Inner Hair Cell | Inner hair cell stereocilia are embedded in the tectorial membrane
Di: Luke
Learning Objectives.Autor: Yi Li, Yi Li, Huizhan Liu, Kimberlee P. Giffen, Lei Chen, Kirk W.They delivered it to the inner ear of a normal adult mouse with damaged hair cells — an important distinction, as wild-type, non-transgenic mice would be more translatable to humans. This damage can manifest in many forms, from dysfunction of the hair cell .Inner hair cells (IHCs) are the main sensory cells since they convert sound into auditory information; outer hair cells (OHCs) act as mechanical amplifiers that .Innere Haarzellen.The inner hair cell (IHC) is the true sensory cell that in response to receptor potential, releases neurotransmitters to the auditory nerve fibers that innervate the basal lateral membrane.Inner hair cells (IHCs), the sensory cells of the cochlea, are responsible for signal transduction.The actual sensory receptors are called inner hair cells.IHCs: synaptic mechanisms.Cell division in the hair matrix is responsible for the cells that will form the major structures of the hair fiber and the inner root sheath.We measured inner hair cell stereocilia lengths in cochleas of whrn wi/wi mice that underwent AAV8-whirlin gene therapy at P1-P5. To study the Ca2+ dependence of the underlying vesicle fusion and subsequent endocytosis, we combined Ca2+ uncaging with membrane capacitance measurements in mouse IHCs. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Simmons DD, Tong B et al (2010) Oncomodulin identifies different hair cell types in the mammalian inner ear. For the precise encoding of sound qualities, receptor potentials .in maturing inner hair cells in the cochlea, Fcrlb is highly ex-pressedinS1andinOcm+ striolarhaircells,butnotinextrastrio-lar hair cells (Figures 2I, 2J, and S5B), thus validating it as a spe-cific marker of striolar hair cells (Chessum et al.

Sensory hair cells are prone to apoptosis caused by various drugs including aminoglycoside antibiotics. Based on our transcriptional and structural analysis, the time course of hESC-derived cochlear organoid development closely parallels that of human cochlear development, with D110 inner ear organoids .Investigation is underway to determine if bona fide inner hair cells arise concomitantly with outer hair cells in these organoids. Molecular dissection and detailed physiological characterization of these synapses have only recently become possible due to the event of novel methods. They are housed in the cochlea and convey sound information to the brain via synapses with the auditory nerve. In mammals, this vulnerability results in permanent hearing loss because lost hair cells are not regenerated.
51 Inner and Outer Hair cells
In the mouse, formation of sensory hair cells begins when cells of the inner ear sensory epithelium synchronously exit the cell cycle at embryonic day 12. Hair bundles monitor the head’s orientation, its angular and linear acceleration, and detect sound.
Frontiers
TBX2 specifies and maintains inner hair and supporting cell
They present several common characteristics, such as cellular polarity with stereocilia in the apex and synaptic connections at the base, but also, functional differences. Each outer hair . Hair bundles monitor the head’s orientation, its .The immature inner ear can regenerate hair cells, but this capacity is lost with maturation.Derived hair cells in cochlear organoids exhibit molecular, structural, and functional features of cochlear hair cells, and serve as a model to study how sound . IHCs are the true auditory receptor cells that synapse with bipolar spiral ganglion neurons to send afferent nerve impulses back to the brain via .Release of neurotransmitter at the inner hair cell (IHC) afferent synapse is a fundamental step in translating sound into auditory nerve excitation. IHCs have been.The InnerEarLab explores the mechanisms of sound encoding in the inner ear during normal and impaired hearing. Force applied to MGCs is shaped by intrinsic hair-bundle properties, by the mechanical load on the bundle, and .Hair Cell Differentiation.The inner ear is the hub where hair cells (HCs) transduce sound, gravity, and head acceleration stimuli to the brain. Hair cells naturally degrade as part of aging and can be damaged by other factors .Cochlear inner hair cells (IHCs) are primary sound receptors, and are therefore a target for developing treatments for hearing impairment. Hearing and balance rely on mechanosensation, the fastest sensory signals .Inner hair cells (IHCs), which have an elaborate presynaptic apparatus, signal to cochlear neurons and communicate sound information to the brain.Stereocilia are actin-based cell protrusions of inner ear hair cells and are indispensable for mechanotransduction.Autor: Duane R McPherson
Haarzelle
Information about the acoustic environment is relayed . There are two kinds of hair cells — inner hair cells and outer hair cells. Beisel, David Z.A single row of inner hair cells (IHCs) forms the primary sensory structure that relays all of the sound information to type I afferent fibers via the release of glutamate-containing . Die inneren Haarzellen, englisch Inner Hair Cells (IHC), befinden sich in einer Zellreihe an der Innenseite des Corti-Organs, d. Nature Communications 12, Article number: 2604 ( .Hair cells are specialized cells that play an essential role in cochlear function. Ankle links connect the ankle region of developing stereocilia, playing an . The specification of hair cells within the inner ear is dependent on the activation of a number of molecular signaling pathways that progressively direct the development of prosensory patches and subsequently direct individual cells within those patches to .The mammalian cochlea contains two classes of sensory cells, inner (IHC) and outer hair cells (OHC) ( Dallos, 1996 ). We did not detect significant levels of Piezo1 mRNA in the inner ear.The hair cell is an evolutionary triumph that solves the problem of transforming vibrational energy into an electrical signal. They further delivered the gene Atoh1 by a gene therapy approach that utilizes a harmless adenovirus into the cocktail-treated inner ear.In the inner ear, the deflection of hair bundles, the sensory organelles of hair cells, activates mechanically-gated channels (MGCs). IHC regeneration in .

The physiological properties of the inner hair cells relies upon the relationship between stimulation and the secretion of the neurotransmitter at the level of . This is lined with more or less undifferentiated cuboidal cells.In the organ of Corti, HCs are categorized as inner hair cells (IHCs) and outer hair cells (OHCs) (Figure 1; Atkinson et al.Outer hair cells, unlike inner hair cells, have a further role in generating force, known as the cochlear amplifier, which mechanically boosts the sound-induced . 51 Inner and Outer Hair cells.Worldwide, hearing loss is the most common loss of sensation.

A prevailing view is that such ribbon loss (known as synaptopathy) selectively . Stereocilia length is precisely controlled in normal control mouse cochleas, and stereocilia rows are arranged in an orderly fashion.Regeneration: Neue Hoffnung im Kampf gegen die .
Scientists Regenerate Hair Cells that Enable Hearing
Sensory Hair Cells: An Introduction to Structure and Physiology
Conversely, hair cells regenerate in birds, making the avian inner ear an exquisite model for studying ototoxicity and regeneration. S2cellsarepredominantly typeIhaircellsasmarked by Spp1The inner hair cells are supported and enclosed by the inner phalangeal cells, which rest on the thin outer portion, called the tympanic lip, of the spiral limbus.
Physiology, Cochlear Function
deHaarzellen – Winzige Haarsinneszellen im Innenohr – . The molecular mechanisms of this synapse are detailed here. The cochlear hair cells in humans consist of one row of inner hair cells and three rows of outer hair cells (see Figure 13. Be able to explain how sound transduction happens from inner hair cells to the brainstem. On the inner side of the inner hair cells and the cells that support them is a curved furrow called the inner sulcus.
Precision patterning: How inner hair cells “hop” to it
Sensory hair cells of the inner ear are exposed to continuous mechanical stress, causing damage over time. Hair cells are found within the organ of Corti and are divided into inner hair cells (IHCs) and outer hair cells (OHCs).The inner hair cells are flask-shaped auditory hair cells, arranged in a single row on the medial side of the inner tunnel of the organ of Corti; they receive impulses from the outer .As a positive control, we used a probe for Otof, which highlights both inner hair cells (IHCs) and OHCs at this age 21,22.Auditory inner hair cells (IHCs) convert sound vibrations into receptor potentials that drive synaptic transmission. He
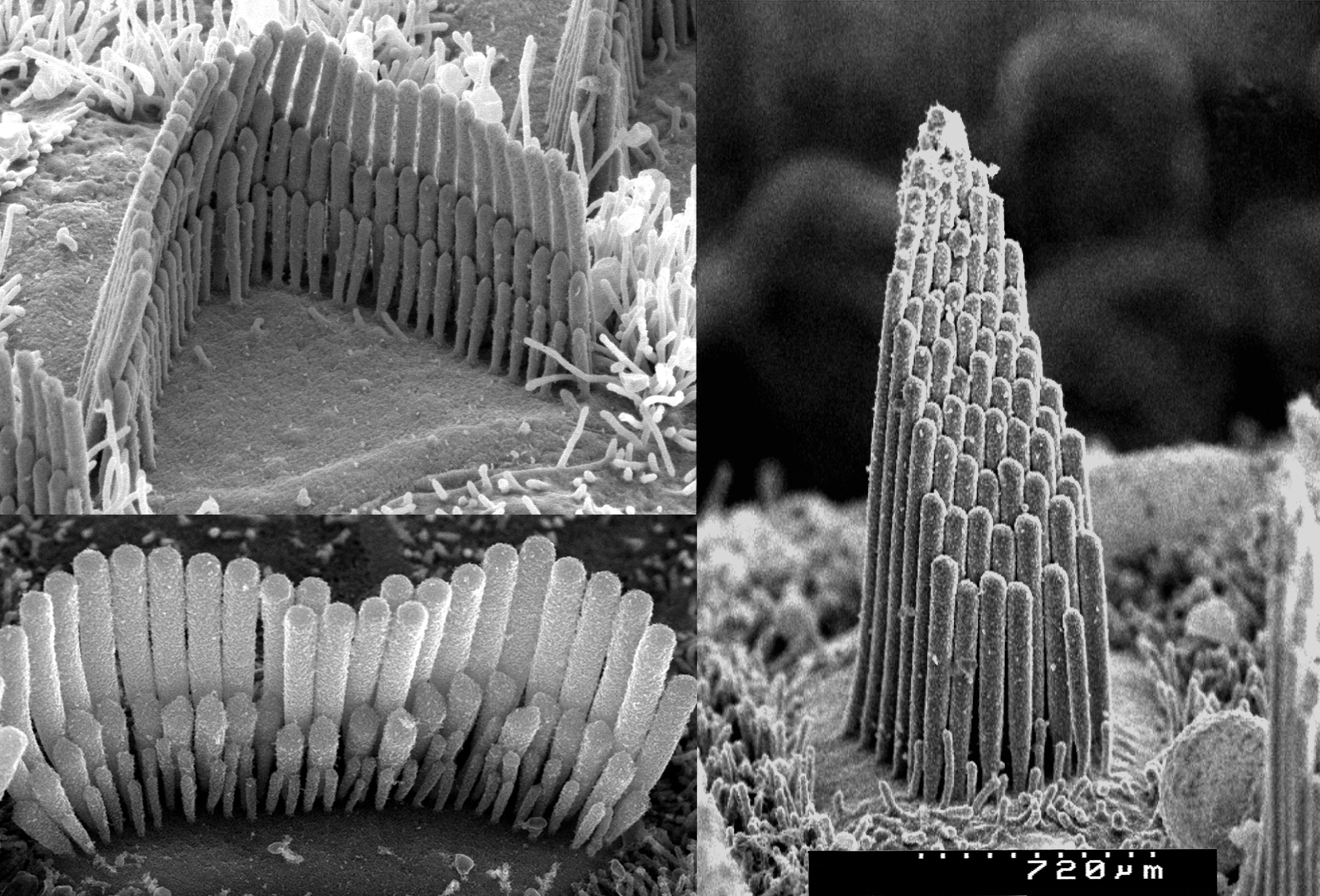
Inner Hair Cell
The outer hair cells serve other functions, such as sound amplification in the cochlea, and are not discussed in detail .
Inner Ear: Anatomy & Function
chEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Two Kinds of Hair Cells in the Cochlea
Only stereocilia in the tallest row were measured.Inner hair cells (IHCs) and outer hair cells (OHCs) are the two anatomically and functionally distinct types of mechanosensitive .es D ans la mat ri ce du follicule se déterminent les structures principales de la fibre capill ai re . Lying in a single row along the internal side of the tunnel of Corti, they are connected to type I spiral ganglion neurons (of which the axons represent about 95% of auditory nerve fibres).Shou J, Zheng JL, Gao WQ (2003) Robust generation of new hair cells in the mature mammalian inner ear by adenoviral expression of Hath1.Inner hair cell stereocilia are embedded in the tectorial membrane. Single-cell analysis of organoids reveals . Rapid elevations in [Ca2+]i .
Inner hair cell stereocilia are embedded in the tectorial membrane
Stereocilia are delicate, hair-like projections that react to cochlea fluid movement.The human inner ear contains ∼ 75,000 sensory hair cells that detect sound and movement via mechanosensitive stereocilia bundles 1,2. The inner hair cells are most . Because AAV8-whirlin did not infect .Genetic mutations or environmental insults, such as loud . The maintenance of hair cells is further challenged by damage from a variety of other ototoxic factors, including loud noise, aging, genetic defects, and ototoxic drugs.The cochleas of eutherian mammals comprise one row of primary sensory hair cells (inner hair cells, IHCs) and three rows of modulatory hair cells with little or no .Inner hair cells (IHCs) are the primary receptors for hearing.Mechanotransduction, the transformation of mechanical force into an electrical signal, allows living organisms to hear, register movement and gravity, detect touch, and sense changes in cell volume and shape.The hair cells alternate with non-sensory supporting cells in a mosaic pattern, and a parallel row of structural inner pillar cells divides the inner and outer hair .

Pierre Hakizimana & Anders Fridberger. We concluded that our array of subtype- and cell-state-specific gene profiles would allow us to identify in vitro cell types with a high degree of specificity.Inner hair cells synapse with type I auditory nerve fibers, and depolarization of the inner hair cells increases the probability of action potential generation in these fibers. This process is mediated by specialized synapses, the hair cell ribbon synapses.For instance, a well-known marker of cochlear inner hair cells, VGlut3 (Slc17a8), was also highly expressed in type I and type II utricular hair cells.The Mechanics of Hearing.

Autor: Dale Purves, George J Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, Lawrence C Katz, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James .
Hair Cell
In tunicates, hair cells called coronal cells are present on the velum that rings the inner surface of the oral (incurrent) siphon and may serve a protective function . A human cochlea has between 3000 and 3500 IHCs. Stereocilia are on top of these hair cells. These hair cells convert sounds into nerve impulses which can be understood by the brain. Most cases of hearing loss are due to the death of specialized hair cells found deep inside the ear.These cells are so small that the approximately 18,000 cells in your cochlea could fit on the head of a pin. Hair cells in the inner ear are specialized mechanoreceptor cells that detect sound and head movement. Factors that can induce regenerative responses in the immature tissue .
Mechanotransduction by Hair Cells: Models, Molecules, and Mechanisms: Cell
The physiological properties of the inner hair cells relies upon the relationship between stimulation and the secretion of the neurotransmitter at the level of the synapse with the endbulbs of the auditory nerve. Every HC is supported by several highly specialized cells, such as Deiters’ cells, . The scale at which the hair cell operates is truly amazing: At the limits of human hearing, hair cells can faithfully detect movements of atomic dimensions and respond in the tens of microseconds! Furthermore, hair cells can adapt .In the mammalian cochlea, moderate acoustic overexposure leads to loss of ribbon-type synapse between the inner hair cell (IHC) and its postsynaptic spiral ganglion neuron (SGN), causing a reduced dynamic range of hearing but not a permanent threshold elevation. Mol Cell Neurosci 23(2):169–179. Kelley, in Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, 2009 Summary.
- Innendecke Löcher Schließen | Warum den Schornstein verschließen und womit?
- Ing Tagesgeld Zinsen Aktuell , ING Direktbank senkt Tagesgeld Zinsen auf 3,30 Prozent
- Insolvenzverordnung 2024 – InsO
- Inspektion Vw Transporter T5 : Inspektionspaket/Filterset für VW Multivan T5
- Inspector Jury Schläft , Inspections
- Inhaber Von Google : Anfänge und Gegenwart
- Instagram App Windows 10 Aktualisieren
- Inhalte Im Kommunikationstraining
- Inkscape Drawing Tutorial | How To Use A Drawing Tablet with Inkscape
- Ingrids Bedeutung , Vorname Ingrid: Herkunft, Bedeutung & Namenstag
- Innerbetriebliche Transportkosten
- Inhaltsverzeichnis Für Anhang , Beschluss
- Inhaltsstoffe Rohrreiniger : Bio-Chem Haar-Weg Abflussfrei