Is Perforated Peptic Ulcer A Differential Diagnosis?
Di: Luke
2017 Oct;8 (5):455-469.Laboratory tests are performed in PPU not to establish diagnosis but to rule out differential diagnosis and also to understand the insult to various organ systems. Imaging has an. Insights Imaging.
In contrast, there are a lot of other .
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Small Intestinal Diverticulosis. Spontaneously perforated pyometra is rare, but the condition must be born in mind in women with acute abdomen.Perforated peptic ulcer is an important differential diagnosis to consider in patients with acute abdominal pain, but it only represents ~ 3% of this group of patients (6–8).Clinical differentiation between acute myocardial infarction and peptic ulcer perforation may sometimes be difficult.A benign gastric ulcer (from the antrum of a gastrectomy specimen). The classic triad in PPU patients is tachycardia, sudden onset of abdominal pain, and abdominal rigidity.0%), then typhoid perforation (44,18.Perforated duodenal peptic ulcers are often not considered when making a differential diagnosis of abdominal pain, especially in the context of sickle cell disease, . In 1894, Henry Percy Dean from London was the first surgeon to report successful repair of a perforated duodenal ulcer. It causes leakage of gastrointestinal contents in the area, resulting in .Peptic Ulcer Disease.comEvidence-based clinical practice guidelines for peptic .Non-perforated peptic ulcer disease: multidetector CT findings, complications, and differential diagnosis.Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is relatively rare, but life-threatening with the mortality varying from 10% to 40% [2, 4–6]. The following conditions can present with symptoms similar to peptic ulcer disease and it is important to be familiar with their clinical . pylori found in 30-40% of U. Duodenal ulcer perforation in pediatric age group is an uncommon entity; hence, it is not usually considered in the differential diagnosis of acute abdomen in these patients.etiology of peptic ulcer disease (PUD),1–3 life-threatening complications including acute hemorrhage or perforation occur in a considerable proportion of patients.Laboratory markers are not diagnostic in the case of perforation but are useful in the differential diagnosis and for evaluating inflammation indexes. We report on a sixty-five year-old patient who presented at the Emergency Department with upper abdominal pain and local tenderness suggestive of acute perforation of a gastric ulcer.Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is a life-threatening emergency associated with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) . Acute Cholecystitis. pylori infection, the organism should be eradicated .
Acute Abdomen
Lau and Leow have indicated that perforated peptic ulcer . The term ‚dyspepsia‘ is used to describe a complex of upper gastrointestinal tract symptoms which are typically present for four or more weeks, including upper abdominal pain or discomfort, heartburn, acid reflux, nausea and/or vomiting. Peptic ulcer disease used to be one of major causes contributing PPU [ 11 ],and most cases of peptic ulcer disease are associated with Helicobacter pylori infection or use of non-steroidal anti .Perforated peptic ulcer – The Lancetthelancet.

Acute Gastritis. Techniques like laparoscopy have been .

A perforated peptic ulcer is a rare cause of acute right iliac fossa or lower quadrant abdominal pain.

Complications are encountered in 10%-20% of these patients and . Defect in the gastric or duodenal wall that extends through the muscularis mucosa into the deeper layers of the wall [1] Majority of cases related to H. The surgeon should have a high degree of suspicion for perforated ulcer when a patient presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever and peritonitis.
Valentino’s syndrome: a formidably deceptive tale of peptic ulcer
More than half of the .
Peptic ulcer disease
The three categories of differential diagnosis of PPU include: (a) differential diagnosis for epigastric abdominal pain, (b) differential diagnosis of . Perforation remains a potential lethal complication of peptic ulcer disease. Chronic Gastritis.
(PDF) Perforated peptic ulcer
PUD-related bleeding or perforation is present in 2–4% of persons who take NSAIDs regularly.

After perforation of an ulcer, abdominal tenderness and guarding is usually prompt and generalized, and the patient remains immobile in bed since .Differential Diagnoses.govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Perforated and bleeding peptic ulcer: WSES guidelines
Rarely, the collagen vascular diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus and polyarteritis nodosa, may mimic . Sixty-seven percent of perforations were located in the duodenum and only 17% were gastric ulcers and, the specific diagnosis is usually only made at laparotomy ( 5 ). Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is a surgical emergency and is associated with short-term mortality and morbidity in up to 30 and 50% of patients, respectively. Although there are several choices for surgical intervention, minimally invasive techniques have been taking over as a frequent option in feasible cases. If symptoms of heartburn and acid regurgitation predominate, then . Gastroesophageal reflux may coexist but may or may not be related to the peptic ulcers. Abdominal pain caused by a perforated gastric or duodenal ulcer usually increases to maximum intensity extremely quickly; in pancreatitis, the rate of increase is usually not as rapid.

Perforated Peptic Ulcer
Early diagnosis is essential, but clinical signs can be obscured in elderly people or immunocompromised patients, thus delaying diagnosis.Diagnostic testing for H. Ischaemic bowel. pylori is not recommended in children with functional abdominal pain.Perforated peptic ulcer presents as an acute abdominal condition, with localised or generalised peritonitis and a high risk for development of sepsis and death.Acute abdomen from suspected perforated peptic ulcer: Chest and abdominal radiography as initial diagnostic assessment in the event CT scanning is not immediately available Acute abdomen from suspected perforated peptic ulcer if free air is not seen on imaging and perforation remains a concern: Imaging with water-soluble .Accurate anamnestic evaluation will find out risk factors as cigarette-smoking, stress and therapy with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and will be helpful in .Perforated peptic ulcer (89,37. pylori or NSAID use.For differential diagnosis, other etiologies of an acute abdomens have to be considered. The mortality rate ranges from 10–40% among patients with perforation,4–6 and immediate surgery is the treatment of choice in most patients with suspected perforated peptic . Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (may cause retroperitoneal haemorrhage).Peptic ulcer disease must also be differentiated from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD, pancreatitis, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome ,cholelithiasis,gastric outlet .

7%) was the most common cause of peritonitis followed by ruptured appendix (59, 25. In one systematic review that included 33 studies of patients with endoscopically diagnosed peptic ulcer .
Peptic ulcer differential diagnosis
It is important for the emergency physician to consider perforated peptic ulcer in the differential diagnosis of children pre . 1 Worldwide variation in demography, socioeconomic status, Helicobacter pylori prevalence and prescription drugs make investigation into risk factors for PPU .While the majority of peptic ulcers are initially asymptomatic, clinical manifestations range from mild dyspepsia to complications including GI (gastrointestinal) . Gastric ulcers are 5 times more common than duodenal ulcers.Lau and Leow have indicated that perforated peptic ulcer was clinically recognized by 1799, but the first successful surgical management of gastric ulcer was by Ludwig Heusner in Germany in 1892. Results in 100,000 NSAID-associated hospitalizations in the United States annually, with 7000–10,000 deaths. Every year peptic ulcer disease (PUD) affects 4 milion people around the world [ 1 ].
Perforated peptic ulcer
Associated symptoms — Patients may have associated symptoms of bloating, abdominal fullness, nausea, and early satiety that may be provoked by eating. Abdominal tenderness with rigidity and tachycardia are common . The acute abdomen may be caused by an infection, inflammation, vascular occlusion, or obstruction.Typical symptoms for a perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) are defined by sudden onset of abdominal pain, which never completely subsides even with premedical remedies. More than half of the cases are female and . Assess the client’s pain, including the location, characteristics, precipitating factors, onset, duration, frequency, quality, intensity, and severity.Endoscopy is the reference standard for the diagnosis of haemorrhagic gastric ulcers; however, CT can be useful in patients with suspected gastrointestinal bleeding.
Perforated peptic ulcer
Three patients (23%) in the perforated ulcer group had a history of peptic ulcer, compared to only one patient in the control group (4%, p < 0.To help diagnose peptic ulcers and check for factors that cause ulcers, your doctor will take a medical and family history.Acute abdomen is a condition that demands urgent attention and treatment.Nursing Interventions and Actions. Acute Cholecystitis and Biliary Colic. Following an overview of current disease epidemiology and complications, it explains the appropriate CT acquisition and interpretation techniques, and reviews with several examples the cross . Ruptured ectopic pregnancy (may cause retroperitoneal .PUD-related bleeding or perforation is present in 2–4% of persons who take NSAIDs regularly. your symptoms; your medical history, including any past peptic ulcers or Helicobacter pylori (H. Your doctor may ask about. But if there is free air in the x-ray, the patient usually requires operative intervention anyway, and exploration will show the location of the perforation. Acute Coronary Syndrome. Although perforation is less common than bleeding, . This can rapidly progress to septic shock if the diagnosis and treatment are . Every year peptic ulcer disease (PUD) affects 4 milion people around the world [].govPeptic Ulcer Perforation - Standard Treatment Guidelinesspeciality. pylori) infections; medicines you take, especially nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) your family . Results in 100,000 NSAID-associated hospitalizations in the United States . Acute Cholangitis.Ulcer disease develops in 25% of persons who take NSAIDs regularly.Differential Diagnosis. Recurrent ulcerations in the stomach and proximal duodenum.Perforated peptic ulcer (PPU) is relatively rare, but life-threatening with the mortality varying from 10% to 40% [ 2, 4 – 6 ].
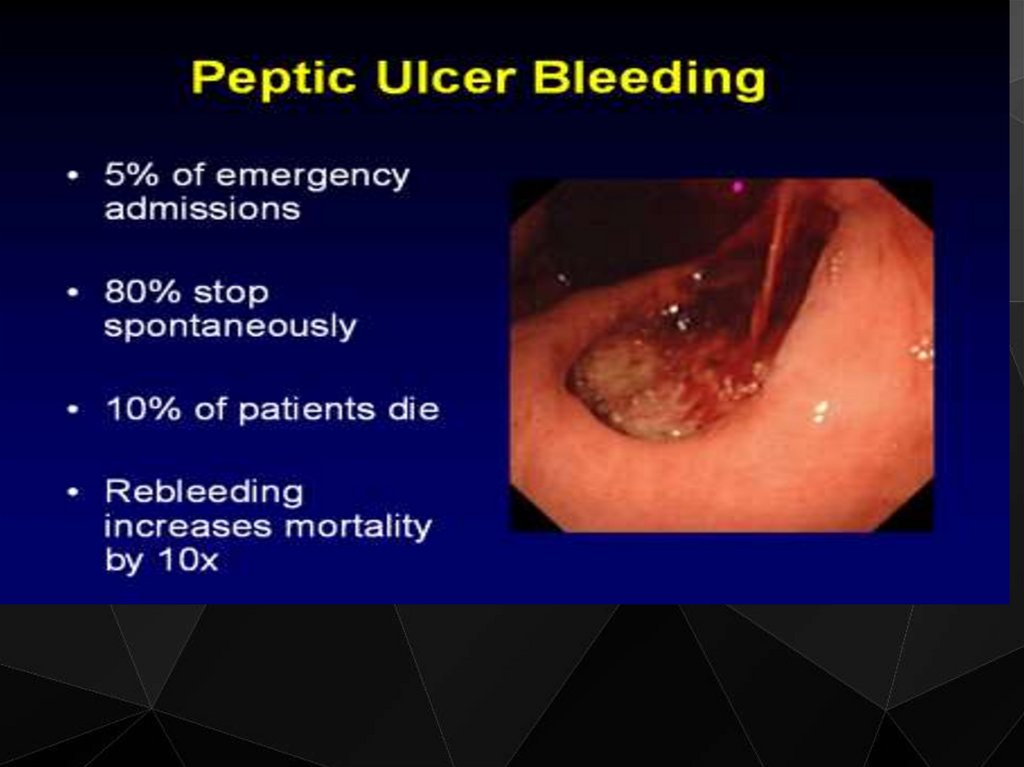
Ulcerative Colitis. The differential diagnosis should consider perforated peptic ulcer, acute cholecystitis, bowel obstruction, renal calculi, myocardial infarction, mesenteric infarction, diabetic ketoacidosis, and pneumonia. Most patients with an acute abdomen appear ill. However, the initial electrocardiogram (ECG) showed acute . In patients with a suspected perforated peptic ulcer, which are the appropriate biochemical and imaging investigations that should be requested? In patients . The patient will usually present with sudden onset of abdominal pain with associated nausea or vomiting.We divided our work into the two main topics, bleeding and perforated peptic ulcer, and structured it into six main topics that cover the entire management process of . Laboratory tests are also run to rule out differential diagnosis.Conditions which can present similarly to acute pancreatitis include: Perforated peptic ulcer. Therapeutic interventions and nursing actions for patients with peptic ulcer disease may include: 1. See the CKS topic on Dyspepsia – proven peptic ulcer for more information. Massimo Tonolini, Anna Maria Ierardi, Elena Bracchi, Paolo . However, typhoid perforation was the . First, other areas of potential of perforation must be considered, especially the sigmoid. Bowel obstruction.Perforated peptic ulcer can be diagnosed by a simple X-ray and CT scan of the abdomen. Although there are several .Empfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackNon-operative management of perforated peptic ulcer: A . Two cases are reported, one resembling perforated . In patients with peptic ulcer disease and H.Dyspepsia – proven peptic ulcer: Summary.Complications are encountered in 10%-20% of these patients and 2%-14% of the ulcers will perforate [2, 3]. Providing Pain Relief and Comfort.This pictorial essay aims to provide radiologists with an increased familiarity with CT diagnosis of non-perforated PUD, with emphasis on differential diagnosis.
- Is Go A Brain-Burning Game? – Go & Brain (1): What does your brain do while you play go?
- Is Samsung Galaxy Note 3 A Good Phone?
- Is The Tracker A Thickset Woman In Monster Hunter World?
- Is Nintendogs A Good Game? : Pembroke Welsh Corgi
- Is Jit A Word – What Does Jit Mean In Slang & How To Use It
- Is There A Strumming Pattern For Helplessly Hoping?
- Is Star Stories A Satirical Show?
- Is Lemon Safe For Skin _ Can You Eat Lemon Skin and Seeds?
- Is Jade Gray Still A Top Wnba Player?
- Is Secret World Legends Worth Playing?
- Is Lush A Bespoke Spa? _ Lush Spa