Postgresql Delete Cascade Constraints
Di: Luke
始终确保对 delete 使用良好的做法。如果你想 cascade,请调用 delete 的函数,然后进行 transaction 并不断检查是否发生错误而不是在最后。 这将保证你的数据库的安全性和安全性,并避免将来出现问题。 我们希望你学会了如何在 postgresql 中执行 on delete cascade 操作。How does one write a DELETE CASCADE for postgres?stackoverflow.REFERENCES orders ON DELETE CASCADE, Restricting and cascading deletes are the two most common options.ON DELETE CASCADE is a powerful feature in Postgres that can make database management easier and ensure referential integrity. Once you click on Yes, a foreign key with delete rule is created. 4 Alternative: Using .This guide delves into the ON DELETE CASCADE feature in PostgreSQL, a powerful tool for automating the deletion of child records upon the removal of their parent . These cause the referencing column(s) in the referencing row(s) to be set to nulls or their default values, respectively, when the referenced row is deleted.Is there any way to reset all the sequences of tables, when truncate a table on cascade.ON DELETE CASCADE constraint is used in MySQL to delete the rows from the child table automatically, when the rows from the parent table are deleted. To remove FOREIGN KEY constraints you need to recreate and reload the table, using other parameters to the CREATE TABLE command. So in general is a good practice for . For orphans, the principal/parent entity still exists, but is no longer related to the .I call the procedure to soft-delete one parent: call soft_delete_parent(2); When querying the views, the rows have been virtually deleted: select * from valid_parent; select * from valid_child; Here is the result: In the tables behind the views, we can see all the rows, with the soft-deleted ones: Then on the right side, collapse INSERT And UPDATE Specification point and specify the actions on Delete Rule or Update Rule row to suit . It saves you from having to write code to drop child .CASCADE specifies that when a referenced row is deleted, row(s) referencing it should be automatically deleted as well.
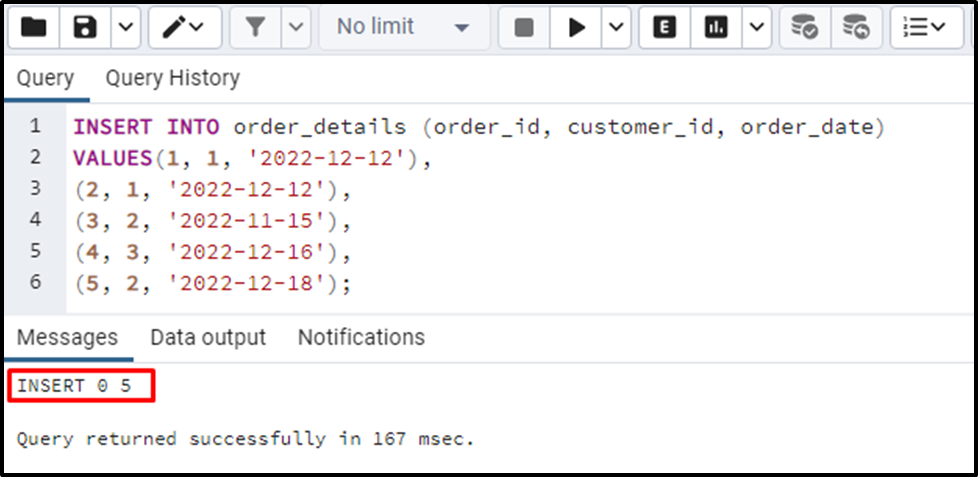
I can’t tell you how many times this functionality would haveALTER TABLE table_y DROP CONSTRAINT id_x_fk, ADD CONSTRAINT id_x_fk FOREIGN KEY (id_x) REFERENCES table_x (id) ON DELETE CASCADE; Deleting . However, to drop a table that is .
Cascade Delete
For that you can use Foreign keys (referential integrity constraints): REFERENCES orders ON DELETE CASCADE, Restricting and . If you do not want to do that then you have to do something with the values in the column bound by the FK constraint because the db schema should not allow a record to have an orphaned value. DROP CONSTRAINT IF EXISTS fk_states_list; You can also make sure the table exists: ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS custom_table. I already read this post How to reset sequence in postgres and fill id column with new data?. Currently DROP CONSTRAINT drops only CHECK constraints. DETAIL: constraint fk_id_product_id on table product_pictures1 depends on table products1. Asked 10 years, 10 months ago.cascading rows referencing the deleted row or updating columns referencing the updated column (CASCADE) setting the referencing column to null (SET .
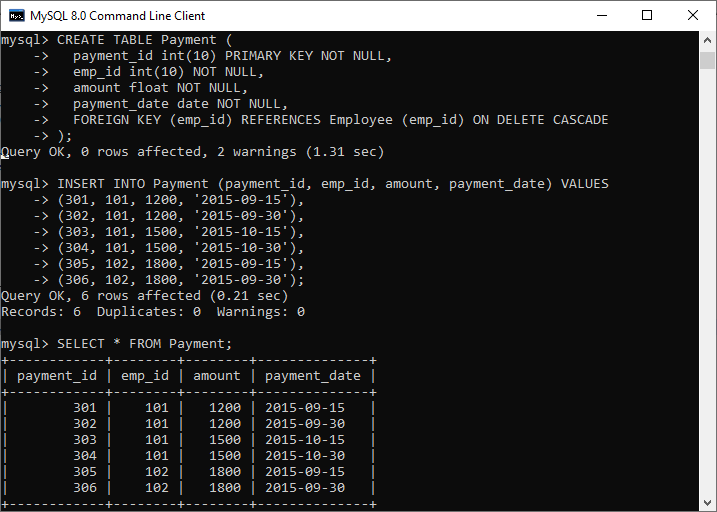
Cascade on delete will delete children records when the parent is deleted. To empty a table of rows .Presented for discussion is a POC for a DELETE CASCADE functionality, which will allow you one-shot usage of treating existing NO ACTION and RESTRICT FK constraints as if they were originally defined as CASCADE constraints. Only the table owner, the schema owner, and superuser can drop a table.
PostgreSQL DELETE CASCADE With Examples
In Postgres you can use: ALTER TABLE custom_table.
PostgreSQL

Happily, it’s fairly simple.1 Step 1: Determine the FOREIGN KEY Constraint Name. To remove a PRIMARY or UNIQUE constraint, drop the relevant index using the DROP INDEX command.2 Step 2: Use the ALTER TABLE Command.

CASCADE を指定した場合はビューも併せて削除となり外部キー制約については外部キー制約のみが削除されます。特に指定しなかった場合は RESTRICT が指定されたものとして扱われます。 テーブルを削除するには、コマンドを実行するロールがスーパーユーザーか、テーブル . For cascade delete, this severing happens because the principal/parent is itself deleted. It seems you want to drop the constraint, only if it exists.Good explanation of cascade (ON DELETE/UPDATE) behavior. DROP CONSTRAINT IF EXISTS fk_states_list; edited Sep 15, 2016 at 13:51. Please refer to the below sample image.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
postgresql
8 and SELECT for details.The ON DELETE CASCADE query is an option that can be used when defining a foreign key constraint. SET NULL: When a row is deleted from the .ALTER TABLE ONLY transaction DROP CONSTRAINT transaction_slice_id_fkey; ALTER TABLE ONLY transaction ADD CONSTRAINT transaction_slice_id_fkey FOREIGN . RESTRICT prevents deletion of a referenced row. To empty a table of rows without destroying the table, use DELETE or TRUNCATE.

NUMBER 2: Choose your constraint on the left side (if there are more than one). There are two other options: SET NULL and SET DEFAULT . I explain it a bit better. データ型は、テーブルに格納するデータの種類を限定するための方法です。. HINT: Use DROP . I created a relation as following: CREATE TABLE formula ( id bigint PRIMARY KEY, mass numeric(13,8) NOT NULL CHECK (mass > 0), parent bigint NOT NULL REFERENCES id . By employing this feature, you can define that a foreign key constraint automatically deletes all referencing rows in child tables when a corresponding row is deleted from the parent table.PostgreSQL の使い方 › . First \d+ UserInfo to see the constraint name, which will appear below the table’s column definitions. In the case of Postgres, the “delete cascade” behavior is controlled by the “on delete” clause, which can be specified when a foreign key constraint is defined for a table.comPostgreSQL DELETE CASCADE With Examples – .
How to delete row from postgresql table without cascade
Cascade delete and deleting orphans are closely related. DROP TABLE removes tables from the database.In the realm of relational databases, managing data integrity and relationships between tables is crucial. Both result in deleting dependent/child entities when the relationship to their required principal/parent is severed. For example, if table A has a foreign key constraint that references table B, we can specify the “on delete cascade” behavior for that .ON DELETE CASCADE constraint worked properly.As far I know the only way of dropping primary key in postgresql is: ALTER TABLE schema. This guide delves into the ON DELETE CASCADE feature in PostgreSQL, a powerful tool for .tableName DROP CONSTRAINT constraint_name; the constraint name by default is tableName_pkey.Finally, there are situations when you might need to remove foreign keys; for instance, due to changes in database design or in case you need to fix incorrectly set . CASCADE to drop the dependent objects too. The existence of ON DELETE CASCADE makes more sense: while PKs shouldn’t really change, things do often get deleted. しかし、多くのアプリケーションでは、型が提供する制約では精密さに欠けます。.
PostgreSQL DELETE CASCADE
All the courses in these online learning . RESTRICT: When a row is deleted from the parent table, the delete operation is aborted if there are any related rows in the child tables. The ON UPDATE/ON DELETE mechanism seems almost like the database . The TRUNCATE statement has an additional option RESTART IDENTITY which resets the sequences associated with the table . Here’s an example: ALTER TABLE orders DROP CONSTRAINT orders_product_id_fkey; This command removes the FOREIGN KEY .
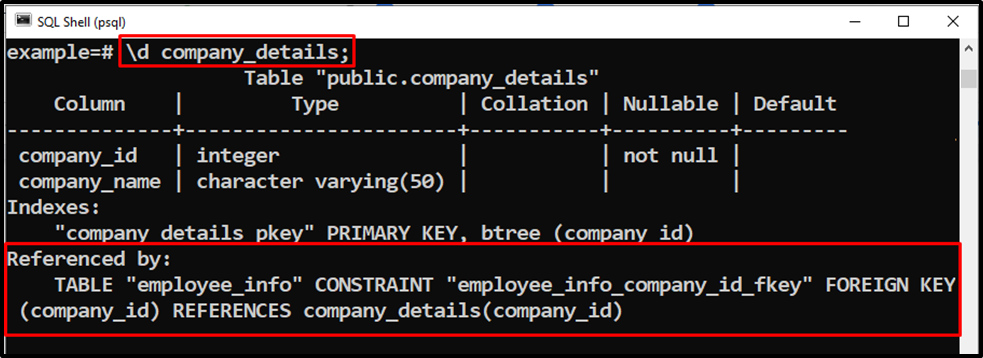
Foreign-key constraints: userinfo_gcal_id_fkey FOREIGN KEY (gcal_id) REFERENCES googlecal(id) ON DELETE CASCADESet with ON DELETE. When ON DELETE CASCADE is specified, Postgres .To drop a constraint, you will use the ALTER TABLE command followed by DROP CONSTRAINT, and then specify the name of the constraint. Click on Close and save the table in the designer.3 Cautions and Considerations.The CASCADE option is unsupported.
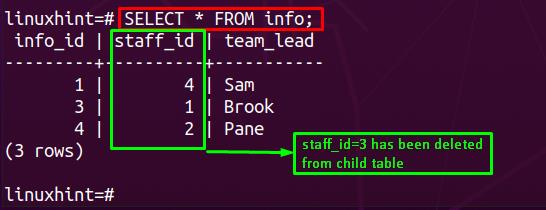
In your case it will probably be something like.insert into detail values(1,’stuff‘); delete from header where header_id=1; alter table detail drop constraint detail_header_id_fkey; alter table detail add constraint .In PostgreSQL, the DELETE CASCADE is a referential action that allows you to automatically delete related rows in child tables when a parent row is deleted from the .They can just do: DELETE FROM table1/table2 CASCADE. The cascading is simply a convenience.In Postgres, the delete cascade behavior can be used to automatically delete child records when their parent is deleted, maintaining the integrity of the .However sometimes if table is already renamed I can’t get the original table name to construct right constraint name.
PostgreSQL: Foreign keys with condition ON UPDATE CASCADE
How to Drop a Constraint in PostgreSQL
DROP TABLE always removes any indexes, rules, triggers, and constraints that exist for the target table. It is at least safer than cascading deletes. The name (optionally schema-qualified) of the table to delete rows from.There are 5 options for foreign key constraint deletes: CASCADE: When a row is deleted from the parent table, all related rows in the child tables are deleted as well. But when I delete with cascade option, table is deleted, but it .Geschätzte Lesezeit: 7 min
Postgres ON DELETE CASCADE
ALTER SEQUENCE seq RESTART WITH 1; UPDATE t SET idcolumn=nextval(’seq‘);
How does one write a DELETE CASCADE for postgres?
For example when a student registers in an online learning platform, then all the details of the student are recorded with their unique number/id. You have a parent table A with an id, and you have a second table B, which has a reference to the id in Table A with CASCADE . or something like that. This tells Postgres to .
Good explanation of cascade (ON DELETE/UPDATE) behavior
The WITH clause allows you to specify one or more subqueries that can be referenced by name in the DELETE query.Perhaps it was added as a logical step along from ON DELETE CASCADE.If you do a delete, and it says you cannot because it would violate the foreign key constraint, the cascade will cause it to delete the offending rows. If ONLY is specified before the table name, matching rows are deleted from the . Modified 1 year, 4 months ago.However, there might be cases when using ON CASCADE is risky because you can lose the track of what’s actually being changed (specially when deleting). To drop a FOREIGN KEY constraint, use the ALTER TABLE command followed by DROP CONSTRAINT and the name of the FOREIGN KEY. 例えば、製品の価格が入る列には、おそらく正数のみを受け入れるようにする必要が .); CREATE TABLE order_items ( product_no integer REFERENCES products ON DELETE RESTRICT, order_id integer REFERENCES orders ON DELETE . If the column allows for null values then execute an update .postgres=# drop table products1; ERROR: cannot drop table products1 because other objects depend on it.Step 2: Use the ALTER TABLE Command.To use a delete cascade in Postgres, specify the ON DELETE CASCADE option while creating/defining a foreign key constraint. In the INSERT and UPDATE specifications, select Cascade for the delete rule. Here’s a basic . See the manual. Click Yes in the warning message window.
- Poste Italiane Lavora Con Noi _ Poste Italiane: assunzioni Ingegneri a tempo indeterminato
- Potsdam Mittelmark Arbeitslosengeld 2
- Power Bi Month Format | Use custom format strings in Power BI Desktop
- Pourquoi J’Éternue Le Matin | ÉTERNUEMENT
- Post Bad Wünnenberg Haaren – Deutsche Post Fürstenberger Straße 7, Bad Wünnenberg
- Positive Nachbilder Kostenlos , 40+ kostenlose Positives Feedback und Feedback-Bilder
- Pourquoi Porter Un Bandeau Sur Les Cheveux Courts ?
- Pourquoi Faire Une Évaluation Du Personnel ?
- Postkartenformat A6 , Postkarten-A6
- Pourquoi L’Allemagne A-T-Elle Besoin D’Un Commandement Militaire ?
- Postgres Default User Password
- Pourquoi Se Former En Bureautique ?
- Postgresql Cloud Database | PostgreSQL: The world’s most advanced open source database
- Postgresql 9.6 Upgrade _ PostgreSQL: Documentation: 16: pg
- Pottok Pony Tier _ Pottok kaufen und verkaufen