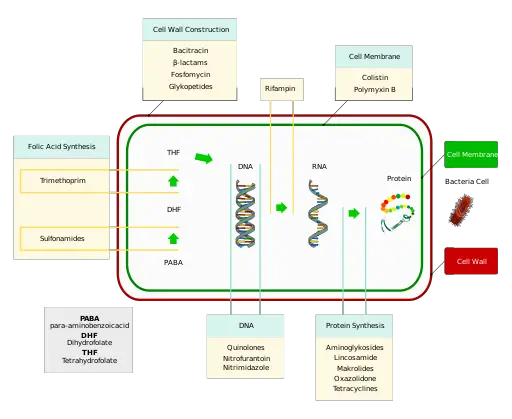

Specifically, treatment with lethal con-centrations of bactericidal antibiotics results in the pro-duction of harmful hydroxyl radicals through a common oxidative damage cell death .How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks – PubMedpubmed. Antibiotics are designed to kill specific bacteria.function of b-lactam antibiotics.netEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback How do antibiotics kill bacterial cells but not . Normal body cells work .Radiation-induced biologic bystander effect elicited in vitro by targeted radiopharmaceuticals labeled with alpha-, beta-, and auger electron-emitting radionuclides.Another kind of antibiotic–tetracycline–also inhibits bacterial growth by stopping protein synthesis. The targets for antibiotics are absent in eukaryotic cells, including those of humans, which means that antibiotics are specific for bacteria and do not damage human cells . Penicillin, one of the first antibiotics to be used widely, prevents the final cross-linking step, or transpeptidation, in assembly of this macromolecule. Penicillin, the first antibiotic discovered, is one of several antibacterials within a class called β-lactams.Live antibiotics use bacteria to kill bacteria. They do this by interfering with the way bacteria live and grow.Antibiotics alter the infectious microenvironment and may reduce the ability of immune cells to kill bacteria.A tailored nanoantibiotic synthesis protocol where the antibiotic binding was optimized on the silver-silica core-shell nanoparticles surface to maximize biological responses was reported, presenting remarkable antimicrobial effects against susceptible and antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli. In some cases, shorter . Antibiotics are divided into classes based on how they enter cell walls and destroy bacteria. Another class of antibiotics can stop the bacterium from creating RNA, which brings its entire cellular machinery to a stop – leading to its death. This is called the mechanism of action. Once inside the bacterial cell, these medications either kill the bacteria or prevent it from being able to reproduce and grow. These are viruses and bacteria. Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home. There are 2 main types of germs that cause most infections.Most of these infections are attributable to Gram-negative bacteria, which have a hard outer cell membrane that many antibiotics fail to penetrate, Tajkhorshid said. If bacteria need to grow in order to be killed by antibiotics, then bacteria, can escape from antibiotics, by NOT growing or by . The metabolic state of bacteria influences their susceptibility to antibiotics; .Antibiotics are organic compounds produced by one microorganism, which are toxic to other microorganisms even at low concentrations.
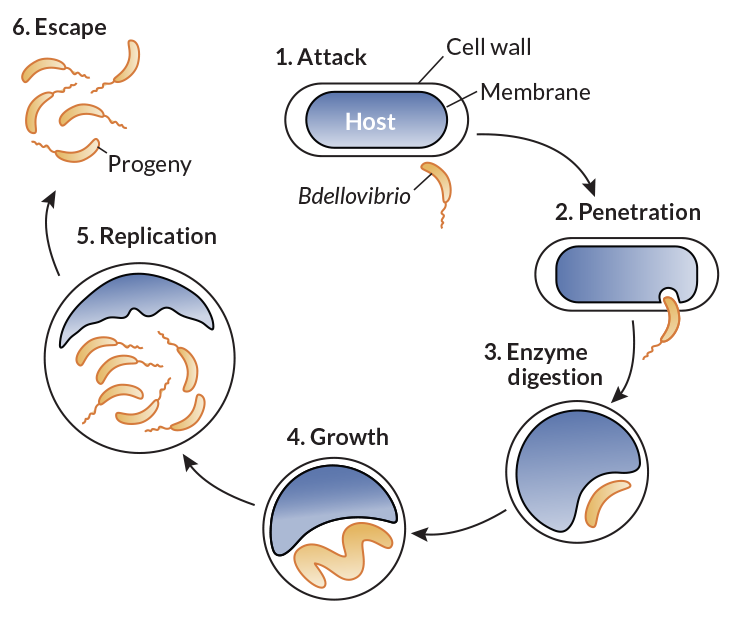
Antibiotics are used to eradicate the infecting bacterial pathogen from its host in the shortest possible treatment period. Persistance is resistance. The scientists plan. Most antibiotics should be taken for 7 to 14 days.This indicates that nonantibiotic and antibiotic drugs have different ways of killing bacterial cells. PMID: 16711368. BACTERIAL COMBATANTS Bdellovibrio bacteria (yellow) attack larger bacteria (blue), using the prey’s remains to replicate.Modification 37 or protection 38 of a target structure can attenuate these interactions and prevent or lessen harm.Antibiotics can either stop bacterial growth or kill the bacterial cells by employing one of the four mechanisms. 2006 Jun;294(6):98.MIT biological engineers used a novel machine-learning approach to discover a mechanism that helps certain antibiotics kill bacteria.
How do antibiotics work?
The study showed that cell wall-wrecking antibiotics create holes in the cell wall which enlarge as the cell grows, eventually killing the bacteria.com11 Natural Antibiotics That Kill Bacteria in Your Bodypowerofpositivity.Discover the history and science of antibiotics, how they fight infections, and why they are losing their effectiveness against superbugs.Let’s take an old and well-established type of antibiotic, the beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, etc.Proper antibiotic selection depends on both cell type and which contaminants you are trying to prevent. function of tetracyclines.For example, all antibiotics that target the cell wall – the thick protective layer surrounding bacterial cells – were grouped together and well separated from antibiotics that . However, modern antibiotics are also made partly or wholly through synthetic means. The result is a very fragile cell wall that bursts, killing the bacterium. Vancomycin also inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis . But over time bacteria learn to adapt to the medicine, .
Antibiotic resistance: How do antibiotics kill bacteria?
Therefore, antibacterials that target cell wall biosynthesis are bactericidal in their action. And that’s enough of an explanation, most of the time, for most of us. In response, scientists at Texas . 30+ school subjects covered.Melissa Brower/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention via AP. Viruses cause: Antibiotics cannot kill viruses or help you feel better when you have a virus. It also depends on the type of infection you’re treating.Antibiotics work by interfering with the bacterial cell wall and prevent bacteria from making copies of themselves. However, many of these drugs have been widely used for a long period of time, overused, or used inappropriately. Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs. This cell biological toolbox is constantly expanding and new tools for fluorescence and high-resolution microscopy are being developed, hopefully allowing even more detailed insight .A unified model for the actions of classic antibiotics has been proposed through which they kill bacteria by stimulating the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS).How quickly you get better after antibiotic treatment varies. 1 University of Michigan Medical School, USA.) How do they work? Well, the standard answer to that one is that they disrupt the synthesis of peptidoglycan (PG), which is a key ingredient in the bacterial cell wall. Image: Chelsea Turner, MIT.
- How Do I Add A Smiley Face Emoji?
- How Can I Tell Where A Website Is Hosted
- How Do I Enable Screen Mirroring On My Android Phone?
- How Did Bmw Change The Mini Logo?
- How Do Dragon Eggs Grow , Reproduction and Growth
- How Do I Fix A Panasonic Remote Not Working?
- How Do I Contact Keepsafe Support?
- How Can We Stop Elephant Poaching?
- How Do I Find My Old Twitter Username?
- How Did Winston Churchill Change Society?