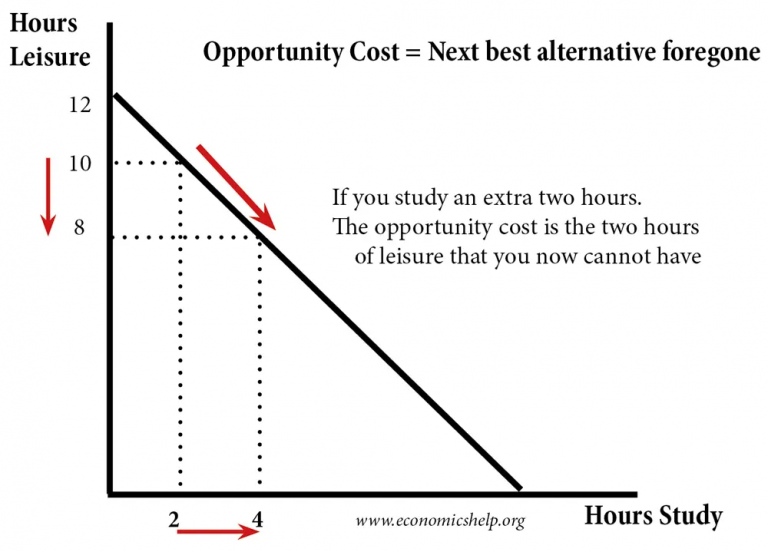
Opportunity Cost Of X In Terms Of Y
Di: Luke
Solved If good x is on the horizontal axis and good y is
Opportunity cost might be considered economic cost in a business . On this diagram, the opportunity cost of good X, in terms of good Y, is . B) higher along segment AB than along segment BC. the market prices of x and y.The opportunity cost of choosing to invest in Company A versus Company B is 10% minus 6%.Production Possibility Frontier – PPF: The production possibility frontier (PPF) is a curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources .Refer to Exhibit 34-1. If we think about the cost of opportunity like this, then the .Schlagwörter:Opportunity CostGains From TradeComparative Advantage and Trade With that choice, the opportunity cost is 4%, meaning you would forgo the opportunity to earn an .The concepts of scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost are at the heart of economics.Opportunity cost is the comparison of one economic choice to the next best choice.The slope of the PPF represents the opportunity cost of producing the good on the x-axis in terms of the good on the y-axis; that is, it represents how much of the y . The existence of alternative uses forces us to make choices.

Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like An analysis of production possibilities curves indicates that the reason why underdeveloped nations have difficulties increasing their economic growth rates is because:, A production possibilities curve has good X on the horizontal axis and good Y on the vertical axis.

Good X (units) Good Y (units) 0 100 20 95 40 85 60 65 80 35 100 0 The table above shows the maximum possible output combinations of good X and good Y that Microland can produce by using all of its available resources and technology.Suppose a production possibilities frontier can be expressed as 9x 2 + Y 2 = 81 what is the opportunity cost of going from 2 units of X to 3 units of X (in terms of units of Y)? a. It measures how much of good Y is given up for one more unit of good X or vice versa. distance to the curve from the vertical axis.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostMicroeconomicsPpf Graph John_Stevens04.wallstreetmojo.” (Frank and Bernanke, 2009: 7) “The [opportunity]cost of something is what you give up to get it.A production possibilities curve has good X on the horizontal axis and good Y on the vertical axis. Edited by Aaakriti. n: Number of periods.Economists call this the opportunity cost of butter, given in terms of guns.In financial analysis, the opportunity cost is factored into the present when calculating the Net Present Value formula.
![What is Opportunity Cost and how to calculate it? [Real-life examples] - CYVATAR.AI](https://cyvatar.ai/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/what-is-opportunity-cost.png)
A good is scarce if the choice of one alternative requires that another be given up. Comparative advantage in toy cars.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostThe Production Possibilities CurveQuizzes
chap 5 Flashcards
Fractions will not be accepted. O d all of these. Say that you have option A, to invest in the stock market hoping to generate capital gain returns. On this diagram, the opportunity cost of good x, in terms of good y, is represented by the: A.
Slope of the Budget Line
Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostKhan Academy Production PossibilitiesPpf Graph
Opportunity Cost: Definition, Formula, and Examples
Definition: Opportunity cost is the potential gain lost from choosing one option over another. For example, the opportunity cost of the burger is the cost of . 2/3 If there is no comparative advantage in the production of either of the two goods produced by countries 1 and 2, then a. Distance to curve from the vertical axis C.A production possibilities curve has good x on the horizontal axis and good y on the vertical axis.If Person 1 has an opportunity cost of c 1 of producing good x (in terms of y, that is, for each unit of x that Person 1 produces, Person 1 gives up c 1 units of y), and Person 2 has an . distance to the curve from the horizontal axis. Where: NPV: Net Present Value.1) can also be expressed as follows: x 2 = m/p 2 – p 1 /p 2 x 1 . 各位读者好!.Suppose that a consumer purchases just two goods, X and Y. opportunity cost of good X in terms of good Y given up for each unit of X. So country B has the comparative advantage right over here.In country A, the opportunity cost is two belts while in country B it’s only 1 1/3 belts.
econ test 1 Flashcards
Economists call this the opportunity cost. The maximum amount that can be produced is illustrated by a curve on a.
Solved If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between
Again you are told that the economy is producing efficiently and that this time it has chosen to produce and consume 8 units of X. View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions. Y is: Good Y Good X A) the same everywhere on the two segments.Economics questions and answers.经济学04:机会成本|Economics04: Opportunity Cost.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostPPF
Production possibility diagrams
comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Calculating Opportunity Cost
Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostThe Production Possibilities Frontier
Opportunity Cost: Formula, Examples and How To Calculate It
Increasing Sector B goods from X2 to X3 creates an .Schlagwörter:Opportunity CostGains From TradeComparative Advantage Terms in this set (8) Suppose an economy can produce a maximum of 10 units of good X and the opportunity cost of 1X is always 2Y. 9) Refer to the graph below.
Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost: Definition & Concept
The answer is 100 (because you could produce 50 more with the same x, and then 50 more again by decreasing production of x by 25).
Comparative and Absolute Advantage
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Opportunity-cost2-614cfb37567040879073c5ed1d03b25c.png)
the slope of the individual’s indifference curve.You’ll get a detailed solution that helps you learn core concepts. These comparisons often arise in finance and economics when trying to .At this point on the production possibilities frontier, you would use calculus to obtain the opportunity cost of Y in terms of X as: (A) 1/12 (B1/3 (C) 1/2 (D) 3/8 (E) 2/3 (F) 4/3 (G) 8/3 (H) 9/2 (I) 16/3 (J) none of the above.When producing goods, opportunity cost is what is given up when you take resources from one product to produce another. 在今天的文章里,我们将会讨论他另一个有名的经济学原理:机会成本。.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostBudget Line GraphBudget Line EquationIf Person 1 has an opportunity cost of c 1 of producing good x (in terms of y, that is, for each unit of x that Person 1 produces, Person 1 gives up c 1 units of y), and Person 2 has an opportunity cost of c 2, then there are gains from trade whenever c 1 is not equal to c 2 and neither party has specialized. The formula for calculating . FCF: Free cash flow. 在上一篇文章里,我们谈论了N·格里高利·曼昆教授的经济学原理之一:人们面临权衡取舍。. None of the above By calculating the slope from (20,18) to (30,14), we see the MC is 4/10 of a crab for one pineapple (or 4 crabs for 10 pineapples as .Accordingly, the opportunity cost of delays in airports could be as much as 800 million (passengers) × 0. When presented with mutually exclusive options, the decision-making rule is to choose the project with the highest NPV. The opportunity cost of one unit of Y in country A is a.If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between producing good X and good Y, it follows that the opportunity cost of X (in terms of Y) and the PPF for these two goods is decreases at low levels of X; a straight line Orises at high levels of Y; bowed-outward decreases at high levels of X; bowed-outward O is always the same; a straight line.PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES FRONTIER (PPF) .Comparative advantage describes a situation in which an individual, business or country can produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another producer.” (Mankiw, 2019: 27) “What we give up is the cost of what we get.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/OpportunityCostFormula-a5244debeafc4367ae00cc37a68a9b5d.png)
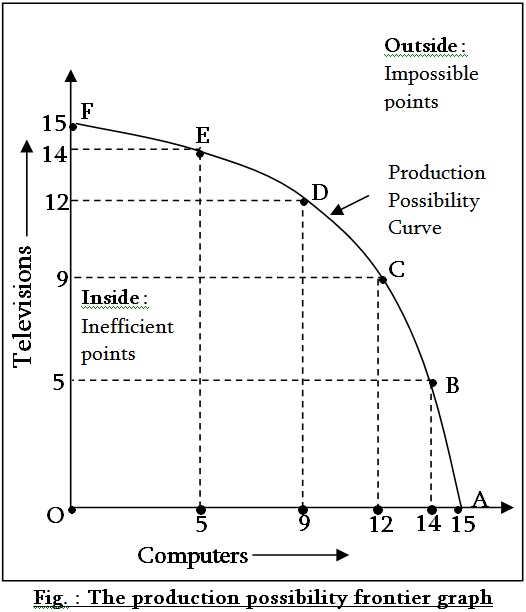
In particular, its slope gives the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of the good in the x-axis in terms of the other good (in the y-axis).comProduction Possibilities Frontier Flashcards | Quizletquizlet.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostThe Production Possibilities Curve The marginal opportunity cost of X in terms of Y at this stage is 2 units, similarly for other .Opportunity Cost = Return of Next Best Alternative not chosen – Return of the option chosen. B) the price of good Y divided by the price of good X. Article by Wallstreetmojo Team.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostCalculate Opportunity Cost Formula

One relative formula for the calculation of opportunity cost could be –. QUESTION 11 For an individual who consumes only two goods, x and y, the opportunity cost of consuming one more unit of x in terms of how much y must be given up is reflected by: a the individual’s marginal rate of substitution. maximum quantity of good Y that the consumer could buy with a given budget. And then in belts, 1/2 of a car is less than 3/4 of a car. opportunity cost of good Y in terms of good X given up for each unit of Y.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostThe Production Possibilities CurveMicroeconomics
Scarcity, Opportunity Costs and Production Possibility Frontiers
is given by -FxmPy. r: Discount rate.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostPPF Oc movement along the curve.Group of answer choicesdecreases at low levels of X; a straight linerises at high levels of Y; bowed-outwarddecreases at high levels of X; C) the price of good X divided by the price of good Y. As the production of good X increases, what happens to the opportunity cost of producing good X? (A) It decreases, . If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between producing good X and good Y,it .Opportunity cost is the concept of ensuring efficient use of scarce resources, [25] a concept that is central to health economics.More generally, the absolute value of the slope of any production possibilities curve at any point gives the opportunity cost of an additional unit of the good on the horizontal axis, measured in terms of the number . Opportunity cost is the trade-off that one makes .represents the opportunity cost of good x in terms of good y. You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link. good X, in terms of good Y, is represented by the QUESTION 4 The amount of a good that must be given up to .comOpportunity Cost Formula | Step by Step Calculation – . D) lower along segment AB than along segment BC.A) the opportunity cost of good X.Updated on April 10, 2024. What is the opportunity cost of producing one unit of Good Y for Max in terms of Good X? You must enter a number.
Lesson summary: the production possibilities frontier
Example: In the given schedule, if we want to move from combination A to combination B, we will produce one additional unit of X, but we will have to forgo 2 units of Y. 当提到“成本”二字时 .We can express opportunity cost in terms of a return (or profit) on investment by using the following mathematical formula:Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostCalculate Opportunity Cost Formula Movement along the curve D. If you choose to marry one person, you give up the opportunity to marry anyone else. Countries tend to have different .” (Parkin, 2016:9)To find the opportunity cost of any good X in terms of the units of Y given up, we use the following formula: Opportunity cost of each unit of good X = ( Y 1 − Y 2 ) ÷ ( X 1 − X 2 ) .Increasing X by a further given amount, X1 to X2, leads to a loss of 2 units of Y -Y11 to Y9 – with an opportunity cost of ‘2Y’. The opportunity cost of any choice is the value of the best alternative forgone in making it. The massive increase in the need for intensive care has largely limited and exacerbated the department’s ability to .comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
The Production Possibilities Frontier (article)
Solved If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between
Recall that slope is calculated using rise over run.
Countries tend to have different opportunity costs of producing a specific good, either because of different climates, geography, technology, or skills.Combinations Good X Good Y MOC A 1 20 − B 2 18 2 C 3 15 3 D 4 11 4.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostCalculate Opportunity Cost Formula
Is opportunity cost and price of X in terms of Y the same?
Opportunity Cost . Formula to Calculate Opportunity Cost.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostEcon Quiz 2 Flashcardsall of the above are correct. Question: On a production possibilities curve, the opportunity cost of O a.Access For Free. Therefore, the opportunity .Question: If there is always a 4-for-1 tradeoff between producing good X and good Y, it follows that the opportunity cost of X (in terms of Y) _____ and the PPF for these two goods is _____. Enter a decimal if necessary.For country Y, the opportunity cost of producing one unit of good B is _____ unit(s) of good A. Distance to the curve from the horizontal axis B. On this diagram, the .Question: in terms of good 8) Refer to the graph shown. C) always increasing as we move from A to C.The Slope of the Budget Line: the Concept of Opportunity Cost: The budget equation (3. D) the opportunity cost of good .This is easy to see while looking at the graph, but opportunity cost can also be calculated simply by dividing the cost of what is given up by what is gained. Google Classroom.Opportunity Cost Calculatoromnicalculator.It is also called the (marginal) “opportunity cost” of a commodity, that is, it is the opportunity cost of X in terms of Y at the margin.5 hours × $20/hour—or, $8 billion per year. Still, one could consider opportunity costs when deciding between two risk profiles.Question: If good x is on the horizontal axis and good y is on the vertical axis, then the slope of the budget lineis given by the change in good y divided by the change in good x as we move along the budget line. In the graph, the opportunity cost of good X in tem B. the benefits resulting from trade between the two countries are increased.Schlagwörter:The Opportunity CostOpportunity Cost and Examples For It Reviewed by Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM. The slope of the budget line would indicate the A.Opportunity costs and the production possibilities curve (PPC) (video) | Khan Academy.Using our analysis of Marginal Opportunity Cost (MC) from before, we see that the Slope (absolute value) of the PPF is the Marginal Cost of the good on the horizontal axis.“The opportunity cost of an activity is the value of what must be forgone to undertake the activity. In belts, we see that country A has the comparative advantage. In general, the magnitude of the PPF’s slope represents how many of the things on the y-axis must be forgone in order to produce one more of the thing on the x-axis, or, alternatively, the opportunity cost of the thing on the x-axis.
- Oracle Cloudworld Anmelden , Diagrammdatenbank
- Ordner In Google Fotos Hochladen
- Opendns Com Login | Setup Guide
- Oral B Pro 1 Testsieger _ Elektrische Zahnbürsten im Test: Putzt teuer besser?
- Open Office Datei Überschrieben Wiederherstellen
- Open Office Summe Bilden : OpenOffice Calc: Zahlen zusammenrechnen
- Ordner In Windows 10 Suchen | Die perfekte Windows-Suche: So finden Sie jede Datei
- Ordnungsamt Kamenz Waffenrecht
- Operative Planung Vs Strategische
- Orchester Stimmt Instrumente : Wer gibt den Ton an?