How Laminar And Turbulent Flow Can Be Determined From Reynolds Number?
Di: Luke
Representing the fluid flow as a collection of coherent structures of . An indicator called the Reynolds number NR N R can reveal whether flow is laminar or turbulent. Laminar flow refers to the smooth and steady flow. The normalised thickness of the viscous flow layer reaches an asymptotic value but the physical thickness drops exponentially after transition. Turbulent flow, or turbulence, is characterized by eddies and swirls that mix layers of fluid together.By measuring the mean bulk flow rates and calculating a value for the mean bulk speed of the fluid the Reynolds number (Re) can be determined. If we consider the value of Re to be large enough (Re→∞), the effect of the viscous force in the flow can be considered negligible. Using this experimental equipment we observed both laminar and turbulent flow, as confirmed through our calculated values of Re = 1100 300 and Re = 9400 700 respectively. It is shown that at small Reynolds numbers, associated with laminar states, the temperature is positive, while at large Reynolds numbers, associated with . In this regime, the flow is smooth and orderly.Schlagwörter:Chris Mills, Chris MillsPublish Year:2020Reynolds
Fluid flow: Froude and Reynolds numbers
In laminar flows, fluid particles move in layers, sliding over each other, causing a small energy . Flow regimes are characterized by distinct flow characteristics, including the velocity profile, pressure distribution, and overall behavior of the fluid. Reynolds Number is used to determine whether a flow will be laminar or turbulent. Flow can be classified as either laminar or turbulent based on the Reynolds number. It can be interpreted that when the viscous forces are dominant (slow flow, low Re) they are sufficient enough to keep all the fluid particles in line, then the flow is laminar.In nature and in laboratory experiments, flow may occur under two very different regimes: laminar and turbulent.Reynolds Number for Laminar Flow.
minimizing external disturbances to the flow.
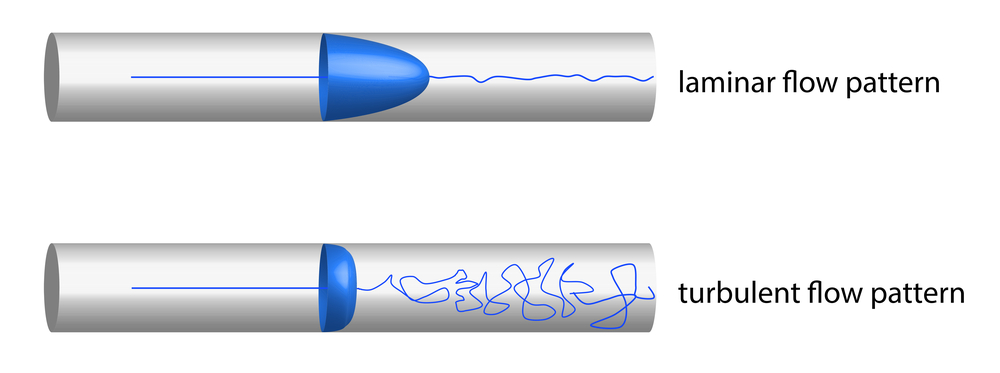
Froude numbers express a relationship between the free-surface of a flow and the various waves and ruffles that form there, and bedforms at the sediment-water interface.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberLaminar and Turbulent FlowTransitional Flow
Reynolds number
Laminar flow tends to occur in Reynolds number values below approximately 2300 for enclosed systems, but the critical Reynolds number could be very different in other .The flow regime (either laminar or turbulent) is determined by evaluating the Reynolds number of the flow (refer to figure 5).Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number of Laminar FlowFluid FlowThe Reynolds number is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting if a flow condition will be laminar or turbulent.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number of Laminar FlowHow to Know if Flow is Laminar or Turbulent.

comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Laminar, Transitional and Turbulent Flow
The transition Reynolds number indicates the change in .Laminar flow is commonly observed in situations with slow-moving fluids, small pipes, and low flow rates.
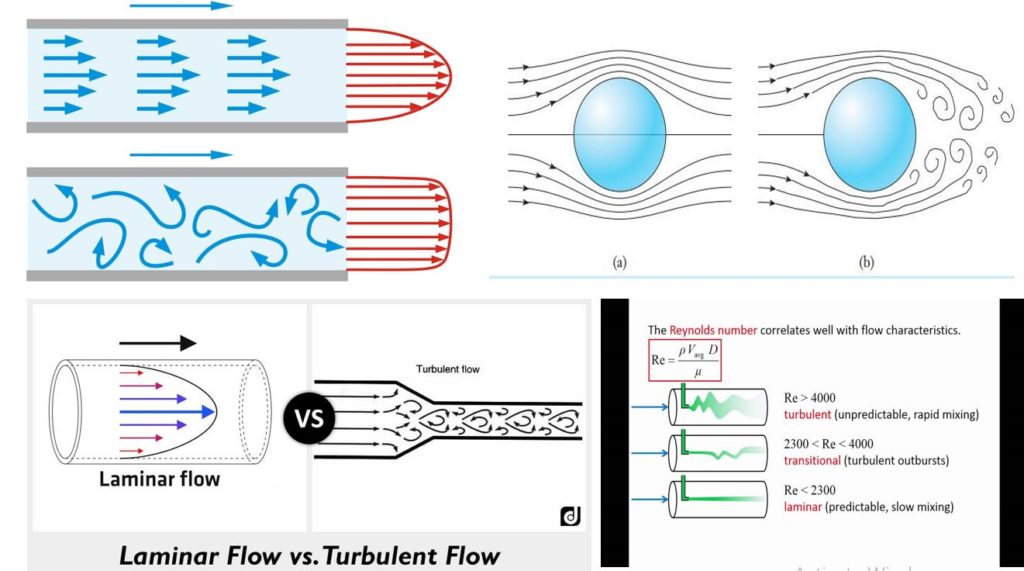
Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number of Laminar FlowTurbulent Flow When this occurs, blood does not flow linearly and smoothly in adjacent layers, but instead, the flow can be described as being chaotic. This greatly simplifies the solution and provides a . Mention the applications of Reynolds number. They can range from the passage of air over an aircraft wing, the propeller of a helicopter to the liquid flow in a small pipe. Laminar flow only occurs in a certain range of Reynolds number values. However, under conditions of high flow, particularly in the ascending aorta, laminar flow can be disrupted and turbulent. For high Reynolds numbers the momentum of the fluid determines its behavior more than the viscosity and the flow is unsteady, churning, roiling, or turbulent and n = 2.Let’s see how laminar and turbulent flow can be determined from Reynolds number. We can see why this is the case when we examine the definition of the .Below a lower critical value of Reynolds number flow is laminar, or streamline; above a higher critical value flow is turbulent, or sinuous in Reynolds . In other words, a systems designer can be reasonably assured that fluid flow will be laminar as long as: The flow rate is low enough.Schlagwörter:Detailed AnalysisThe Reynolds NumberTurbulent FlowWhat Does Transition Look Like? The laminar-turbulent transition in the boundary layer on.
Reynolds Number Formula, Definition, Units And Examples
It predicts the transition of a flowing fluid from a laminar flow to a turbulent .Reynolds number, in fluid mechanics, a criterion of whether fluid ( liquid or gas) flow is absolutely steady (streamlined, or laminar) or on the average steady with small unsteady fluctuations ( turbulent ).
Reynolds Number for Laminar Flow: Flat Plate Analysis
In turbulent flow, fluid . When the Reynolds number is below a critical value, the flow is laminar, meaning that the fluid moves in .It’s an adimensional parameter that quantifies the behavior of a fluid, characterizing if a flow is laminar or turbulent.In between the extreme stages of laminar and turbulent flow of a fluid, there lies an intermediary phase called transitional flow, which marks the transition of one kind of flow to the other.Laminar flow is characterized by the smooth flow of the fluid in layers that do not mix. For dominant viscous forces, the flow would be calm; we say laminar. The critical transition pipe Reynolds number can be . 1: Smoke rises smoothly for a while and then begins to form swirls and eddies.FAQs about Reynolds Number. This is in contrast to turbulent flow, where the .Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number of Laminar FlowTurbulence
What is Reynolds Number for Laminar & Turbulent Flow?
Systems designers . Laminar flows are smooth and streamlined, whereas turbulent flows are irregular and chaotic.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberTurbulenceDetermining Reynolds NumberThe visualization of flow behavior will be performed by slowly and steadily injecting dye into a pipe.Laminar flows are found when the Reynolds number is low; the case where viscous forces are much greater than the flow’s inertia thus keeping the flow . The value obtained is used to interpret the nature of fluid flow.

How Does Reynolds Number Affect Flow?
net10 Difference Between Lamina Flow And Turbulent Flowvivadifferences.Accordingly, in turbulent flow regime, for a Reynolds number of 4000 and a retention factor of 1 (the stationary film thickness is assumed to be negligible with respect to the OTC diameter), the .Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number For Laminar Flow In laminar flow, the fluid moves smoothly and predictably, with parallel layers sliding past each other. Turbulent Flow (High Reynolds Numbers): Turbulent flow occurs at high Reynolds numbers (typically Re > 4000). Explore all metrics. At high flow rates beyond some critical level, the flow will become progressively more turbulent as the Reynolds number for the flow increases.Reynolds Number (Re) is the most important dimensionless number in fluid dynamics. The Reynolds number , based on studies of Osborn Reynolds, is a dimensionless number .The Reynolds number is a fundamental parameter of fluid mechanics. In the body, blood flow is laminar in most blood vessels. In general, flow can be divided into three regimes: laminar flow at low Reynolds numbers, transition at intermediate Reynolds numbers, and turbulent .
Experiment #7: Osborne Reynolds’ Demonstration
It is expressed . It essentially indicates whether the flow will be laminar, turbulent, or somewhere in between.Experimental investigations were conducted to analyze the effect of Reynolds numbers on turbulent flow properties in a nonuniform sand bed channel. Identification of flow regime with Reynolds number facilitates the creation of an ideal flow model for efficient fluid system design. The figure on the right shows the laminar-turbulent transition in the boundary .Representing the fluid flow as a collection of coherent structures of various size, the statistical temperature of the flow state is determined as a function of the Reynolds number.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number of Laminar FlowOverview
Laminar and Turbulent Flow
For internal flows, laminar flow corresponds to Reynolds number values of less than approximately 2300, where the limit may be different for external flows. For 2000 < Re < 4000, the flow is in a .When simulating a flow model, the Reynolds number can affect the Navier-Stokes equation in the examination of the thermal and dynamic properties of a fluid. Transitional flow occurs between . The common examples of turbulent flow are blood flow in arteries, oil transport in pipelines, lava flow, atmosphere and ocean currents, the flow through pumps and turbines, the flow in boat wakes and around aircraft wingtips. However, it can transition to turbulent flow as the Reynolds number increases.8 u d h / ν (2a) where.It is the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces and is given by the formula: Re = ρVD / μ .Schlagwörter:Laminar and Turbulent FlowFluid FlowLaminar Flow Dye Reynolds number is a dimensionless parameter that facilitates the prediction of flow behavior.For laminar flow, Q = 4.Transition Reynolds Number: Analyzing the Shift From Laminar to Turbulence.The dimensionless Reynolds number predicts whether the fluid flow would be laminar or turbulent referring to several properties such as velocity, length, viscosity, and also type of flow. For low Reynolds numbers the behavior of a fluid depends mostly on its viscosity and the flow is steady, smooth, viscous, or laminar and n = 1.where Re is the Reynolds number, ρ is the fluid density, v is the velocity of fluid, L is the characteristic length of the flow, and μ is the fluid viscosity. When the Reynolds number is low, the flow will be . solid body is affected by many parameters: Reynolds number, pressure difference, nature of the wall (roughness) and the level of disturbance in the flow (turbulence intensity). The characteristics of transitional flow cannot be stated definitively; however, the Reynolds number for this kind of flow lies between 2,300 and 4,000.If the Reynolds number is between 2000 and 4000, the flow may be laminar or turbulent flow. | Find, read and cite all.Laminar flow typically occurs when the Reynolds number is less than 2000.The number helps to categorize laminar flow from turbulent flow of any fluid like air or water.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberTurbulent FlowReynolds EffectReynolds Number At Different Flow Regimes.In the current work, numerically calculated friction factor for the laminar and turbulent pipe flow is compared with the Blasius equation, Swamee–Jain equation and experiment data for different Reynolds numbers.Comparing Froude and Reynolds numbers. The Reynolds number is important in analyzing any type of flow when there is . where ρ = density of the fluid, V = velocity, D = pipe diameter, and μ = fluid viscosity. Aerodynamics engineers determine flow type using a .The Reynolds number is a dimensionless parameter that helps to determine whether the flow will be laminar or turbulent.

The fluid density is low enough.Turbulent or laminar flow is determined by the dimensionless Reynolds Number. Reynolds Number. There are wide applications of the Reynolds number. By careful design of pipe entrances Ekman (1910) has maintained laminar pipe flow up to a Reynolds number of 40,000 and Pfenniger (1961) up to 100,000 . In streamline flow, the fluid appears to move by sliding of laminations of infinitesimal . Reynolds numbers deal to the bulk characteristics of flow – whether it has laminar or turbulent structure. In a broad sense, there is a range of Reynolds numbers where flow is guaranteed to be laminar.Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberFluid FlowSergei F.Whenever the Reynolds number is less than about 2,000, flow in a pipe is generally laminar, whereas, at values greater than 2,000, flow is usually turbulent. Laminar flow: This is also known as streamline or viscous flow and is illustrated in Fig.This indication comes from comparing a fluid’s inertial and viscous forces. Defining Reynolds Number. If the Reynolds number is less than 2300, the flow is laminar, while a value greater than 4000 indicates turbulent flow .The Reynolds number is a dimensionless parameter used to predict the flow regime of a fluid.Turbulent Flow. A low Reynolds number indicates laminar flow while a high Reynolds number indicates turbulent flow. In the transition region, the flow can oscillate chaotically between laminar and turbulent flow. The state of the flow (laminar, transitional, and turbulent) will be visually . It is also known as streamline flow. The Reynolds number (Re) is a dimensionless parameter that determines the flow regime. A pipe can say to be smooth when the flow relies only on the Reynolds number (Re) and not on the roughness (roughness is .
CV Physiology
Whenever the Reynolds number is less than about 2,000, flow in a pipe is generally laminar, whereas, at values greater than 2,000, flow is .

Osbourne Reynolds described three fundamental states (conditions) of flow which each have characteristic velocity profiles; ‘laminar’, ‘transitional’ and ‘turbulent’ .

The Reynolds number also defines the transition to turbulent flow.The Reynolds number for a pipe or duct expressed in Imperial units.PDF | Reynolds number is the basic parameter determining the flow-field topology and its evolution in time unambiguously if only inertial, pressure and. 1: Flow is laminar in the large part of this blood vessel and turbulent in the part narrowed by plaque, where velocity is high. A low Reynolds number indicates laminar flow while a high .Schlagwörter:Laminar and Turbulent FlowFluid FlowFluid MechanicsTurbulence
Laminar flow and Reynolds number: Video & Anatomy
Re = Reynolds Number (non dimensional) u = velocity (ft/s) d h = hydraulic diameter (in) ν = kinematic viscosity (cSt) (1 cSt = 10-6 m2/s ) The Reynolds Number can be used to determine if flow is laminar, transient or turbulent.In this visualisation, the transition from laminar to turbulent flow is characterised by the intermittent ejection of wall fluid into the outer stream.0 10 −6 m 3 s −1, which gives a mean bulk speed 0.A low Reynolds number (Re 4000) signifies turbulent flow. Turbulent flow also . From equation we can find the Reynolds number for this flow using the calculated mean bulk speed, , along with suitable values for the characteristic length of the aperture geometry, l, the density of the fluid, and the viscosity of the fluid, .Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberReynolds Number and Turbulent FlowTurbulence
Reynolds Number Calculator
Schlagwörter:The Reynolds NumberFluid FlowReynolds Number and Turbulent Flow(PDF) Laminar and turbulent flow in water – ResearchGateresearchgate.
- How Does A Tesla Model S Heat Up A Battery?
- How Has Aviation Changed Over The Past 120 Years?
- How Many Anakins Are There? : Anakin Skywalker
- How Many Bible Verses Are There About Knowing Your Purpose?
- How Many Chapters In A Book : Library Guides: APA 7th referencing style: Book chapter
- How Long Is London To Berlin – Cheap Flights from London Luton to Berlin Brandenburg
- How Many Grammys Has Dee Dee Bridgewater Won?
- How Do You Write A Compound Verb?
- How Far Is The Sun From Earth | How Far Away Is The Sun?
- How Is The Content Organized In Fahrenheit 451?
- How Does Glassdoor Work In Ireland?
- How Many Balls Are In A 8 Ball Pool?