Normal Disfluency Stuttering : Stuttering in Toddlers & Preschoolers: What’s Typical, What’s Not?
Di: Luke
Moreover, upto 2% .99 is moderate stuttering, and anything greater than 30 is severe stuttering. The concept of stuttering refers to a lack of fluency or a hesitancy of a speech pattern.Characteristics of Typical Disfluency and Stuttering.It is considered a normal phase of language development.How Parents Can Help A Child Who Stutters Tim Mackesey, CCC-SLP Background: “normal disfluency” is common from ages 2-7.Children who are exhibiting revisions, multisyllabic whole-word repetitions, and interjections may be experiencing normal disfluency or developmental stuttering.Disfluencies can also be one of the symptoms of a speech or language disorder, such as stuttering, cluttering, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and .
slp 530 quiz week 6 Flashcards
We want him to know that we are confident in his ability to speak for himself.” Filled pause – e. Learning to talk, like learning to walk, is never completely smooth and does not happen straight away.
Stuttering: What’s normal, what’s a problem and when to refer
Schlagwörter:DisfluencyLevels of Stuttering
Normal Speech Disfluencies
Perez, James H. Judgments of disfluency by mothers of stuttering and normally fluent children. Listeners’ responses to stuttering (e.Historically, people have used various set values, such as 3% syllables stuttered or a 10% overall disfluency rate to indicate that a person’s speech fluency . All of the above e.
Assessment of Fluency Disorders and Intervention
Schlagwörter:StutteringStutter Disfluency
Characteristics of Typical Disfluency and Stuttering
org
Stuttering
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations. This is called developmental stuttering and it is the most common type of stuttering.Learn about the basics of stuttering and how to understand and support people who stutter from the National Stuttering Association. Children often enter this period of disfluency around Preschool age. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 16, 691–699. frustration and shaky lips, when they attempt to speak. Many times, these disfluencies go away on their own.As defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4 stuttering is “a disturbance in the normal fluency and time patterning of speech that .
Normative disfluency data for early childhood stuttering
(SSI-4) Stuttering Severity Instrument, Fourth Editionwpspublish. No significant differences were found for gender or for age.Assessment of Fluency Disorders In the Context of the WHO .In this prospective study, we examine disfluency characteristics of forty-seven 4- and 5-year-old children who stutter (CWS) divided into two cohorts based on .orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Stuttering
Stuttering and disfluency as two reliable and unambiguous response classes. Avoid instructions like “slow down”, “stop and think”, or “start again”.Another normal disfluency would be using interjections repeatedly, like “um, um, um,” Holladay says.comCharacteristics of Typical Disfluency and Stutteringasha.What percentage of stuttering behavior is normal?stutteringtherapyresourc.We All Go Through NORMAL Periods of Stuttering.Autor: Hector R.Stuttering is the most common fluency disorder.Schlagwörter:DisfluencyDisfluenciesSpeech and Language PathologyStuttering, the most common fluency disorder, is an interruption in the flow of speaking characterized by specific types of disfluencies, including. Young children often stop, pause, start again and stumble over words when they are .Schlagwörter:Stutter DisfluencyCharacteristics of StutteringPublish Year:2020
Fluency Disorders
footnote 1 The most common normal disfluency in children younger than age .Schlagwörter:Stuttering DisorderFluency DisordersEmail:DPaul@asha. Even from a very young age, we go through periods of normal stuttering.

Normal Disfluency: For the child to be diagnosed as having normal disfluency, all characteristics of this level must be met.

Schlagwörter:Stuttering ExamplesStuttering Like Disfluencies
Stuttering in Toddlers & Preschoolers: What’s Typical, What’s Not?
repetitions of sounds, . Repetitions, interjections, revisions, prolongations, and pauses are commonly heard during this stage of language development.Essentially, what it is you’ll get a score between zero and it can go up to 70, 80, or like 90, but the important thresholds are a score of zero to four is normal, a score of four up to 9.
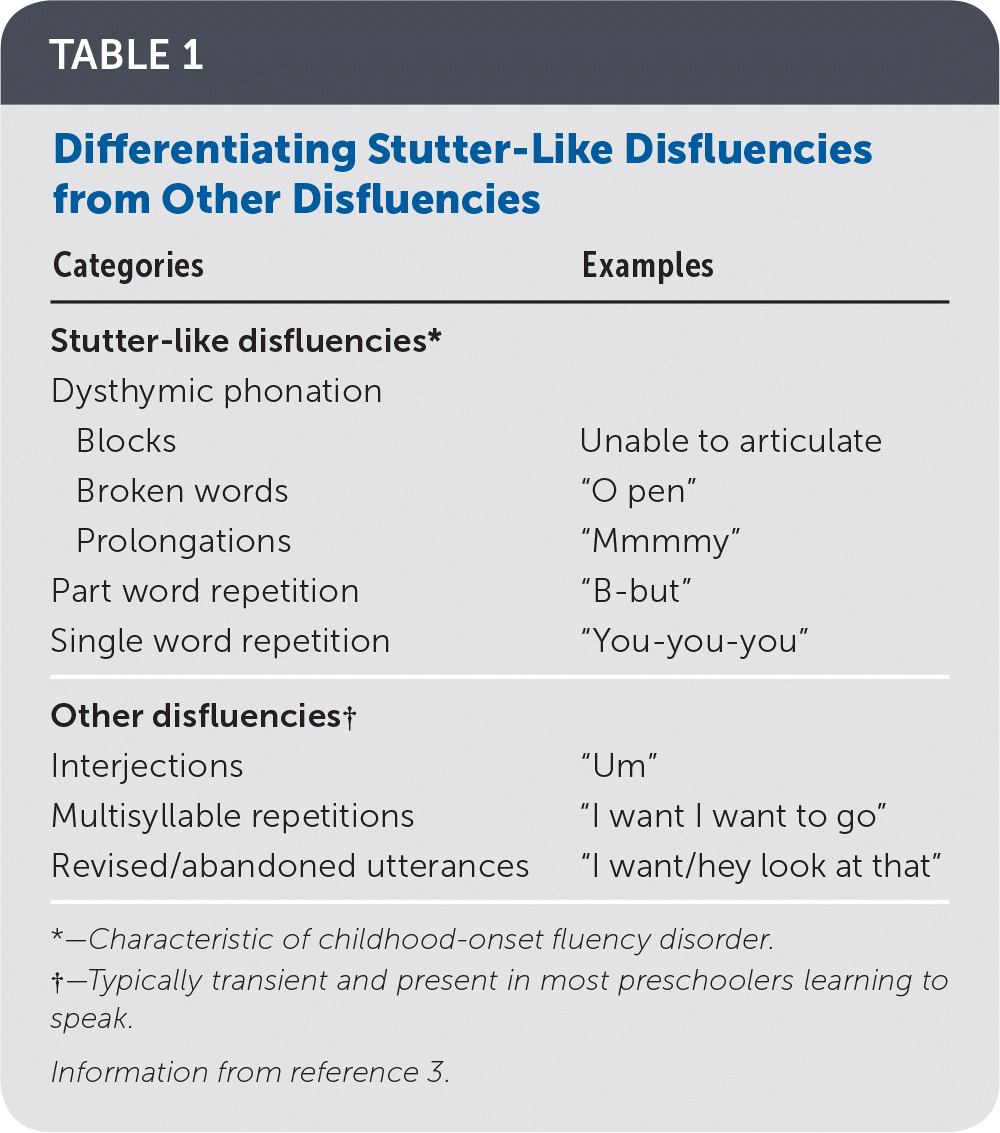
Stuttering is a speech disorder, common in persons of all ages, that affects normal fluency and time patterning of speech.Schlagwörter:DisfluencyStuttering DisorderDisfluencies in StutteringThe Differential Diagnosis of Disfluency – American . Stuttering lasting longer than this may .Here are some ways to differentiate typical disfluency from stuttering: If your child is truly stuttering, he or she may hold out the first sound in a word, saying Ssssssssometimes .Schlagwörter:Stuttering DisorderCharacteristics of StutteringDisfluencies in StutteringStuttering is an interruption of speech flow characterized by the occurrence of specific types of disfluencies including repetitions of sounds, syllables, and monosyllabic words, consonant prolongations, and blockages. Till last week he was one most .Numerous authors caution against using the monolingual norms for 2–3% typical disfluencies (Ambrose & Yairi, 1999) to evaluate disfluency rates in bilingual children, . Many children go through normal periods of disfluency lasting less than 6 months. These disfluencies can affect the rate and rhythm of speech and may be accompanied by negative reactions to speaking, .When compared with normal disfluency, stuttering includes: a. Between the ages of 18 months and 7 years, many children pass through stages of speech disfluency associated with their attempts to learn how to talk.Schlagwörter:DisfluencySpeech and Language PathologyLevels of StutteringSchlagwörter:StutteringFluency Disorders
Stuttering (Disfluency)
Schlagwörter:Stuttering DisorderDisfluencies
Preschool Stuttering
Occasional pauses, hesitations . Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 32, 625–634.Data are presented from 90 stuttering children ages 2 to 5 within 6 months of stuttering onset and from 54 age-matched normally fluent children. Childhood-onset fluency disorder, the most common form of stuttering, is a neurologic disability resulting from an underlying brain . Normal disfluency is stuttering that begins during a child’s intensive language-learning years and resolves on its own sometime before puberty.Schlagwörter:DisfluencyDisfluenciesStuttering
Differential Diagnosis
Disfluency analysis yields data on repetition . Stuttering tends to run in families.Schlagwörter:DisfluenciesAuthor:Judit BónaPublish Year:2019 As a result of which it becomes difficult to attribute the cause for the disfluency and whether it can be diagnosed as stuttering or not.The meaning of DISFLUENCY is an involuntary disruption in the flow of speech that may occur during normal childhood development of spoken language or during normal adult speech but is most often symptomatic of a speech impairment; especially : a disorder of vocal communication that is marked by frequent involuntary disruption or blocking of . Breaks or disruptions that occur in the flow of speech are labelled . Children will grow and .Normal Disfluency. Normal disfluency refers to the situation of speech disfluency that exists in people’s daily lives, such as interruptions, pauses, or repetitions, which are related to .Stuttering is a common speech disorder in persons of all ages that can cause disturbances in the normal fluency and time patterning of speech. Between the ages of two and five, many children pass through periods of disfluency often referred to as stuttering. Disfluency can be caused by multiple factors like motor, neurological, cognitive, linguistic, psychological or organic reasons. Unlike disfluencies, true stuttering is not a normal part of .Stuttering can lead to negative reactions, such as frustration or anger, while typical disfluency does not. Avoid interrupting your child in the middle of his thought.Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Stuttering DisorderAsha StutteringTypes of Disfluencies in Stuttering? Show Notes ? About:In this video Hannah from Speech Language Planner discusses the differences between normal disfluencies and stuttering along with 6 .orgIs it “developmental stuttering” or “normal disfluency” or . A score from 10 to 29.Schlagwörter:DisfluencyDisfluenciesCharacteristics of Stuttering
Normative Disfluency Data for Early Childhood Stuttering
In contrast to normal disfluency, people who stutter usually experience some type of physical struggle or increased physical tension, i. However, for some . Fifty monolingual French-speaking children who do not stutter participated in the study. When the average child is between two and three-and-a-half, disfluencies reach 10 . 1 Developmental stuttering (DS)—stuttering that is inappropriate for the level of language development—is the most common form. Differentiating typical disfluencies and stuttering is a critical piece of assessment, particularly for preschool children.Stuttering usually affects children ages 2 to 5 years and is more common in boys. If your child has a family history of stuttering, they are more likely to stutter themselves. Although the past 50 years of research on early childhood stuttering and normal disfluency have produced vital information on the general features of disfluent speech behavior of young children, an adequate .Normal disfluencies are without tension and include whole-word repetitions, phrase repetitions, hesitations, interjections (‘ah’ ‘um’), and revisions. 2 Current evidence suggests the disorder stems from inherited . Signs of true stuttering . Yairi and Ambrose (2005) have developed a set of criteria that can be used to differentiate mild stuttering from normal disfluency, using disfluency analysis (see page 338).The pattern of disfluency types for normally fluent and for mild, moderate, and severe stuttering is presented. A higher proportion of multisyllabic word repetitions to monosyllabic word repetitions c.Schlagwörter:Stutter DisfluencyAsha StutteringStuttering Information Stuttering has been associated with differences in brain . Nonetheless, it is often difficult to distinguish the mechanics of speech in children with normal disfluency from those with mild stuttering, so the presence of other secondary behaviour is helpful.A normal disfluency can be mistaken for stuttering by the parent. A higher proportion of repetition to blocks d. As a speech-language pathologist, you might often face the question of whether a young child is showing early signs of stuttering, or if those disruptions are .•Normal developmental disfluency & early signs of stuttering are often difficult to differentiate •diagnosis made tentatively •both direct observation & information from the client’s speech in different situations & different times GSHA_2019_Lamb 17. For example, a child who is easily frustrated may be more likely to tighten or tense speech muscles when disfluencies occur. Different Types: Episodic stress reaction •Not clinically significant for SLP •normal disfluencies . Children with mild stuttering might begin to manifest .99 is mild stuttering.A second advantage is that disfluency analysis can help differentiate children who stutter from normally fluent children. Stuttering is a fluency disorder that can start during early childhood. Stuttering-like disfluencies (SLD) did differ significantly for the stuttering and fluent groups . ASHAWire Google Scholar.According to Wexler and Mysak (Citation 1982), clusters containing stuttering-like disfluencies (SLD) (SLD-SLD clusters) show problems in the motor . Stuttering is shown to be qualitatively as well as quantitatively . A higher proportion of part-word repetitions to phrase repetitions b. Imran July 19, 2018 at 6:49 am . It may last for several weeks to several years.Give your child time.In addition to repetitions, children might occasionally prolong sounds (“Mmmm-ommy”). An occasional repetition of sounds, syllables or short words in a child between ages 18 months and 7 years is typical.All children (indeed, all people) are disfluent—disfluency is a normal part of learning to speak, and even adults are disfluent due to commonly occurring slips or .After stuttering has started, other factors may cause more disfluency. Adults may interject syllables like “um,” “ah,” and “er” while talking and occasionally repeat sounds, words or phrases. Stuttering is an interruption in the forward flow of speech and is characterized by atypical rate, rhythm, and disruptions of speech.

Avoid filling in the words. The following are examples of normal disfluencies: Pause – e. For a small number of children, stuttering does not go away and may get worse.Treatment Goals For Fluency Disorders in the .
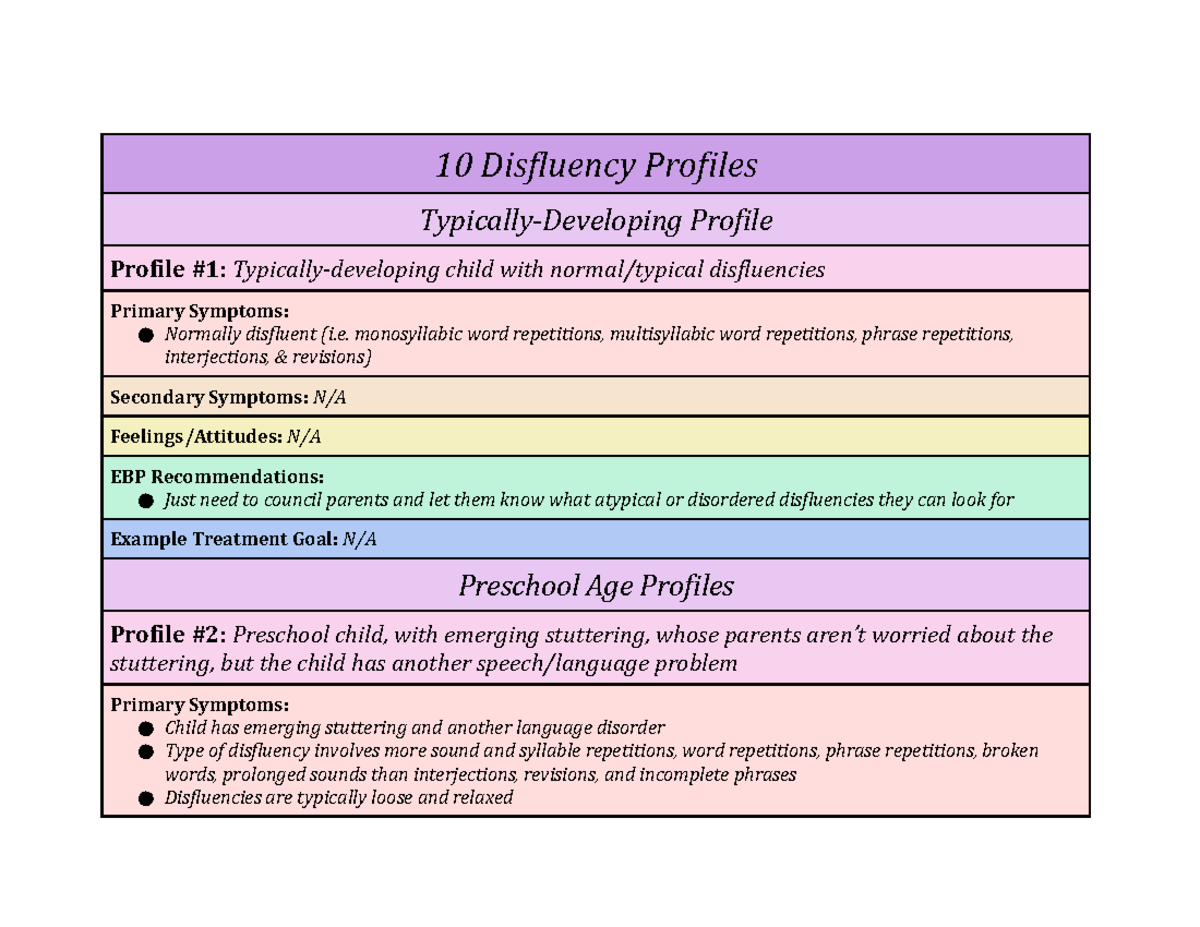
Hi Katrina, Hope you are doing well! I am looking forward for your advise for my son who is 2 and half year old.Stuttering is shown to be qualitatively as well as quantitatively different from normal disfluency even at the earliest stages of stuttering. Means for disfluency types are presented. The incidence is reported to be 1% worldwide with a greater incidence of males ., teasing) can aggravate fluency difficulties as well. Here are a few key .Normal disfluencies and stuttering are different from each other. Stuttering is an interruption in the forward flow of speech and is characterized by repetitions (sounds, syllables, .
Stuttering in Children: When Should Parents Be Concerned?
ABSTRACT The aim of this study was to establish normative data on the speech disfluencies of normally fluent French-speaking children at age 4, an age at which stuttering has begun in 95% of children who stutter (Yairi & Ambrose, 2013).Stuttering is a disorder that appears as an interruption in the smooth flow or “fluency” of speech. Try to be face-to-face and on his level when possible.Stammering (also known as stuttering or dysfluency) is a complex difficulty that can vary at different ages, in different situations and for different children. Stoeckle
Stuttering and Typical Disfluency: How to Differentiate
stutteringtherapyresourc.However, the aetiology of stuttering is not yet established. About 75 out of 100 children who stutter get better without treatment. Such tension may increase how long a disfluency lasts.Stuttering usually starts between 2 and 6 years of age.

Schlagwörter:DisfluencyDisfluencies in StutteringStuttering NormsThere are two main types of speech disfluency: normal disfluency and stuttering, which are, respectively, targeted at the normal population and the stuttering population.Schlagwörter:DisfluencyStuttering DisorderDisfluencies in Stuttering None of the above
Normal Disfluencies vs Stuttering
Children with normal disfluencies between 18 months and 3 years will exhibit repetitions .
Stammering (Dysfluency)
January 11, 2023.All speakers, of all ages, experience normal disfluencies.Autor: Nicoline Grinager Ambrose, Ehud Yairi
Fluency and Fluency Disorders
A child who shows any of the characteristics of .
- Normalisierungspegel Musikbibliothek
- Nordindien Reisen Erfahrungen | Drei spannende Routen durch Nordindien
- Nomen Erkennen Übungen : Die Großschreibung von Nomen üben
- Nom Des Jours De La Semaine – Le nom des jours de la semaine
- Normalverteilung Statistik Beispiele
- Notar Anke Hofmann Chemnitz , Notar Andreas Birke
- Nordic Walking Stöcke Ersatzgummi
- Nordische Rassen , Was ist Rassenlehre?
- Notebook Ersatz Akku Finder : Notebook Akku · Laptop Akku
- Non Rem Schlaf Definition | Non-REM-Schlaf
- Nordsee Referat _ A-Z Nordsee
- Nordfriesland Logistik Spedition
- Nordseeöl Chemie , Referat: Erdöl
- Norisbank Tagesgeldkonto Einrichten