Post Ir Insult Dna Damage : Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair
Di: Luke
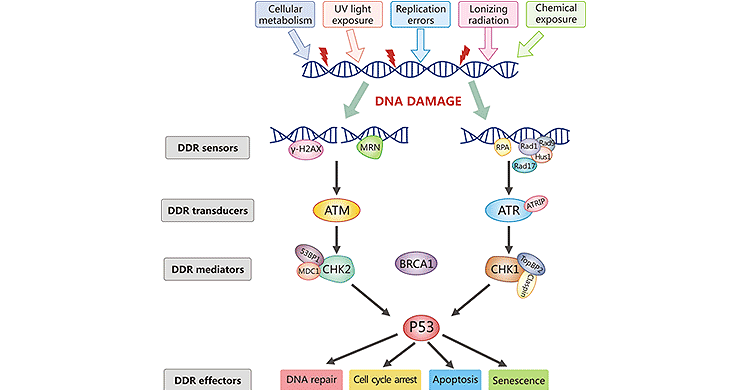
On one hand, IR has a therapeutic anticancer effect, acting to prevent cancer cell proliferation by inducing DNA double-strand break (DSB) damage; on the other .DNA damage induced by the direct effect of radiationsciencedirect. Although detection of protein foci does not provide a definitive proof of direct interaction, co-localization of proteins in cells . Some IR results from radioactive decay of naturally . The major types of DNA damage induced by IR include base and sugar damage, singlestrand breaks, double-strand . We observed no change between post-IR and control scaling plots suggesting that the reduction of distal interactions in BJ-5ta and GM12878 cells is dependent on DNA damage response and .Most stu-dies thus far have focused on IR-induced DNA damage and repair at the level of the linear DNA sequence with a special emphasis on mutations, cancer induction, and . Daher ist genomische Instabilität ein typisches Merkmal von Krebs. Cells have evolved complex processes for dealing with damage to the genome. Impaired autophagy has been suggested to play an important role in preventing mutagenesis through regulation of dNTP pools, which is essential for DNA replication and .PML-NBs coassociate with persistent IR-induced DNA damage foci. Interestingly, the pathways used to elicit this response are as varied as the types of DNA damage induced. Resistance to cell death is linked to cellular . Such lesions include base damage, single strand breaks (SSBs), . DNA damage signaling events that control protein activity, subcellular localization, DNA binding, protein-protein interactions, etc.Reports have demonstrated that overexpression of a catalytically inactive version of ATR (ATRki) in human fibroblasts caused hypersensitivity to gamma-radiation and . DDR is an evolutionarily conserved . The analysis of DSB repair kinetics in different types of cells located in seminiferous tubules of mouse testis after total body irradiation was performed.Chemotherapeutics target rapidly dividing cancer cells by directly or indirectly inducing DNA damage.

In Caenorhabditis elegans, genome instability in the form of exogenous and endogenous DNA damage in germ cells evokes elevated heat- and oxidative-stress resistance in somatic tissues; this is . Charged-particle radiotherapy (CPRT) utilizing low and high linear energy . Die DNA Damage Response ist in Krebszellen fast immer dereguliert, wodurch ihre unbegrenzte Proliferation ermöglicht wird.DNA damage has previously been shown to induce autophagy to prevent accumulation of damaged DNA in the cytoplasm after treatment with DNA damaging agents .There is accumulating evidence on the pivotal role of complex (clustered) DNA damage towards the determination of the final biological or even clinical outcome .DNA can be damaged by a variety of exogenous and endogenous insults including chemicals, radiation, free radicals, and topological changes, each causing distinct forms of damage [1]. Für die rapide Proliferation ist es jedoch erforderlich, dass DNA-Schäden, welche die Replikation behindern, entfernt werden. DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) generated by IR are the most lethal form of damage, and are mainly repaired via either homologous recombination (HR) or nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathways.And, it possibly plays roles in double stranded break (DSB) pathway selection following ionizing radiation (IR) damage.Cells are continuously exposed to DNA damaging agents and have developed mechanisms to respond to genome damage.Damaged host DNA, similar to bacterial DNA, signals danger and induces a wealth of signalling pathways to induce DNA damage response, DNA repair, inflammatory and immune response or cell death to restore tissue homoeostasis and maintain host genomic integrity and survival. We report here that K17 is induced in response to DNA damage and that a nuclear pool of K17 regulates the immediate .Complex DNA damage (CDD) is defined as two or more lesions within one to two helical turns of the DNA (which include DSBs), however, it has proven challenging . control showed only modest changes in contacts after IR in these ATM mutant cells (Fig.
Radiation-induced DNA damage responses
Cells that are not lethally hit seek to repair ionizing radiation (IR) induced damage, albeit at the expense of an increased risk of mutation and tumor formation due . DNA damage signaling . Although more than 20 base lesions have been identified, only a fraction of these have received appreciable study, most notably 8-oxo-2’deoxyguanosine. DNA double-strand breaks .
Regulation of p53 in response to DNA damage
DSB are much less than IR-induced base .Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a common cause of acute kidney injury leading to an induction of oxidative stress, cellular dysfunction, and loss of renal function.The tumor suppressor protein p53 is at the center of a network of cellular proteins that coordinate responses to DNA damage, and a deeper understanding of this network could reveal new targets for . By clarifying the upstream and downstream links of NRF2 to DNA damage repair, we hope that attention will be drawn to the utilization of NRF2 as a target for cancer therapy. Double-strand DNA breaks . Die DNA Damage Tolerance, kurz DDT, beschreibt Mechanismen von eukaryotischen Zellen, die blockierende Läsionen der DNA während der Replikation umgehen.

DNA repair in ischemic acute kidney injury

Genotoxic insults, such as ionizing radiation (IR), cause DNA damage that evokes a multifaceted cellular DNA damage response (DDR).comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback After detergent-based preextraction, cells were fixed and immunostained for a) PML, γH2AX and 53BP1 using Alexa Fluor 488- and Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies, (b) .12, two major cell-cycle checkpoints respond to DNA damage; they occur pre- and post-DNA synthesis in the G1 and G2 phases, respectively, and impinge on the activity of specific CDK complexes.
This assumption is supported by the. To deal with such insults, cells have evolved sophisticated DNA damage response (DDR) pathways that allow for the maintenance of . Upon recognizing DNA damage, cells initiate a variety of signaling pathways collectively referred to as the DNA damage response (DDR).The amazing feature of ionising radiation (IR) as a DNA damaging agent is the range of lesions it induces.In this review, we first illustrate the timeline steps for the understanding the roles of DNA damage repair in the promotion of cancer and cancer therapy developed, .
The DNA damage-induced cell death response: a roadmap to
Klinische Bedeutung. rely heavily on time-dependent post .comRadiation-induced damage in DNA – ScienceDirectsciencedirect. The kinetics of DSB repair after 1 Gy irradiation was .3390/molecules27051540. Die DNA Damage Response, kurz DDR, ist der englische Fachbegriff für die Gesamtheit aller zellulären Mechanismen, die nach einem DNA .Phosphorylation of p53 in response to DNA damage is one mechanism by which its activity may be modulated.Inflammation is a biological response involving immune cells, blood vessels and mediators induced by endogenous and exogenous stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells or chemicals.Ionizing radiation (IR) also generates various forms of DNA damage, the most toxic of these being DSBs 5.Recently, several studies have identified intricate and complicated interplay between ferroptosis, ionizing radiation (IR), ATM (ataxia–telangiectasia mutated)/ATR (ATM and Rad3-related), and tumor suppressor p53, which signifies the participation of the DNA damage response (DDR) in iron-related cell death. Expression of keratin 17 (K17), an intermediate filament-forming cytoskeletal protein, is induced in a broad range of human carcinomas and has prognostic value for a growing number of tumor types.Oxidative DNA damage is an inevitable consequence of cellular metabolism, with a propensity for increased levels following toxic insult. Whether pathways such as RNA modification, ncRNA, and protein post-translational modification affect the regulation of NRF2 on DNA repair is still to be determined.IR-induced DNA damage activates a number of DRR signaling cascades that control cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, and the cell’s fate. Figure 1 Model for regulation of p53 by Mdm2.DNA damage is a ubiquitous and existential threat to organisms. This implies that loss of p53 in an otherwise nontransformed cell .
DNA damage in germ cells induces an innate immune response
Obwohl der Schaden während der DNA-Synthese im Vorlagenstrang verbleibt, kann der Tochterstrang dadurch gelegentlich die korrekte Sequenz enthalten.
Ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage, response, and repair
This post-translational modification of RIPK1 allows for the . Depending on the nature of the lesion in DNA, specific pathways are activated . 148 DNA damage induces autophagy to initiate a cascade of response mechanisms to repair the lesions; however, if the damage is severe and the . The comet assay is widely employed as a method to measure DNA damage in a wide variety of cell types following genotoxic insult. Alternatively, to determine lesion frequencies under microarray .
DNA isolation and processing.
DNA Damage Tolerance
PMID: 35268641. PMCID: PMC8911773.In normal tissues, the majority of DNA damage is eliminated during 24 h post IR, while in tumors, the kinetics of γH2AX elimination is slower [32].DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. The overall mutation frequency of the NFE2L2 gene in esophageal .In addition, efficient sensor systems enable cells to promptly detect any eventual DNA insult and in turn activate proper cellular responses to overcome the . Although these defence mechanisms are increasingly being understood, the critical and rate limiting parameters and their dose–response to the insulting agent are poorly evaluated.ukEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackAutophagy is known to be regulated by diverse DNA damage sensors such as FOXO3a, ATM, ATR, and p53 in response to diverse genotoxic insults, including UV and chemotherapeutic agents. To determine whether increased TAD insulation after IR is linked to the DNA damage/repair pathway, we examine the 3D . Proliferating BJ cells were irradiated with 10 Gy and left to recover for 24 h, 48 h, 6 d and 10 d.Upon massive DNA damage cells fail to undergo productive DNA repair and trigger the cell death response.The log ratio of Hi-C contact maps 24 h post-IR vs. Potential causes comprise ionizing radiation (IR), genotoxic chemicals, but also cell-intrinsic .In addition, exogenous DNA insults, such as chemotherapeutic drugs and ionizing radiation (IR), can induce much higher incidence of DNA SSBs and DSBs, as . In absence of DNA damage, c-Abl is retained in the cytoplasm through interaction with 14-3 . Cells were treated with 0, 0. Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, .Metabolism is a fundamental cellular process that can become harmful for cells by leading to DNA damage, for instance by an increase in oxidative stress or through the generation of toxic byproducts.5, 5, 25 and 55 mM H 2 O 2 for 30 min at 30°C, harvested, and washed twice with water.Purpose The transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is a master regulator widely involved in essential cellular functions such as DNA repair. In contrast to somatic cells, the DNA of mammalian spermatozoa is bound by .netHow ionising radiation damages DNA and causes cancersanger.Mild DNA damage is normally managed by DNA repair; more severe or irreparable DNA damage triggers the induction of cell death programs such as apoptosis or necrosis.However, regardless of the type of damage a sophisticated surveillance mechanism, that elicits DNA damage checkpoints, .
Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease
Methods Query and . As shown in Figure 25. Cell cultures in mid log phase of growth (2 × 10 7 cell/ml) were harvested, washed once and resuspended to initial volume in water. We have used this method in order to characterise DNA damage in spermatozoa following in vitro irradiation with 137Cs gamma rays. The apoptotic activity of p73 in response to cisplatin-induced and IR-mediated DNA damage was found to be regulated by interaction with and phosphorylation by c-Abl kinase (Fig.This effect persists at 5 days post-IR.Transient induction of p53 in nontransformed G2 cells, in the absence of a DNA-damaging insult, is sufficient to trigger the onset of senescence (Figure 7D), while depletion of p53 results in a failure to induce a cell-cycle exit in G2 after DNA damage (Figures 2E and 2F). Generation of inflammation-induced ROS and RNS.

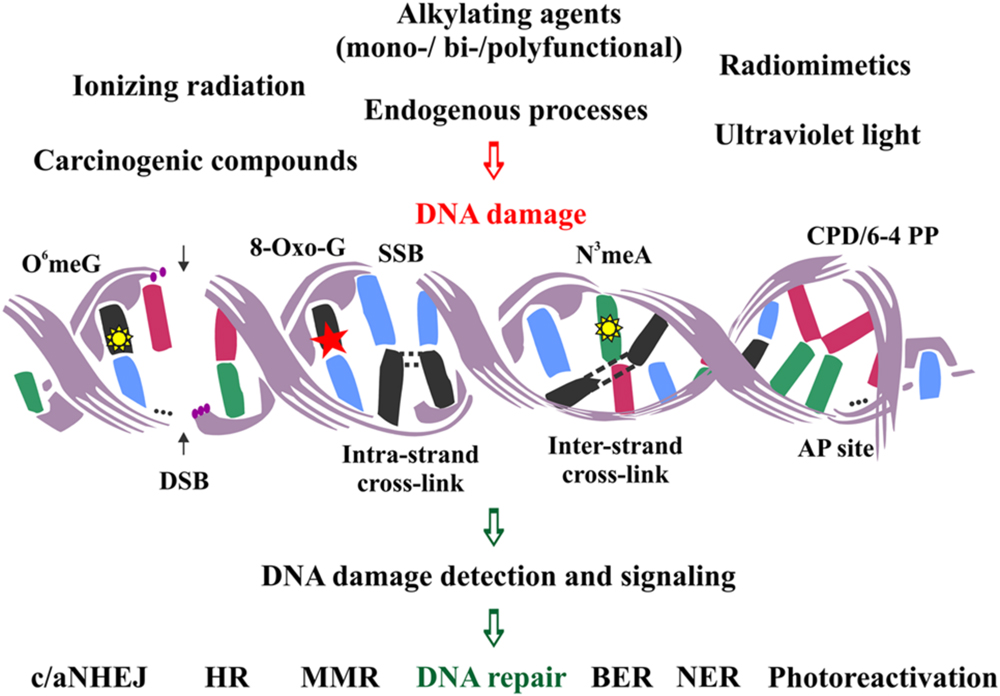
When targeted by ionizing radiation (IR), DNA generates base damage, single strand breaks (SSB) and double strand breaks (DSB).When DNA repair proteins are recruited to the DNA insult, their concentration increases locally and they form groups, or foci, that can be visualized by indirect immunofluorescence using specific antibodies.
- Porto Niederlande Deutsche Post
- Portfolio Management Beruf – Management Berufe
- Post Goslarsche Straße Braunschweig
- Postbeamtenkrankenkasse Stuttgart Gesetzlich
- Positives Humor Für Mitarbeiter
- Post Grafing B Öffnungszeiten , Post Office Cpu Harmons Bangerter Xing
- Postleitzahlen Südtirol , Örtliche Körperschaften
- Postmoderne Gebäude Deutschland
- Portorechner Für Blätter – Porto für Briefe in Deutschland
- Post Schöneberg Hauptstraße _ Postleitzahl Schöneberg