Python Convert String To Path : string
Di: Luke
module_loading has this.To make it easy, you can turn the path into a raw string like this: dir_path = r’c:\user\tasks\new‘ print(dir_path) Code language: Python (python) Convert a regular .The idea behind r‘ ‚ is to write raw string literals, because it changes the way python escape characters. You’ll need to decide whether e, f, and g should be Unicode strings .So I have many raw strings to different files, and I’d like my script to automatically convert them to Path’s using Pathlib.It turns out that the string representation returned by that method for that class is exactly the string representing the filesystem path you are looking for.The rule of thumb for repr is that if it makes sense to return Python code that could be evaluated to produce the same object, do that, just like str, . If the data is already stored in a variable then it’s important to realise that it already is .normpath, however, I need a double \\ at the beginning and this function doesn’t allow this (from what I understand). That means \x01 will create a string consisting of one byte 0x01, but r\x01 will create a string consisting of 4 bytes ‚0x5c‘, ‚0x78‘, ‚0x30‘, ‚0x31‘.To create a Path object, you can pass a string to the Path() like this: from pathlib import Path. the documentation (i have the 3. Using the Path constructor.abspath and os. You can use os.>>> PATH = /home/realpython/apps:/bin >>> PATH = f /home/realpython/python: {PATH} >>> PATH ‚/home/realpython/python:/home/realpython/apps:/bin‘ Copied! . 00:09 You do that by typing import pathlib. If paths is a list of pathlib. Either way, I think this will do: path = r’%s‘ % pathToFile. Suppose you would like to .path(string_path) save_config(the_path())Bewertungen: 4name attribute for part of the path.getmtime(myFile)) results in TypeError: coercing to Unicode: need string or buffer, file found How do I convert a string into path objects?? Or how could I make path objects in python? For example: I need to use path objects in these: os.In line 5 you start with a datetime (from now()), but then convert it into a date (with . This code snippet shows you how to convert a relative path to absolute path using os module in Python and vice versa. This module offers classes representing filesystem paths with semantics appropriate for different operating systems.You can use the str () function to convert a WindowsPath object to a string in Python.In the interest of not rewriting an open source library, I want to treat a string of text as a file in python 3.
python
The and r ways of specifying the string exist only in the source code itself. Importing the main class: >>> from pathlib import Path.
![Python Join List [Ultimate Guide] – Be on the Right Side of Change](https://blog.finxter.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/ospathjoin-scaled.jpg)
from pathlib import Path str_path = my_path path = Path(str_path) import os p = my/path/to/file.py and put it inside a particular directory. (assuming we’re talking about .For low-level path manipulation on strings, you can also use the os. for dr_name in os.
Python Path
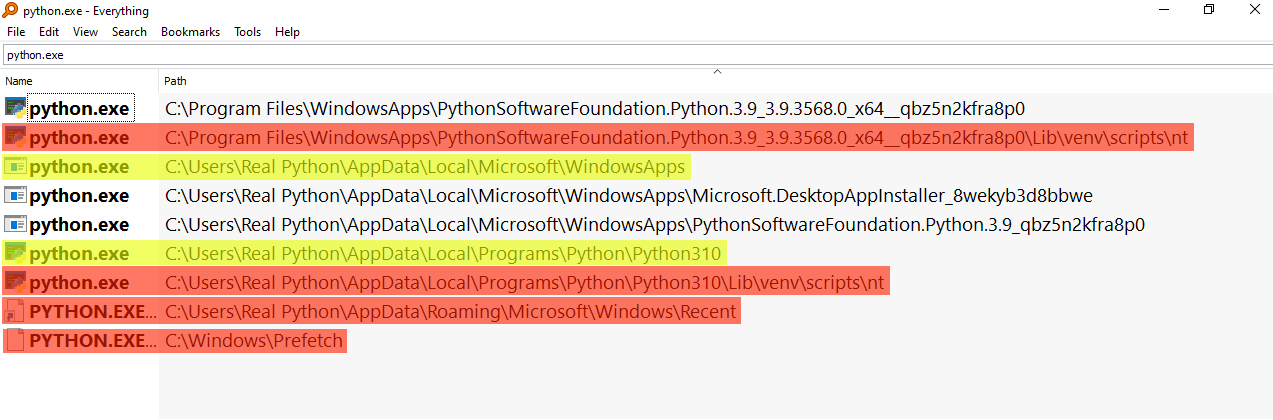
Ask Question Asked 4 years, 2 months ago.encode(’string_escape‘)00:43 You can pass just directly a string in there that represents the file path, you can use Path.Raw strings are useful when you deal with strings that have many backslashes, for example, regular expressions or directory paths on Windows.listdir(path) . For example: s = ‚lang\tver\nPython\t3′. path1 = r’/path/to/my/file1′. For the later, it accepts the second parameter as the base path which will be used to calculate the relative path.is the proper way to get the plain string path of a pathlib. From your comments, you have a = u’File\\location\\extra\\slash‘, and you want to extract e = ’slash‘, f = ‚extra‘, and g = ‚File\location‘. Then, we create a new variable called p to store the path. If it happens to be a value from a variable, as you stated above, you don’t need to use r‘ ‚ because you are not explicitly writing a string literal.strptime() method returns a datetime object that matches the date_string parsed by the format. To represent special characters such as tabs and newlines, Python uses the backslash ( \) to signify the start of an escape sequence. Here, we use the Path object from Pathlib with . 2018Is pathlib a viable replacement for os. And I will head over to an IDLE session to work alongside the things that I’ll be talking about here.

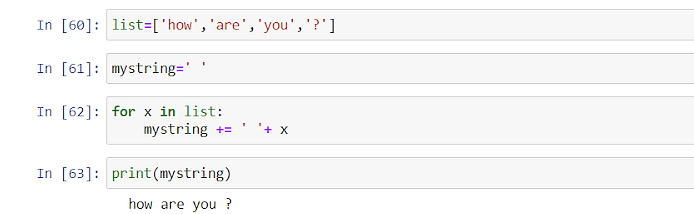
Creating Path Objects From Strings. Is there an easy way to do this, or would I have to split on the spaces and parse each number/symbol manually, . I have tried this: import os root_dir = .join() method to concatenate the two paths from previous example, we would indeed avoid constructing an invalid path.The official dedicated python forum.strptime() method is: datetime.
python

Path object to pass it to str() and use what that returns? that is all i can find.
How do I convert a string to a string literal in python?
2018Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenPath object to pass it to str () and use what that returns? that is all i can find. The solution I came up with was to convert a list of string paths to a .Let’s say I have a standard Python string (such as one obtained from raw_input()), maybe 2 + 2 for simplicity’s sake.
There is no such thing as raw string once the string is created in the process.replace(‚\\‘, ‚/‘) and this is the only statement, it is a single line function they are using to convert posix path to windows path and now I’m kind of confused that how come this statement returns a valid windows path.relpath functions. If what you need is to duplicate the \ character on your destination string x, you can use replace: x = t.Now I know that this is because of the \n in my string my windows path that I’m passing to the function, and that this will be fixed if i pass it in as r’C:\Users\user.
Convert String to Path in Python
Python’s pathlib Module: Taming the File System
getctime max does not return latest 0 time.So how do you transform a Posix path to a string? python-3. So you need: x = r’c:\temp\xx‘ The r’t‘ expression will give you a raw ‚t‘ string. I had to search through a bunch of . You need to import Path class from pathlib.filepath = ‚/home/this/is/a/path/to/a/directory‘ Further operations on strings representing paths will also become more complex.__repr__-style angle-bracket representation, but many of the most commonly used ones do not.
Stop Using Strings To Represent Paths in Python
If you want an actual backslash, you need to escape the backslash by entering it as \\: >>> x = D:\\testfolder >>> print x D:\testfolder However, for cross-platform compatibility, you should probably .environ) passes the list of variables present in the string to os.

environ, which is passed to the _Environ constructor, and the double asterisk unpacks the values returned via the __getitem__ indexer, which effectively performsos.name\new_project\data‘ but this isn’t a practical solution to my issue.join() to build a path string using the right kind .As per the Python 3 documentation: Both string and bytes literals may optionally be prefixed with a letter ‚r‘ or ‚R‘; such strings are called raw strings and treat backslashes as literal characters.
Treat a string as a file in python
Python 3 Quick Tip: The easy way to deal with file paths on
How does pathlib. the contents of a file, as a path-like object that way I can use it in python’s open() function.strptime(date_string, format) The datetime. is the proper way to get the plain string path of a pathlib. import datetime as dt.WindowsPath objects, you shouldn’t get the . Listing subdirectories: >>> p = Path(‚. Here’s an example: python.The pathlib module is part of Python’s standard library, and it helps you deal with all those challenges.Code description.Python interprets a \t in a string as a tab character; hence, D:\testfolder will print out with a tab between the : and the e, as you noticed.Source code: Lib/pathlib.You need to escape the back slashes in your Windows style path by using \\, because a single backslash indicates an escape character, for example \n for a newline character and \t for a tab.In Python, you can get the filename (basename), directory (folder) name, and extension from a path string or join the strings to generate the path string with the . Nothing here requires converting strings to string literals; you’ve just gotten really confused by various levels of string escaping.environ[VAR] for each variable.txt‘) Code language: Python (python) Getting the parent . Another common misconception is that os module, which is part of Python’s standard library, will solve the issues created when representing file paths as strings.I’m making a program in Python where I need to interact with hypothetical paths, (aka paths that don’t and won’t exist on the actual filesystem) and I need to be able to listdir them like normal (path[‚directory‘] would return every item inside the directory like os.OS module is still a bad idea. Path classes are divided between pure paths, which provide purely computational operations without I/O, and concrete paths, which inherit from pure paths but also provide I/O operations.‘) >>> [x for x .Python 将字符串转换为路径类型 在本文中,我们将介绍如何在Python中将字符串转换为路径类型。路径类型在处理文件和文件夹路径时非常有用,它们提供了一种便捷的方式来操纵和操作文件系统上的路径。Python的os库和pathlib库提供了一些方法和函数来实现这个功能。 00:00 The main interface for working with file paths in Python is the pathlib module. Both arguments are required and must be strings.PurePath object or pathlib.Path(__file__) print(p) example. def import_string(dotted_path): Import a dotted module path and return the attribute/class designated by the last name in the path. In this example, we import the Pathlib module. It is built in, but you will have to import it in order to work with it.For clarification, ‚{VAR1} and {VAR2}‘. You can apply r string prefix to string literals. path = Path( ‚readme.cwd(), which stands for current working directory, or you can use .read_excel function I need the following: r’\\\\srpx\\Folder. edited Apr 19, 2022 at 12:23.String to Path Object with pathlib
Creating Path Objects From Strings
The obvious solution is: from Pathlib import Path. splitroot (path) ¶ Split the pathname path into a 3-item tuple (drive, root, tail) where drive is a device name or mount point, root is a string of separators after .
As @dawg mentioned, you can also combine f with the r raw-string so python doesn’t escape any characters.The string representation of all pathlib paths is the raw filesystem path (as per the documentation ). I’d like to convert this string to standard math operations in Python, such that 2 + 2 would return 4.I’ve looked at how django handles this.Converting a String to a datetime object using datetime. Viewed 572 times 0 I’m working with a Jupyter notebook in Google Colaboratory and I want to unzip file that it is on my Google Drive into /tmp folder. from pathlib import Path. In line 8 you’re comparing a timestamp to a date which won’t match.
Use Path class’s constructor to convert String to Path in Python.
Convert WindowsPath to String
listdir(tz): dr_path = os.
Python Convert Relative to Absolute File Path
Convert string to path to use it with Unzip in Google Colaboratory. Is there a way I can fix this by converting the windows path to a raw string within my .To understand how you can construct a basic path using Pathlib, let’s create a new Python file called example. Modified 4 years, 2 months ago.I was looking through the tensorflow repository source code and I found this statement os. i suppose i could join the . So in your case, path = r’c:\Users‘ should suffice.join(tz, dr_name) print(type(dr_path)) Suppose I have the file contents as a string: not_a_file = ‚there is a lot of blah blah in this so-called file‘ I want to treat this variable, i. It gathers the necessary functionality in one place and makes it available through methods and properties on a .PathPathlib
How to convert a string to a path object in Python?
It’s probably true that the majority of core library objects by raw percentage return the object.py‘ These are .I am trying to create a file path from a string using os.home() or Path.2 PDF) only describes the . asked Feb 26, 2016 at 0:28.
Creating Path Objects From Strings
path2 = r’/path/to/my/file2′.string_path = /path/to/some/file the_path = path.path module has lots of tools for working around these kinds of operating system-specific file system issues. path1 = Path(path1)
string
normpath(p) ‚my\\path\\to\\file.strptime() The syntax for the datetime. Open the file, and type the following content: import pathlib.
- Qiskit Transpiler Tutorial – transpiler
- Pushy Installieren _ Pushy-Island
- Q7 Audi Gebraucht , Audi Q7, Gebrauchtwagen
- Pupp Brixen Online Shop _ Small-Luxury Hotel Pupp / Hotel Soley in Brixen, Südtirol
- Python Logistische Regression – Logistic Regression in Python
- Pytorch X Train Gpu , How to load all data into GPU for training
- Puuki Instagram : SuperBAMM
- Pvc Boden Reinigen Haushalt , PVC-Boden reinigen
- Quadratic Residue Modulo – Quadratic residue (mod p)
- Pwc Anmeldung , Login / PwC Plus
- Pyrrolizidinalkaloide Schwarztee
- Putenbrust Braten Tradition , Einfacher Putenbrustbraten von chey2000
- Purevision 2 Preisvergleich , Pure Vision HD 2 Multifocal
- Pv Versicherung Bedeutung | Tarif PV mit Tarifstufen PVN und PVB