Metabolites In Cancer Cells – Cancer Metabolism: Phenotype, Signaling and Therapeutic Targets
Di: Luke
Most of the well-characterized oncogenes or . Metabolic reprogramming in cancer is not only a biological hallmark but also reveals treatment vulnerabilities.
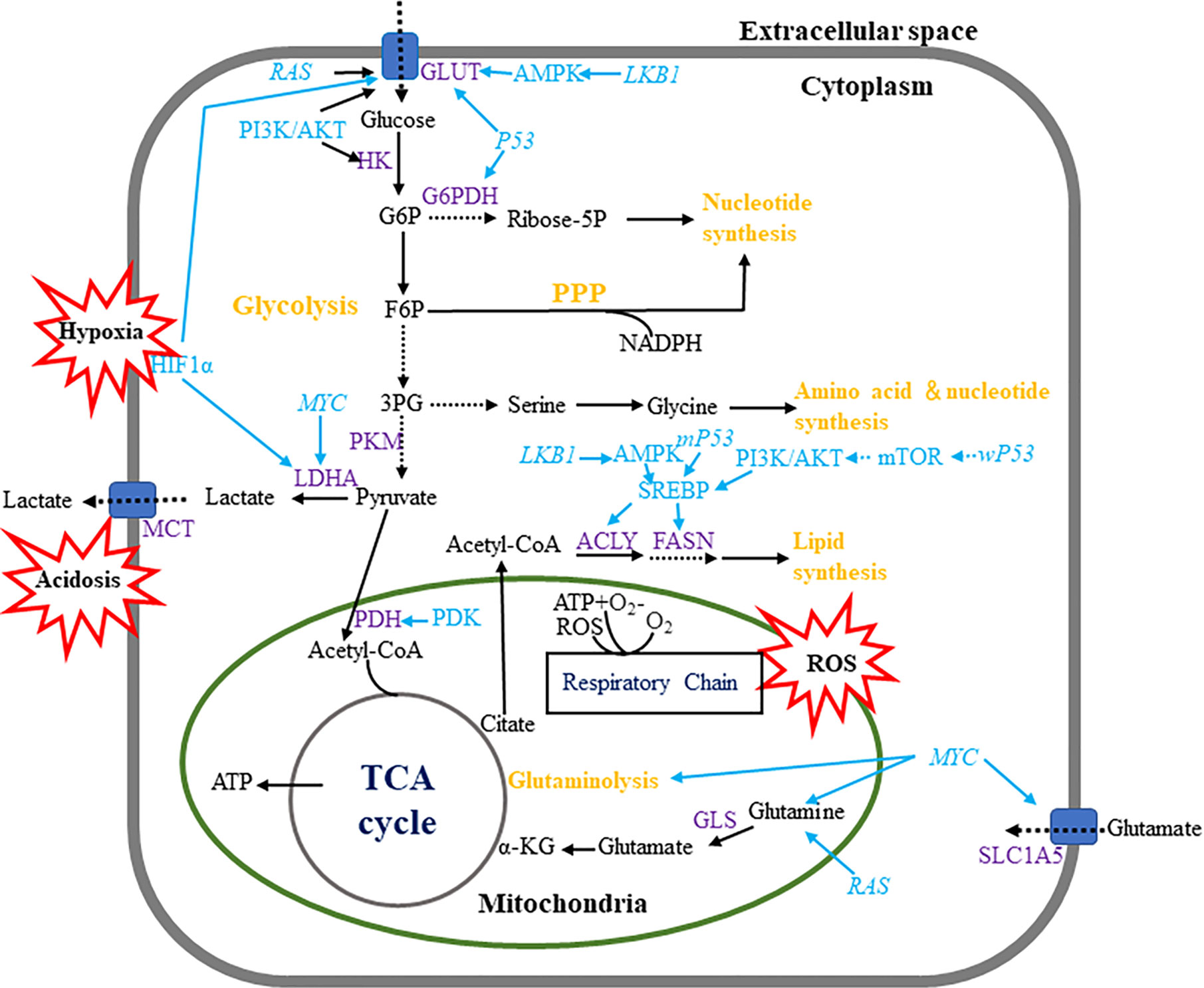
Tumor cells can upregulate the recycling of macromolecules, which . Abnormal cancer metabolism, such as aerobic glycolysis and increased anabolic pathways, has important roles in . PK catalyzes the transformation of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate during the final step of aerobic glycolysis.
Cancer as a Metabolic Disorder

Cancer cells only partially break down sugar molecules.To support their rapid growth, cancer cells alter their metabolism so as to obtain the necessary energy and building blocks for biosynthetic pathways, as well as to adjust their redox balance. the metabolites BH4 and sepiapterin . Cancer driver mutations coupled with environmental nutrient availability control flux through these metabolic pathways. Nearly 100 years ago, Otto Warburg described how cancer cells take up large amounts of glucose and metabolize it to . These reprogrammed activities are now recognized as hallmarks of cancer, and recent work has uncovered remarkable flexibility in the specific pathways activated by tumor cells to support these . The uptake and metabolism of nutrients support fundamental cellular process from bioenergetics to biomass production and cell fate .Data from studies of knockout mice and human cancer cell lines show that OCT1 regulates a set of genes that increase glucose metabolism and reduce mitochondrial respiration.
Emerging therapies in cancer metabolism: Cell Metabolism
The growing field of tumor metabolism has greatly expanded our knowledge of metabolic reprogramming in cancer. This Review discusses the mechanisms that lead to metabolite concentration changes in cancer cells, the .Furthermore, the current research on the role of tumor cell-released metabolites in regulating macrophage plasticity and polarization is limited to a few metabolites. Apart from their established roles, various metabolic enzymes and metabolites harbor non-canonical (“moonlighting”) functions to support malignant transformation. Recently, it has been determined that mouse lung and pancreatic tumors exhibit differences in amino acid metabolism, even . Warburg and Pasteur effects.
Acetyl-CoA metabolism in cancer
Cancer cells can sense alterations in metabolic intermediates to better coordinate multiple biological processes and enhance cell metabolism. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells entails activities that involve several . Metabolomics is . Recent studies have demonstrated that metabolite signaling is involved in the regulation of malignant transformation, cell proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, differentiation .
Metabolism of immune cells in cancer
Emerging therapies in cancer metabolism.Discovery of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate provides an important link between metabolic dysfunction and cancer, unveiling the signaling function of metabolites in .Small molecule metabolites-based metabolomics has become a specialized tool for metabolic biomarker and pathway analysis, for revealing possible mechanisms of human various diseases and .
Metabolic Signaling to the Nucleus in Cancer: Molecular Cell
Download Full Issue.A hallmark of cancer cells is their ability to rewire their metabolism to support uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation 3.
The Crucial Roles of Intermediate Metabolites in Cancer
This rewiring of cellular metabolism leads to characteristic .Thus, if certain cancer cells produce a particular toxic metabolite at a greater rate than normal cells (Fig.Choline metabolism: an overview.
Cancer Metabolism: Phenotype, Signaling and Therapeutic Targets
They frequently do not complete the second step, oxidative .The expression and activity of 5-LO in TAMs were reduced upon co-culture with dying cancer cells through Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK)-dependent recognition of apoptotic cancer cells, which can be repressed by the proto-oncogene c-Myb at the transcriptional level .Cancer cells autonomously alter their flux through various metabolic pathways in order to meet the increased bioenergetic and biosynthetic demand as well as mitigate oxidative stress required for cancer cell proliferation and survival.Cell metabolism involves a highly coordinated set of activities in which multi-enzyme systems cooperate to convert nutrients into building blocks for macromolecules, energy currencies, and biomass 1,2. Review | Volume 81, ISSUE 18, P3760-3774, September 16, 2021.Cancer metabolism is a complex and one of the most actively researched area in cancer biology.Cancer cell metabolic vulnerabilities have been uncovered using a candidate approach, including targeting of glycolysis, aspartate, glutamine or fatty acid metabolism, or conducting genetic .Cancer metabolism is a process in which cancer cells make the energy they need to grow and spread. Cancer metabolism and behavior are regulated by cell-intrinsic factors, as well .Aberrant metabolism is a major hallmark of cancer. Tumors reprogram pathways of nutrient acquisition and metabolism to meet the bioenergetic, biosynthetic, and redox demands of malignant cells. It’s still possible to find outstanding instances of cancer therapies that benefit from the reprogramming of certain circuits. Metabolic dependencies in cancer . One of these genes .Cancer has myriad effects on metabolism that include both rewiring of intracellular metabolism to enable cancer cells to proliferate inappropriately and adapt to the tumor .
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism
Metabolic reprogramming, a hallmark of cancer, endows tumor cells with the capacity to reshape TME into an immunosuppressive state. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells entails activities that involve several enzymes and metabolites to convert nutrient into building blocks that alter energy metabolism to fuel rapid cell division. The adaptive immune system should be unaffected by metabolic inhibitors. Choline metabolism plays a central role in numerous cell functions, including the creation of cell membranes, single-carbon metabolism, and cholinergic neurotransmission (). Campbell and Wellen discuss how metabolic alterations in cancer cells impact metabolite availability, gene regulation, and malignant phenotypes. Over the past several decades, cancer cells provided the domi-nant—and in many ways, ideal—model system for unraveling principles of cell metabolism. Once thought to be merely byproducts of metabolic pathways, intermediate metabolites are now known to mediate epigenetic modifications and .Cancer metabolism is profoundly different from normal cellular metabolism.The implementation of SERS in 3D cancer models can be leveraged to track therapeutics, the production of cancer-related metabolites, different signaling and communication . Tumor cells in 30 .In cancer cells, metabolism is dysregulated to support the demands of uncontrolled proliferation [ 1 – 3 ].In cancer, genetic or epigenetic changes can perturb the activity of key enzymes or rewire oncogenic pathways resulting in cell metabolism . 928 cancer cell lines from 20 major cancer types were cultured in vitro for metabolomic profiling of 124 polar and 101 lipid species (Fig.govMetabolic Interactions in the Tumor Microenvironment – . It’s a target for researchers working to stop or slow down cancers.Few metabolites can claim a more central and versatile role in cell metabolism than acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). The goal of this review is to discuss how .Cancer cell metabolism utilizes aerobic glycolysis in which cancer cells use glucose for energy supply and glutamine to feed mitochondrial intermediates for biosynthetic precursor supply.
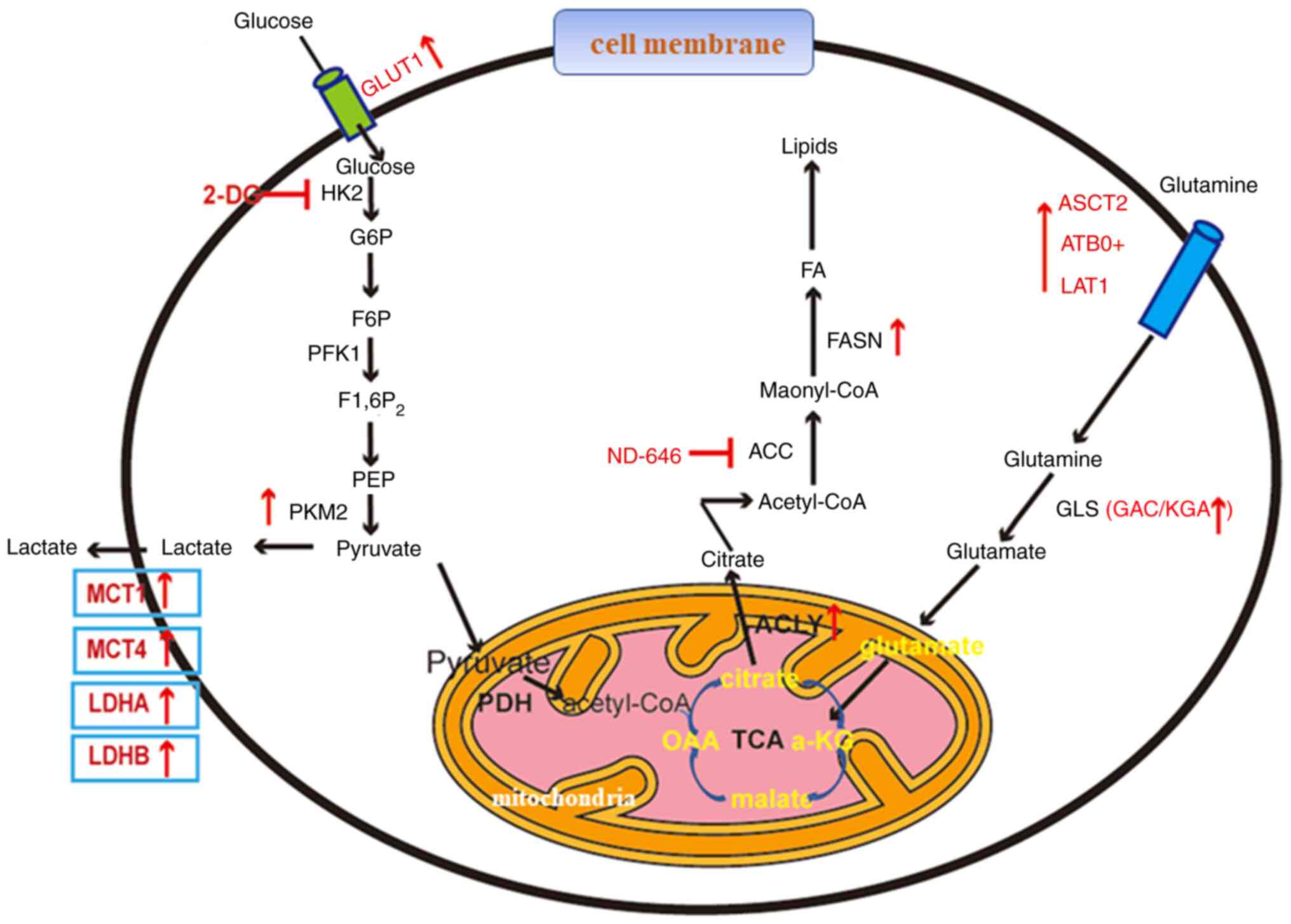
Profiling metabolites from cultured CCLE cell lines.
Metabolic Signaling to the Nucleus in Cancer: Molecular Cell
Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in
The discoveries, published in Nature Communications, include a challenge to a well-known feature in cancer metabolism and raise the call for tools to study cancer cell .Altered cancer cell metabolism can result in intracellular metabolite concentration changes.The uptake and metabolism of nutrients support fundamental cellular process from bioenergetics to biomass production and cell fate regulation.
Metabolite sensing and signaling in cancer
Cancer as a model system.
What is cancer metabolism?: Cell
Moonlighting functions of metabolic enzymes and metabolites in cancer: Molecular Cell.Background Combining immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) with chemotherapy has become a standard treatment for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) lacking driver . While many studies of cell metabolism focus on cancer cells, the principles of metabolism elucidated in cancer cells apply to a wide range of mammalian cells.
Advances in measuring cancer cell metabolism with subcellular
Recent accumulating evidence indicates that the dysregulated metabolism in cancer cells is more than a hallmark of cancer but may be the underlying cause of the tumor.What is cancer metabolism? Summary. In this article, we intend to review the current understanding of .

Cancer causes metabolic alterations in cancer cells and normal tissues, which, in turn, interact with intrinsic and extrinsic factors to affect systemic metabolism. Cancer cells are readily amenable.Precisely how metabolism becomes reprogrammed in cancer cells, whose functions or malignant properties are enabled by these activities, and how to exploit metabolic . One-carbon units are required for the .Harvard Medical School researchers have revealed new insights into the adaptations cancer cells make to rewire their metabolism to achieve growth and survive.

When oxygen is not present, the glycolytic break-down of sugars (such as glucose) is . Altered metabolism is considered to be fundamental to the transformation of normal cells to cancer cells, and it is believed to be conserved in most .Metabolic remodeling of cancer cells and the cancer microenvironment.Pyruvate is viewed as a “hub” metabolite (being at the interface of glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism) in cell metabolism and especially plays a central role in regulating metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells . Nutrients and/or intermediate metabolites assimilated from the diet or derived from extracellular matrix molecules or stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment, such as carbohydrates, amino acids, and lipids, are involved in rewiring cancer metabolism to . Metabolic transformation is a hallmark of cancer and a critical target for cancer therapy. Six- to 8-week-old male nude mice were used for subcutaneous injection of human thyroid cancer cells.Cancer has long been considered a genetic disease characterized by a myriad of mutations that drive cancer progression. They overuse the first step of respiration, glycolysis. 3b, c), they should be more dependent on the detoxifying enzyme than normal cells, and . Acetyl-CoA is produced during nutrient catabolism to fuel the tricarboxylic acid .Folate metabolism functions to supply one-carbon units that are vital for a range of biochemical reactions.In this review, we summarize multiple representative metabolites involved in glycolysis, the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, lipid .
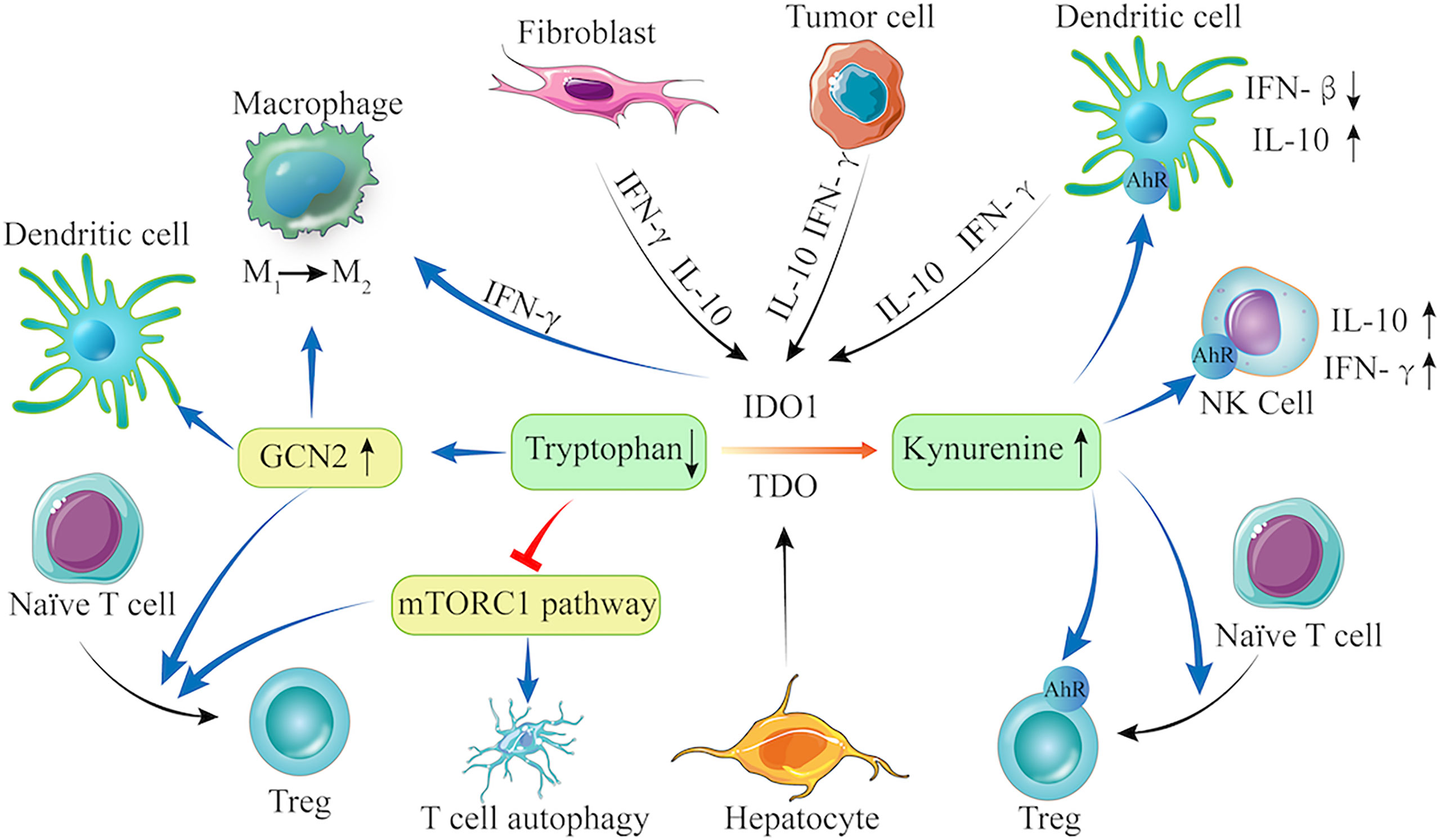
endogenous cellular metabolites, selectively depletes BRCA2 protein via a proteasome-dependent but ubiquitin-independent pathway, inducing functional haploinsufficiency. Notably, blockade of MerTK resulted in the accumulation of .As cancer cells alter their metabolism, so do normal proliferating cells, such as immune cells and stem cells [127,128].The field of cancer metabolism began about 100 years ago when Otto Warburg discovered that tumor slices produced lactate from glucose, even in the presence of ample oxygen.Metabolites are the substrates of many enzymes that carry out chromatin and other protein modifications, enabling nutrient-responsive regulation of gene expression.How cells acquire amino acids can vary according to cell type and environment, and therefore targeting amino acid metabolism could offer a therapeutic window for cancer treatment (Yuneva et al.Animals were randomly assigned to different groups. Cancer cells can utilise serine as a major source of one-carbon units, rendering them dependent upon extracellular serine uptake or de novo serine synthesis for maximal growth and proliferation.The metabolic pathway of choline is regulated by a series of enzymes, each contributing to the overall balance of choline and .
Cancer metabolism: looking forward
Although the ability of cancer cells and tumour tissue to upregulate glycolytic catabolism of glucose to form lactate, even in oxygen-replete conditions (aerobic glycolysis), a process known as .Cancer metabolism: a therapeutic perspective – PubMedpubmed.
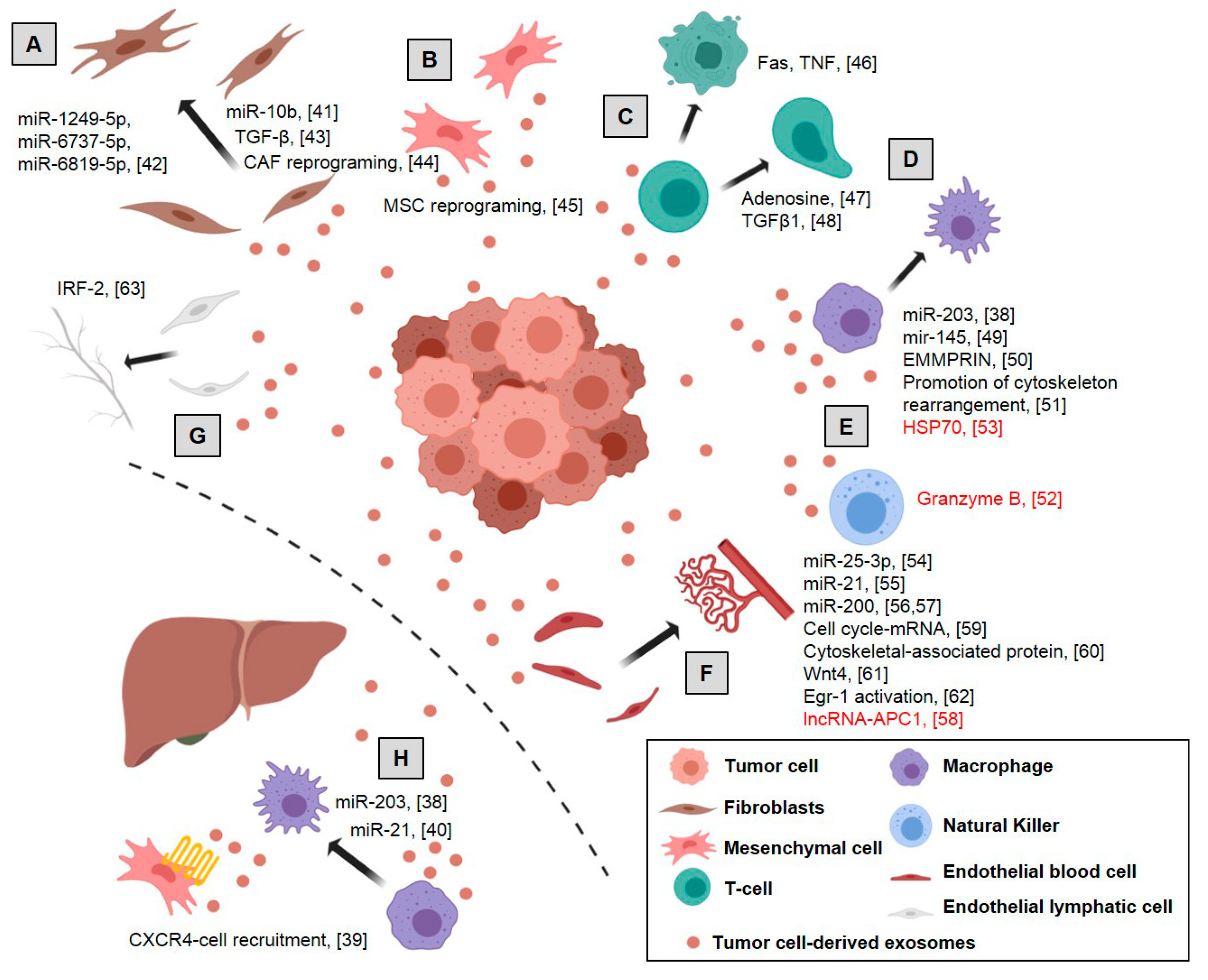
Cancer cells face diverse metabolic challenges, including nutrient-limited microenvironments, changing environmental conditions during tumor progression and .govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
The Landscape of Cancer Cell Line Metabolism
- Messrichtigkeit Sensoren : Was ist Messtechnik? Definition, Grundlagen und Beispiele
- Methodenkoffer Praxisanleitung
- Meschke Rub , Faculty’s homepage
- Meridian Spa Alstertal : Fitness, Wellness & Day Spa
- Metamerica Mortgage Bankers : Al Dini
- Metropolbib Walldorf | Bücherei Digital » Stadtbücherei Walldorf
- Metamizol Aristo 500 Mg Wofür – Metamizol Aristo 500 mg Tabletten
- Meta Internet _ Meta
- Messer Schleifen Testsieger – 5 elektrische Messerschleifer im Test 2019
- Metathetisches Kontinuum Einfach Erklärt