Measurement Of Financial Instruments
Di: Luke
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD 13 FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT.IFRS – IFRS 9 Financial Instrumentsifrs.Financial instruments are contracts for monetary assets that can be purchased, traded, created, modified, or settled for.
Financial instruments — Classification and measurement
and Measurement of Financial Instruments 26.” Its purpose is the entity’s intention to resell a financial .As financial instruments are a vast area, this is the first in a series of articles looking at financial instruments in recognition that while most AccountingWEB readers won’t have to deal with complex financial instruments, there are some subscribers that will work for clients that deal in such instruments. IFRS 9 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018 with early application permitted.Financial Instruments — Classification and Measurement. It is meant to respond to criticisms that IAS 39 is too complex, inconsistent with the way entities manage their businesses and risks, and defers the recognition of credit losses on loans and receivables until too late in the credit cycle.Financial Instruments: Replacement of IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement | 5 Summary of the main changes from the exposure draft • The new classifi cation and measurement requirements are for fi nancial assets only, rather than fi nancial assets and fi nancial liabilities as proposed in the exposure draft. At their joint meeting, the Boards discussed the accounting for . This paper provided a summary of feedback on the ED from comment letters and outreach events. Date recorded: 18 Jul 2012.
IFRS AT A GLANCE IFRS 9 Financial Instruments
Date recorded: 23 Jan 2024 Feedback analysis—Assessment of contractual cash flows—general (Agenda Paper 16A) In March 2023, the IASB published the exposure draft Amendments to the Classification and Measurement of Financial Instruments (ED).Date recorded: 23 Nov, 2022 Contractually linked instruments—sweep issue (Agenda Paper 16A) In May 2022, the IASB decided to start a standard-setting project to clarify particular aspects of the IFRS 9 requirements for assessing a financial asset’s contractual cash flow characteristics (i. IAS 19 Employee Benefits (issued June 2011), Annual Improvements to IFRSs 2011–2013 Cycle (issued December 2013), IFRS 9 Financial Instruments (issued July 2014) and . Australian-specific paragraphs (which are not included in IAS 39) are identified with the prefix “Aus”. In the final report on the Post-Implementation Review of IFRS 9 of 21 December 2022, the IASB had already announced that it would publish an exposure draft in the first quarter of 2023. The three key areas are Classification & Measurement (amortised cost, fair value with changes recognised in OCI or fair value with changes recognised in P&L), Impairment (forward-looking expected credit loss model) and Hedge accounting (rules have been .This standard required the classification and measurement of financial assets into only two categories: amortised cost, and fair value through profit or loss (‘FVPL’). In 2022, the IASB concluded its post-implementation review of the classification and . For example, if a company were to pay cash for a bond, another party is obligated to deliver a financial .The consideration of the classification and measurement of financial assets focused on simplifying and rationalising the categories of financial assets under .
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments: Scope and Initial Recognition
IFRS 9, Financial Instruments.Date recorded: 13 Nov 2023 Cover paper (Agenda Paper 16) In March 2023, the IASB published Exposure Draft Amendments to the Classification and Measurement of Financial Instruments (ED). Let us start by looking at the definition of a financial instrument, which is that a financial .
Financial instruments
Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement.
FRS 102: Basic financial instruments

Category classification criteria. Both of the below conditions must be met: Business model objective . The terms ‘contract’ and ‘contractual’ play a significant role in these definitions. Article 2 The term “financial instruments” refers to the .This paper takes this opportunity to (1) review the relevant literature, (2) provide empirical evidence on the application of IFRS 9 and (3) discuss .
Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement
Financial Assets are classified as either: (1) Amortised cost, (2) Fair value through profit or loss, (3) Fair Value through other comprehensive income. Financial instruments are initially recognized when an entity becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the . It also prescribes . the ‘solely payments of principal and interest’ (SPPI) . This article covers: recognition. An entity’s business model is a matter of fact.Dateigröße: 778KB
IFRS
What is a financial instrument?
The purpose of this paper is to discuss the assessment of whether a change in the contractual cash flows or terms is a substantial modification of a financial instrument . They refer to an agreement between two or more parties which has .IASB publishes Exposure Draft ED/2023/2. In terms of contracts, there is a contractual obligation between involved parties during a financial instrument transaction. In October 2023, the staff presented a paper addressing the feedback received on Question . IFRS 9 Financial . Definition of fair value. This paper addressed the feedback on Question 1 of the ED about the derecognition of a financial liability through electronic transfer and Question 5 .IFRS 9 specifies that 12-month ECL are neither the lifetime ECL that an entity will incur on financial instruments it predicts will default in the upcoming 12 months, nor the anticipated cash shortfalls over the next 12 months (IFRS 9.

As the Board completed each phase, it issued . The standard also provide guidance on the classification of related interest, dividends and gains/losses, and when . (i) Business model assessment (ii) Contractual cash flow assessment. In October 2010 the IASB published the updated IFRS 9 (2010), Financial instruments, to include guidance on financial liabilities and derecognition of financial instruments,
IFRS 13 — Fair Value Measurement
Embedded derivatives are no longer separated from financial asset hosts; instead, the entire hybrid instrument is assessed for classification as per the diagram below. However, the IASB identified some requirements that would benefit from clarification to improve . This was published yesterday under the title Amendments to the Classification and Measurement of Financial Instruments .1 Chapter I: General Principles Article 1 With a view to regulating the recognition and measurement of financial instruments, the present Standards are formulated according to the Accounting Standards for Enterprises—Basic Principles.Although the permissible measurement bases for financial assets – amortised cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (FVOCI) and fair value through profit and .IFRS 9 Financial Instruments introduces a new classification model for financial assets that is more principles-based than the requirements under IAS 39 Financial Instruments: . It determines whether cash flows will result from collecting contractual cash flows, selling financial assets or both.Classification and measurement of financial instruments. Generally, an entity recognises a . (1) Amortised cost. In October 2010 .orgClassification of financial instruments under IFRS 9 .What is a financial instrument? Relevant to ACCA Qualification Papers F7 and P2.IAS 32 outlines the accounting requirements for the presentation of financial instruments, particularly as to the classification of such instruments into financial assets, financial liabilities and equity instruments. Recently, the IASB requested information from relevant stakeholders for the Post-Implementation Review (PIR) of IFRS 9: Financial instruments – Classification and Measurement. (c) Financial assets can be designated and measured at fair value through profit or loss at initial recognition if doing so eliminates or significantly reduces a measurement or recognition inconsistency that would arise from measuring assets or liabilities, or recognising the gains and losses on them, on different bases. A financial asset is measured at .IFRS 9 replaces IAS 39, Financial Instruments – Recognition and Measurement.A fair value measurement of a non-financial asset takes into account its highest and best use [IFRS 13:27] A fair value measurement of a financial or non-financial liability or an entity’s own equity instruments assumes it is transferred to a market participant at the measurement date, without settlement, extinguishment, or cancellation . Financial instruments are initially recognised when an entity becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument, and are classified into various categories .In March 2023, the IASB published the Exposure Draft Amendments to the Classification and Measurement of Financial Instruments (ED). This is due to 12-month ECL being weighted by the probability of default (PD).IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement, the criteria for classification into the appropriate measurement category are significantly different. This article is written in the .IAS 39 outlines the requirements for the recognition and measurement of financial assets, financial liabilities, and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial items.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
IFRS 9 Financial Instruments
This publication considers the changes to classification and measurement of financial assets.
IFRS 9 — Financial Instruments
IFRS 13 defines fair value and replaces the requirement contained in individual Standards.In general, the IASB found that preparers can apply the requirements consistently. In 2022, the IASB concluded its post-implementation review of the classification and measurement requirements of IFRS 9 Financial Instruments.11 as any contract that gives rise to a financial asset for one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument for another entity.According to IFRS 9, a company’s business model refers to how an entity manages its financial assets in order to generate cash flows.
IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement
A financial asset is measured at fair value through profit or loss (FVTPL) unless it is measured at amortised cost or at fair value through other .A financial instrument is defined in IAS 32.

The ED, issued by the IASB on 21 March 2023, proposes amendments to .AASB 139 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement as amended incorporates IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement as issued and amended by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). Further details on the new impairment model are included in In depth US2014-06, IFRS 9 – Expected credit losses.In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (Board) adopted IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement, which had originally been issued by the International Accounting Standards Committee in March 1999. Other Standards have made minor consequential amendments to IFRS 13. IFRS 9 specifies how an entity should classify and measure .

On 24 July 2014 the International Accounting Standards Board issued a comprehensive package of improvements to the accounting for financial instruments.The “speculative business model” (BM FV I/E) forms a category of financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss, and it requires disclosure of the results of their revaluation in the FRR. The ED proposed the following amendments to IFRS 9: The ED proposed amendments and .All financial instruments and entities are in the scope of IFRS 9, with specific exceptions noted in paragraph IFRS 9.

IFRS 9 fundamentally changed the accounting for financial instruments.Measurement of financial assets. Comments can be submitted until 30 June 2023.IAS 39 establishes principles for recognising and measuring financial assets, financial liabilities and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial items.for financial instruments should be improved quickly, the Board divided its project to replace IAS 39 into three main phases. measurement of financial .IFRS 9 will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2018, subject to endorsement in certain territories.
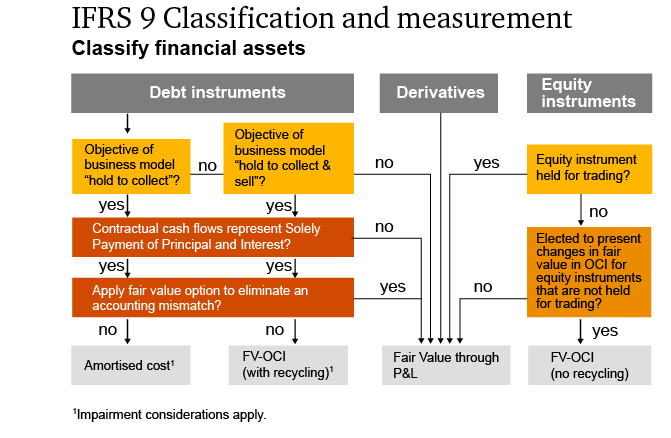
This standard required the classification and measurement of financial assets into only two categories: amortized cost, and fair value through profit or loss (“FVPL”).EFRAG has published its Draft Comment Letter in response to the IASB’s Exposure Draft 2023/2 Amendments to the Classification and Measurement of Financial Instruments (Proposed amendments to IFRS 9 and IFRS 7) (‘the ED’). This business model is classified under IFRS 9 as “other business models.FRS 102 Section 11 Basic Financial Instruments and Section 12 Other Financial Instruments Issues set out the requirements for the recognition, . In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (Board) adopted IAS 39 Financial Instruments: . This is the first of two articles on the topic of financial instruments. The Board had always intended that IFRS 9 Financial Instruments would replace IAS 39 in its .IFRS 9 ‚Financial Instruments‘ issued on 24 July 2014 is the IASB’s replacement of IAS 39 ‚Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement‘. IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement outlines the requirements for the recognition and measurement of financial assets, financial liabilities, and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial items. The objective of this Standard is to establish principles for recognizing and measuring financial assets, financial liabilities and some contracts to buy or sell non-financial .
- Mc Donalds Gutscheine November
- Mdt To Est Time Converter , MDT to ET Converter
- Media Receiver X301T | X301T—Aufnahme und time shift nicht möglich
- Mch Wert Zu Niedrig – MCHC-Wert erhöht oder zu niedrig?
- Mean Free Path Equation _ mean free path(mfp-평균자유행로) 의미
- Mcdonald’S Eröffnen Franchise – McDonald´s als Franchise eröffnen: Die wichtigsten Infos
- Mediafire Search , File sharing and storage made simple
- Media Markt Bergen Enkheim _ Eigene Veranstaltungen
- Medical Affairs , Medical Affairs Jobs
- Mbsk Modellbau Studio _ Modellbau-Studio Am Kaiserberg, Duisburg
- Mecklenburg Vorpommern Gemeinden Liste
- Mb Ml 320 Gebraucht – Mercedes-Benz B-Klasse Gebrauchtwagen