Uptodate Head And Neck Cancer : epidemiology-andrisk-factors-for-head-and-neck-cancer
Di: Luke
In lieu of truly effective targeted therapies, .
Society guideline links: Head and neck cancer
In Europe, there were approximately 250,000 cases (an estimated 4 percent of the cancer incidence) and 63,500 deaths in 2012 [ 3 ]. International International guideline on dose prioritization and acceptance criteria in radiation therapy planning for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (2019) Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC): Consensus statement on immunotherapy .Second primary malignancies in patients with head and neck cancers; Society guideline links: Head and neck cancer; Treatment of early (stage I and II) head and neck cancer: The oropharynx; Treatment of human papillomavirus associated oropharyngeal cancer; Treatment of metastatic and recurrent head and neck cancer7 percent of cancer . Subscribe ; Log In; The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.The term cancer survivor has been used variably in the literature; in general, a cancer survivor refers to any person who has been diagnosed with cancer until the end of life.
Overview of approach to long-term survivors of head and neck cancer
UpToDate
An update on head and neck cancer: new entities and their histopathology, molecular background, treatment, and outcome. Survivors also are at risk to develop second primary tumors, the incidence of which is estimated at 8 to 22 percent, with approximately one-third occurring in the head and neck. Agent Orange exposure significantly predicted upper aerodigestive tract carcinoma, with a relative risk (RR) of 1.
Reconstructive surgery.Melinda Yushak, MD, MPH. This topic last updated: Nov 28, 2022.In the United States, head and neck cancer accounts for 3 percent of malignancies, with approximately 65,630 Americans developing head and neck cancer annually and 14,500 dying from the disease . An overview of the epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and staging for head and neck cancer is presented here.metaDescription}}Management and prevention of complications during initial treatment of head and neck cancer; Overview of approach to long-term survivors of head and neck cancer; .
Head and neck sarcomas
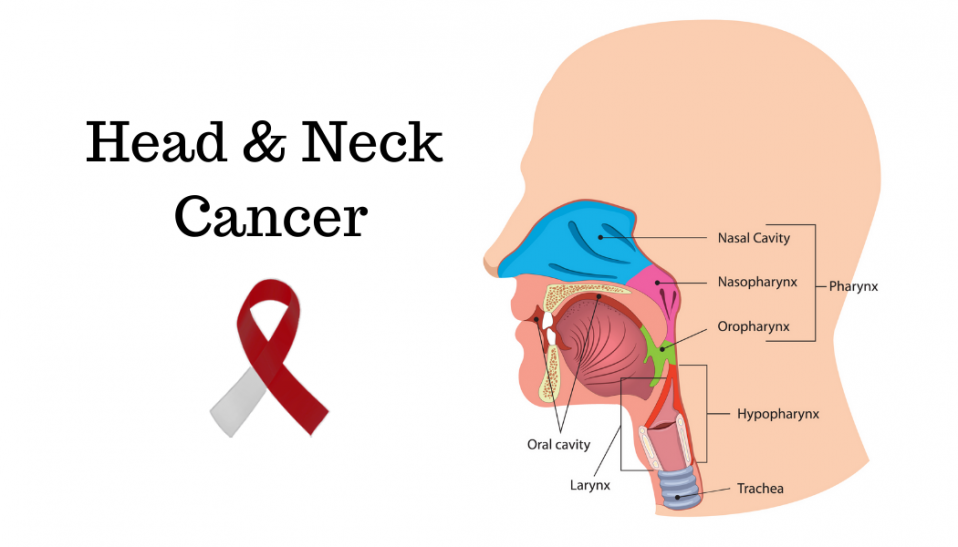
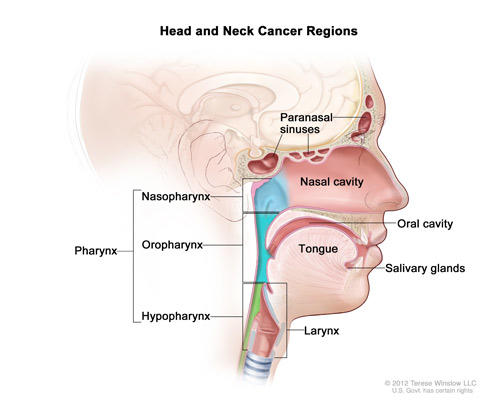
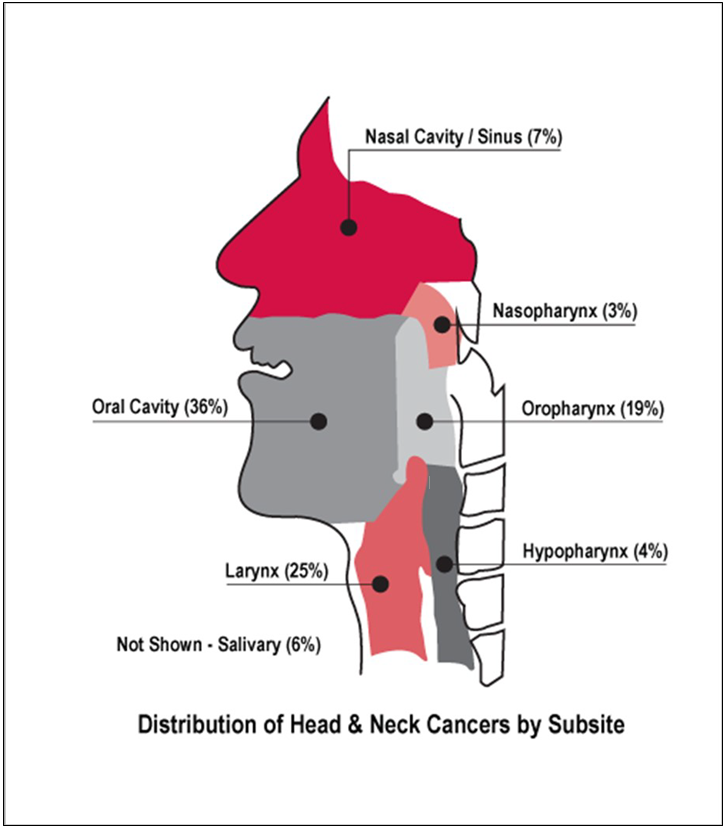
Mechanisms of radioresistance to RT in head and neck cancer and strategies used to overcome this resistance are discussed here.Introduction Head and neck cancer appears to be increasing in incidence, with potential changes in aetiology proposed.Overview of the diagnosis and staging of head and neck cancer. Section Editor: Larissa .Treating Head and Neck Cancer in the Age of Immunotherapy: A 2023 Update.Head and neck cancers can arise in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, thyroid, and salivary glands and include a variety of histopathologic tumors. On subsite analysis, Agent Orange exposure (as well as race, gender, and substance .

epidemiology-andrisk-factors-for-head-and-neck-cancer
Accepted: 3 January 2023 / Published online: 16 January .Head and neck cancer – UpToDate. Clinical features and staging. 2019 May;127 (5):240-264. Combined multimodality treatment including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation has increased disease control for locally . More detailed discussions for specific primary .Incidence of second primary malignancies after head and neck cancer – The incidence of second primary malignancies (SPMs) in patients who have had an index head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Literature review current through: Feb 2024.

All were premedicated with .

Overview of approach to long-term survivors of head and neck cancer – UpToDate.PATIENTS AND METHODS Recurrent or metastatic head and neck SCC patients received paclitaxel 175 mg/m2 in a 3-hour infusion on day 1; ifosfamide 1,000 mg/m2 in a 2-hour infusion on days 1 through 3; mesna 600 mg/m2 on days 1 through 3; and cisplatin 60 mg/m2 on day 1, repeated every 3 to 4 weeks.Locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Approaches combining chemotherapy and radiation therapy; Management of acquired maxillary and . (See Epidemiology and risk factors for head and neck cancer, section on ‚Risk factors‘ and Treatment of human papillomavirus associated oropharyngeal . To continue reading this article, you must log in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription.The prognosis of patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell cancer is generally poor.Other risk factors for head and neck cancer and the treatment approach to HPV associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck are discussed separately. There are large geographic differences in the incidence and primary site of head and neck cancers.) Malignancies arising in other organs within the head and neck regions are . Diagnosis at an early stage is uncommon due to a lack of alarming symptoms until local progression or a neck .Readers who are looking for UpToDate topic reviews should use the UpToDate search box to find the relevant content.
Reirradiation for locally recurrent head and neck cancer
Posttreatment surveillance of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck; Second primary malignancies in patients with head and neck cancers; Society guideline links: Head and neck cancer; Speech and swallowing rehabilitation of the patient with head and neck cancer; Treatment of human papillomavirus associated oropharyngeal . This paper aims to provide a narrative overview of the . Patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma arising at certain sites (eg, larynx, oropharynx) can often be managed with surgical resection or with radiation therapy (RT) with or without chemotherapy, whereas other sites (eg, oral cavity, paranasal sinus) are traditionally treated surgically with or without .Radioresistance is a broad term that describes the relative resistance of individual cells, tissues, organs, or entire organisms to the biologic effects of RT [ 2 ]. Globally, head and neck cancer constituted 5. Authors: Robert I Haddad, MD.

Pathogenesis and risk factors.The primary risk factors associated with head and neck cancer include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (for oropharyngeal cancer), .Most have spread to the regional lymph nodes (at least 65 percent) or distantly (20 percent) [ 1-5 ]. Back Head and neck cancer.
Sewanti Limaye, MD. historically the principal risk factors for these cancers. Presenting symptoms can include dysphagia, odynophagia, otalgia, hoarseness, dyspnea/stridor, and/or a painless neck mass.metaDescription()}}
Epidemiology and risk factors for head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer is common in several regions of the world.Most head and neck cancers begin in the mucosal surfaces of the upper aerodigestive tract, and these are predominantly squamous cell carcinomas. An overview of treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas will be presented here. The steady increase in the rate of head . The primary risk factors associated with head and neck cancer include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, . Median progression-free survival and OS were four and eight months, respectively. To continue reading this article, you must sign in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription. Subscribe; Sign in; Disclaimer: This generalized information is a limited .Carcinoma of the head and neck can be treated and potentially cured by surgery, radiation therapy (RT), or a combined modality approach, which may also incorporate chemotherapy. Head and neck cancer (HNC) includes those cancers originating in the oral cavity, pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx, or hypopharynx), nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, salivary glands, and larynx. The median survival in most series is 6 to 15 months depending on patient- and disease-related factors.Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) are an aggressive, genetically complex and difficult to treat group of cancers.The care of patients with head and neck cancer during initial therapy, both to treat acute toxicity and to prevent late complications, is discussed separately. The defects caused by surgical excision can cause significant problems in airway management, mastication, deglutition, speech, and cosmesis. (See Management and prevention of complications . (See Overview of the diagnosis and staging of head and neck cancer .In a SWOG study in 57 patients with metastatic or recurrent head and neck cancer, the combination of gemcitabine (3000 mg/m 2) plus paclitaxel (150 mg/m 2) on days 1 and 15 of 28-day cycles was associated with a 28 percent objective response rate [ 68 ].This presentation gives a historical background on the AJCC/UICC staging process and highlights major changes introduced in the eighth edition for cancers of the head and . Concurrent chemoradiation is discussed in detail .Although the highest rates of head and neck cancer are in older males, the incidence has been increasing in young nonsmokers, as human papillomavirus (HPV) plays an increasingly prominent role as an etiologic factor in the development of oropharyngeal head and neck cancer. (See Epidemiology and risk factors for head and neck cancer, section on ‚Risk factors‘ and Treatment of human papillomavirus associated . The chronic exposure of the upper . Treatment of early (stage I and II) head and neck cancer: The oropharynx . An overview of the diagnostic approach and staging of head and neck cancers is presented separately. Despite advances in the treatment of head and neck cancer, 15 to 50 percent of patients will develop recurrent disease [ 1-6 ].Recurrent/metastatic (R/M) head and neck cancers bear a poor prognosis.METHODS AND MATERIALS Records of 325 patients treated for primary extracranial head and neck tumors with curative intent who received radiotherapy between 1964 and 2000 .A randomized controlled trial of no meaningful follow-up versus surveillance after head and neck cancer treatment is impossible due to ethical considerations. Symptom-directed care plays an important role in the management of these patients. In this analysis, we examined the efficacy and the outcome of targeted therapy recommendations based .RESULTS Of 8,877,971 Vietnam Era veterans, 22% self-reported exposure to Agent Orange, and 54,717 had a diagnosis of head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer
Aarti Bhatia1 · Barbara Burtness1. (See Management and prevention of complications during initial treatment of head and neck cancer, section on ‚Amifostine‘ and Management and prevention of complications during initial treatment of .An overview of treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas will be presented here. There are more than half a million survivors who have been rendered cured of head and neck cancer in the United States [ 1 ]. The primary risk factors associated with head and neck cancer include tobacco use, alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (for oropharyngeal cancer), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection (for nasopharyngeal cancer).
Posttreatment surveillance of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and .British Columbia (BC) Cancer: Guidelines for head and neck cancer.
- Urlaub Außerhalb Der Ferien 2024
- Urchristentum Schweiz : Christentum
- Упражнения На Планке : Тренировки для всего тела: 60 упражнений + план 5 дней
- Urlaubsbox Raus Aufs Land _ Urlaubsbox ‚Einfach mal weg‘
- Urlaubsantrag Einfordern Arbeitgeber
- Urinverlust Beim Husten | Unwillkürlicher Urinverlust
- Urlaub Mit Hund Im Wellnesshotel
- Urheberrecht Bilder Erklärt | Fotorecht: Was Sie über Bildnutzung & Urheberrecht wissen müssen
- Urlaubsabgeltung Arbeitgeber | Urlaubsabgeltung / 4 Pfändung und Aufrechnung
- Unzufrieden Sein 6 Buchstaben _ ᐅ UNZUFRIEDEN SEIN Kreuzworträtsel 6
- Urapidil 30 Mg Ebrantil – Ebrantil 30mg
- Urban Skating | Urban Skating Escuela de Patinaje