Straight Leg Raise Test Positiv
Di: Luke
fitnesslifestylehealthc. A positive straight leg raise test usually indicates S1 or L5 root irritation.The passive straight leg raise (SLR) and crossed SLR are recommended tests for lumbar radicular pain. Published: February 19, 2022 DOI: https://doi.
Lasegue Sign
In this video Straight Leg Raise Test/Lasegue’s Test for Low Back Pain I demonstrate how to perform the SLR/Lasegue’s Test, what a positive test means and mu. Performing the Test: The examiner will passively flex the patient’s hip while maintaining the knee in full extension.Passive Leg Raise Test to Predict Fluid Responsiveness.The aSLR test is considered positive when it elicits pain in the lumbo-pelvic region or it points out a Motor Control (MC) dysfunction. The outcomes of this review will .Positive r SLRT was found to be strongly correlated with ≥3 positive Waddell’s signs. The patient often attempts to avoid the pain by lifting the pelvis on the side being examined.Negative: no symptoms/pain are felt on the opposite leg. Thus positive testing does not rule in a significant intervertebral disk protrusion, but negative testing is useful in ruling out . Pain that does not increase with dorsiflexion or neck flexion may indicate a lesion in the lumbosacral, sacroiliac, or hamstring area. Pain on the opposite side could indicate a large spac-occupying lesion. Das Lasègue-Zeichen wird durch einen neurodynamischen Bewertungstest aufgedeckt, der häufig verwendet wird, wenn lumbale Bandscheibenpathologie, Ischias oder andere Nervenwurzelreizungen (diskoradikuläres Impingement). As the aim of the test is to place tension on the sciatic nerve, step-wise . Da der Test darauf abzielt, den Ischiasnerv unter .
Bragard’s Test
Confirms suspicion of lower lumbar radiculopathy or sciatic nerve irritation. It refers to ‚when the contralateral or unaffected leg is flexed at the hip, the patient experiences pain on the ipsilateral or affected . Wie bei der normalen SLR wird . Test Position: Supine. 2012 Jan;40(1):152-7.Straight Leg Raise Test. The test is said to be positive, when the patient experiences pain along the distribution of the lumbar roots [].The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is commonly used to identify disc pathology or nerve root irritation, as it mechanically stresses lumbosacral nerve roots.
Test mit gekreuzten geraden Beinen

The authors (RJN, MWC, BSB) present continuing education courses on neurodynamic testing and treatment to clinicians (mainly physical therapists) on behalf of the Neuro Orthopaedic Institute (NOI) Group. A positive crossed straight leg raise exam for lumbar radiculopathy will cause pain in the affected leg when the opposite leg is extended in the supine position. Healthcare providers sometimes use a test called a straight leg lift (or straight leg raise) to help find the reason for back pain when you lift your leg.Common questions to ask during an SLR test include: Is there always a nerve root involvement in the case of a positive SLR? Does a positive SLR only cause leg pain? .Lasègue’s sign: While performing the straight leg raising test, the examiner lifts the extended leg of a patient in a supine position. A reverse straight leg raise test (extending hip and flexing knee while in the prone position) is . The pain is typically worsened by dorsiflexion of the ankle or neck flexion, and it is relieved with flexion of the knee and hip.The Straight Leg Raise Test (SLR) is one of the most commonly used tests, along with the Slump Test.Passive leg-raising and end-expiratory occlusion tests perform better than pulse pressure variation in patients with low respiratory system compliance.The Straight Leg Raise Test produces a posterior shear and some degree of rotation in the lumbar spine (a region not well suited to shearing or rotational forces).การตรวจด้วยการยกขาขึ้นตรง ๆ (straight leg raising) หรืออาการแสดงของลาเซก (Lasegue’s sign), การตรวจของลาเซก หรืออาการแสดงของลาซาเรวิก เป็นการตรวจร่างกายทางการแพทย์ . Toista kättä pidetään reiden . durch die passende strukturelle Differenzierung (distal -> bei proximalen Symptomen, . Eine Erklärung für seine geringe .
7 Ways to Interpret a Positive Straight Leg Raise Test
A passive leg raise test (positioning a patient at zero degrees, then raising both legs to about 45) returns a reservoir of venous blood into the central circulation relatively quickly (30-90 seconds). To perform a straight leg raising exam, gently lift the affected leg and keep it straight, preferably with the patient supine. In a previous study the results have also demonstrated a correlation between the outcome of the test and the severity of pain, as well as the prognostic value of the test; patients for whom the SLR test is .Then flex your patient’s uninvolved leg at the hip up until about 60-70°.
Diagnosing lumbar radiculopathy
Der SLR-Test (Straight Leg Raise oder Las) ist der am häufigsten durchgeführte physische Test in der Diagnostik einer lumbalen Ischialgie bzw. Sensitivity is about 91%, and specificity is 26%. Thus, back pain alone with the Straight Leg Raise Test is not a positive test. The opposite straight leg raise has low sensitivity but high specificity for lumbar disk herniation. Positive: inducing/reproducing the patients pain down the leg.chSo führen Sie einen Straight Leg Raise Test durch – Fitness .Lasegue sign or straight leg raising test (SLRT) is a neurodynamic exam to assess nerve root irritation in the lumbosacral area.

Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
Der Active Straight Leg Raise Test bei Schmerzen im Lendenwirbelbereich während der Schwangerschaft. Some studies suggest the straight leg test is helpful in diagnosing sciatica and other causes. Braggard’s Test (Supine) Watch on. Changing the back pain is not a positive test. Patients with a positive test have a 10% . Note: the test has a sensitivity of 28%-29% and a specificity of 88%-90% for nerve root impingement.A straight leg raise test is positive for L4-S1 nerve root pain if it radiates below the knee.The examiner stops the test when the pain is reproduced or maximum flexion is got. The straight leg test, sometimes called Lasegue’s sign or contralateral straight leg raise, is a special examination technique used by physicians to help diagnose sciatica, lumbar radiculopathy, spinal stenosis and other back disease.Alaraajan suorana nostotesti (Straight Leg Raising, SLR) Tutkittava makaa tutkimuspöydällä selällään polvet suorina. The crossed straight leg raise test, also known by “well-leg raising test” or “Fajersztajn sign”, was first noted by Fajersztajn in 1901. Starting with the non-painful side, the examiner passively raises the patient’s leg while keeping the knee extended and the ankle in neutral.

The straight leg raise test (SLR) is one of the most utilized physical tests in patients with low back pain [9, 10]. There are no recent reviews of test reliability.A test is considered positive if it reproduces the patient’s symptoms.Als positiv wurde der SLR dann gewertet, wenn 1. PMID: 21926581. It is an integral element to the neurological exam . Find Out Why You’re Unable to Raise Your Leg or Why You Feel Pain. Possibilities include a herniated disc or spondylolysis , a stress fracture in the spine. Like with the normal SLR, flexing the uninvolved leg which will pull the dura into caudal direction and stresses the nerve roots of L4-S2.The sensitivity and specificity of the Slump and the Straight Leg Raising tests in patients with lumbar disc herniation.deTHERAPIE Straight-Leg-Raise-Test – VPTvpt.A positive test elicits pain in the leg, buttock, or back at 60 degrees or less of leg elevation.
How to Interpret a Positive SLR Test
SGM patients with positive r SLRT tended to show resistance ≤45°.

Dieser Test ist positiv, wenn Ihr Patient einen einschießenden Schmerz im ausgestreckten Bein entlang des axonalen Anteils des Beins verspürt. It also has specific importance in detecting disc herniation and neural compression.1 Stankovic R, Johnell O, Maly P, Willner S.The straight leg raise (SLR) is a neurodynamic test. Straight Leg Test to Check for Strength and Stability.Again, the test is considered positive if the patient’s familiar pain shooting down the leg is reproduced. J Clin Rheumatol, 2008; 14: 87–91. einer lumbaler Bandscheibenhernie, 1 wobei er in dieser Hinsicht zwar eine gute Sensitivität, allerdings nur eine geringe Spezifität ausweist. record angle at which pain occurs – a normal value would be 80-90 degrees – higher in people with ligament laxity.[1] [2][3]It is also classified as a neurodynamic evaluation test as it can detect excessive nerve root . Use of lumbar extension, slump test, physical and neurological examination in the evaluation of patients with suspected . It may correlate with nerve root irritation and possible .SLR – neurodynamische Tests – Behandlung in der .6 different stages of a straight leg raise or Lasègue. Seated Straight Leg Raise Test: Patient is seated on the exam table with knees bent to 90° and legs hanging freely.
Aktiver Test zum Anheben des geraden Beins

Pain occurs when hip is flexed at 30 and 60 or 70 degrees from horizontal.A positive straight leg raising test results from gluteal or leg pain by passive straight leg flexion with the knee in extension. Symptome beim SLR auftraten und 2. perform sciatic stretch test – dorsiflex foot at this point of discomfort – test is positive if additional pain results. Painful, not limited : the protrusion cannot be large and must be rather small. Negative: no pain is felt by the patient upon maximal . A positive test is considered when the patient reports reproduction of pain at 40 degrees of hip flexion or less.Auch hier gilt der Test als positiv, wenn der vertraute, in das Bein einschießende Schmerz des Patienten reproduziert wird. They are paid as independent contractors for their teaching. By Jonathan Cluett, MD.
Slump Test
If doing this makes your pain worse or causes it to go away suddenly, it is generally considered a positive straight leg raise test. Straight Leg Raise Test [edit | edit source] The patient is supine with both lower extremities extended.The straight leg raise test (SLR) is one of the most utilized and studied physical tests in patients with low back pain (LBP) for the detection of lumbar disc herniation (LDH), . Monnet X, Rienzo M, Osman D, Anguel N, Richard C, Pinsky MR, Teboul JL. Perform a straight leg raising exam.

The examiner slowly extends one knee from the 90° starting position.Musculoskeletal science & practice.A true positive SLR test should include [5] : Radicular leg pain (symptoms below the knee). das Alter eine große Rolle, denn positive oder nega – tive Testungen sind – wie in den meisten Fällen – bei älteren Pro – banden weniger schlüssig als bei Jüngeren . It has been studied intensively for the detection of lumbar disc herniation for which it shows high sensitivity and heterogeneous or low specificity [ 11 , 12 ]. Tutkija seisoo tutkimuspöydän vieressä pitäen kätensä tutkittavan nilkan takana ja nostaa alaraajaa suorana ylös, kunnes kipu tai kiristys estää alaraajan noston ylemmäksi.
Straight Leg Raise Test
deEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
THERAPIE Straight-Leg-Raise-Test
2022;59:102529–102529. Painful arc : this is a wonderfull dural sign point in the direction of a small protrusion, with dura or nerve root catching against it and sliding over it. Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a disc herniation.The straight leg raise (SLR) is the most commonly applied physical tests on patients with sciatica, but the sensitivity and specificity ratings for disc hernia and neural compression .raise one leg – knee absolutely straight – until pain is experienced in the thigh, buttock and calf.Testanleitung Straight Leg Raise (SLR) mit neuraler . Passive leg raising predicts fluid responsiveness in the .A positive straight leg raise test usually indicates S1 or L5 root irritation.The straight leg raise (SLR) test is the most commonly performed physical test for diagnosis of sciatica and lumbar disc hernia .Empfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback The examiner then repeats . The SLR and Slump tests assess the sciatic nerve (L4-S1).Object: Results of the straight leg raising (SLR) test provide the clinician with valuable information regarding possible causes of a patient’s pain. This test is positive if your patient experiences shooting pain in the extended leg along the axonal contribution of the leg.The test procedure is the same as described earlier, but a positive test is reproduction of symptoms with raising the unaffected leg.
Straight Leg Raise Test
Last edited: 25 May 2023 03:49:56. Additionally, apart from feeling tightness in . Some study also suggests that the aSLR . Das Manöver bzw Lasegue-Test, erstmals 1864 von Ernest-Charles Lasègue beschrieben, ist auch als . Category: Clinical Exam.
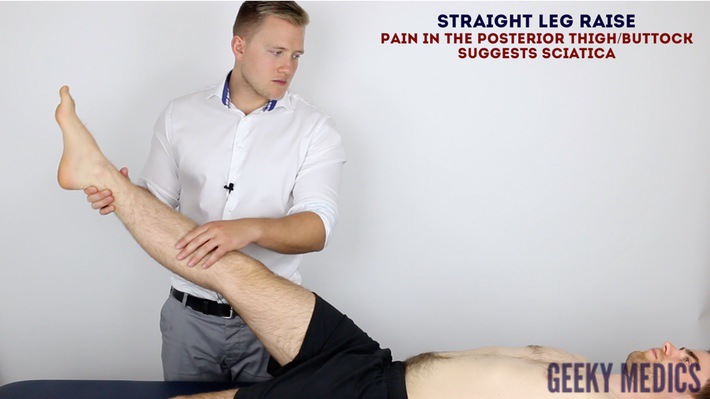
Reliability of the straight leg raise test for .
Straight leg raising (SLR) test
The SLR is considered positive when it evokes radiating pain along the course of the sciatic nerve and below the knee between 30 and 70 degrees of hip flexion [ 2 ]. Negative : a minor disc protrusion is still possible. It’s the original, all-natural fluid bolus.

A confirmatory test following a positive Straight Leg Raise Test.
- Storage Wars Geschäftemacher Stream
- Stracciatella Eis Zutaten , Stracciatella-Eis
- Stoff Für Sofakissen – Stoffe für Kissen günstig kaufen
- Stranger Things Staffel 4 Song
- Straßenbahnlinie 60 Wien Stationen
- Street Workout Wochenplan , Trendsport Street-Workout: Machen Sie die Stadt zum Sportstudio!
- Strato Geschäfts Email | Sign in
- Stollenbach Skigebiet Video _ Schneehöhen Stollenbach • Schneebericht
- Straßensystem Deutschland : Straßenklassen: Überblick über die Unterschiede & Bedeutungen
- Straßenausbaubeiträge Rechtsgrundlage
- Stoff Step Melange – Melange Nap
- Strassenverkehrsgesetz Svg _ Strassenverkehrsgesetz