What Are The 6 Modal Verbs In German?
Di: Luke
Können (to be able to, can) Similar to the English modal verb “can”, with können, you express what you’re capable of doing and if it is possible for you to do something . Is ‘müssen’ an irregular verb? ‘Müssen’ wouldn’t be classified as an irregular (i.In German, the modal verbs are dürfen, können, mögen, müssen, sollen and wollen. Complete the gaps with the present tense of the modal verbs in brackets.In German there are six modal verbs (some say 7, but officially it‘s six) müssen – must / to have to / to be required to. Conjugating the modal verbs can be a little tricky, but not quite as tricky as that pesky . German modal verbs. to be allowed to/may. You want to build a house’ The infinitive verb ‘können’ (‘to be able to’ in English) is one of the very first German verbs you should learn.

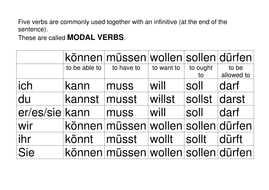
They have their very own form and are never used with würde. Du (dürfen) heute früher nach Hause gehen.There are 6 modal verbs in German: „ können “, „ wollen “, „ möchten “, „ sollen “, „ müssen “, „ dürfen “.
Modal Verbs in German: Everything You Need to Know
The modal verb describes the relationship of the subject to the action, which is then expressed by the second verb.müssen – must, to have to. The finite tenses: Present tense [ Präsens] = Based on the infinitive form, perhaps with a present tense stem change. Darfst du mit ins .
German modal verbs
‘Können’ is a common German verb that you’ll need to use in various tenses and moods in order to communicate in everyday spoken & written German. ‘Möchten’ is a common German verb that you’ll need to use in various tenses and moods in order to communicate in everyday spoken & written German.German has six modal verbs. They include können (can), müssen (must), dürfen (may), sollen (should), wollen (want), and mögen (like).In German, these verbs are können, mögen, dürfen, müssen, sollen, and wollen. They include können (can), müssen (must), dürfen (may), sollen (should), wollen . Reflexive verbs.
How to use modal verbs in German
Alle Zeitformen und Modi für das Verb „haben“ auf einen Blick Übersichtliche Aufbereitung der Konjugation von „haben“ in Tabellenform Flexionstabellen von Duden
German Müssen Conjugation
The verbs können and müssen are modal verbs.Mögen’s subjunctive case, möchten (would like to), is also a very commonly used word in the German language and is treated exactly like a modal verb, but isn’t usually included in the six as an example.The verb mögen is used frequently in the Konjunktiv II: möchten, which is why some people believe mistakenly that möchten is the infinitive of another verb.The 6 German modal verbs are können (to be able to / can), müssen (to have to / must), sollen (to be supposed to / should), wollen (to want to / wish to), dürfen (to be allowed to / may) and mögen (to like). Verbs that are always reflexive.That is the power of German modal verbs.

Whereas, all the other modal verbs are always used in combination with another verb in the infinitive form. Modal verbs (summary) Modal verbs usually modify another verb in the sentence – the main verb. Rather than simply stating an action, modal verbs allow you to speak about it. Factual description of an action: Ich stehe auf. dürfen – to be allowed to / may / can. Let’s take a look at their conjugation and a few sample sentences.LEARN MORE WITH OUR APP: https://www. A German translation of the English .The 6 German modal verbs are können (to be able to / can), müssen (to have to / must), sollen (to be supposed to / should), wollen (to want to / wish to), dürfen (to be allowed to .
German Modal Verbs
Mögen can be the only verb in a sentence. English has modal verbs like can, may, must, and will. Learn German modal verbs usage and find out verbs types, examples and common mistakes. – I can do this job. The modal verb describes the . dürfen – may, to be allowed to. können = can / be able. Example: Ihr wollt ein Haus bauen.In both English and German, modal verbs are used to express necessity or possibility. tenses that are formed using the main verb plus one or more auxiliary verbs. Of course, you can use the passive voice in combination with a modal verb. Actually, you could imagine the modal verbs as a kind of helping . The 3 verbs mean to like.

Modal verbs express whether you can, want to, must, should, or .
Verbs in German Grammar
6 Must-Know German Modal Verbs in Present Tense
The difference is: schemecken: It is only used for food and drink. Before we continue, let’s take a look at the modal verbs and their meanings: können. Here quickly all modal verbs in their KII form: dürfen – ich dürfte (I should be allowed) können – ich könnte (I should be able to) mögen – ich möchte (I would like) In English, these verbs are must, should, shall, will, etc. Ich kann diese Arbeit erfüllen. Certain verbs are always reflexive; they can’t be used without the reflexive pronoun. They are usually used in conjunction with other verbs, but they can also be the sole verb in a sentence. In a sentence in the present tense, the modal verb is conjugated and the second verb remains in the infinitive. But it is important that you don’t mix up this kind of helping verbs with others like “haben” and “sein” as they are from a different kind. The modal verb will be on the second position of the main clause and the infinitive will be at the end of the sentence, just like in sentences in the active voice. sollen = should (order / .
German Modal Verbs [6 Verbs You Need To Know!]
Modal verbs (summary)

Haben and sein are also types of helping verbs, but not in the same way that modals are; these two .com?pr=modCORRECTION: 3:11 Du musst schlafen. What are modal verbs? .Switch language now! „Können“ is a modal verb which means can.

können – can, to be able to.Modal Verbs in Perfect Tense as Full Verbs: Habe gewollt.In German grammar, there are six modal verbs.Formal: Sie sollen. You may go home early today. It’s mostly used when talking about abilities with können – gekonnt, obligations with müssen – gemusst, or preference with mögen .The modal verbs are: dürfen (English: to be allowed to) können (English: to be able to) mögen (English: like to ) müssen (English: must have to) sollen (English: should do) . sollen – should / to be supposed to. müssen = must / have to. Active: Der Schüler muss den Text schreiben. Modal verbs are commonly used in combination with other verbs to create complex sentence structures. The student has to write the text. Modal verbs can be thought of as “helping verbs,” but only in the sense that they clarify or provide more information.Modal Verbs – Konjunktiv II. The full list of modal verbs is available here.German has 6 tenses: 2 finite tenses, i.German has six modal verbs: dürfen, können, wollen, sollen, müssen and mögen. Learn German the most effective way and reach your language goals faster: take private German lessons or German classes online from the comfort of your own home!
German Möchten Conjugation
Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb in German that express possibility, necessity, or ability. Here are the main uses of dürfen: Meaning to be allowed to or may. It is a special type of verb, . In German, these verbs . German modal verbs . Ich (können) dir helfen. Er (wollen) nachher einkaufen gehen. The German modal verbs are dürfen to be allowed to, können to be able to, mögen (möchten) would like to, müssen must/have to, sollen should, wollen want.How to Use German Modal Verbs in the Perfekt Tense When you use a modal auxiliary in the present perfect tense, it generally works like it would any other time. They clarify, for example, whether it is possible or necessary to do something.What are the 7 modal verbs in German? There are really only 6.The German language knows the following six modal verbs : können (can), wollen (want/would), sollen (should), mögen (want), dürfen (be allowed to), müssen (must) In a .‘Können’ conjugations translate to ‘I can / am able to, etc. können – can / to be able to. They express an attitude about an action & occur with an infinitive that expresses the action.German modal verbs. These words allow you to express what you’re supposed to .
The Modal Verbs in German (die Modalverben)
You still have a lot to learn. Modal verbs are used to indicate a possibility or necessity.Modal verbs: können and müssen.
The 6 German Modal Verbs
You will be given several sentences with blank spaces, and you will also be provided with their corresponding modal verbs. In German there are six modal verbs: German Modal Verb.
The modal verbs in German are: dürfen (to be allowed) können (to be able to) mögen (to like) müssen (must, to have to) sollen (should, to be supposed to) wollen (to want) . Modal verbs are .

Modal verbs are very useful in German. Updated on October 08, 2017. English equivalent. Before we continue, let’s . strong) verb, . Because they’re a type of auxiliary verb (helper verb), they’re used alongside the infinitive form of the main verb of a sentence. Grammatical terms in German: das Modalverb: Modal verbs are verbs that often refer to a second verb and add information.
The Modal Verb „können”
As mentioned, these verbs are “assisting” another verb in a sentence. Common examples of modal verbs include can, should, and must .The 6 German modal verbs in their infinitive form are: dürfen = may / be allowed. What are modal verbs in German grammar? German has six . mögen – to like / to enjoy. Modal verbs are used to express certain hypothetical conditions, such as . How to Conjugate the 6 Modal Auxiliary Verbs. Differences between mögen, gefallen and schmecken mögen vs gefallen vs schmecken.German modal verbs are typically used to add meaning to or modify the main verb of a sentence, and there are several common modal verbs that are important to know. Actually, you could imagine the modal verbs as a kind of helping verb. tenses that are formed using just the main verb, and 4 compound tenses, i. Rule 1: When we want to use the perfect tense with a modal verb as a full verb, we build this with the auxiliary haben and the past participle with ge. wollen – to want.Modal verbs in German are also commonly associated in a sentence with other verbs (although this is not true for every single sentence involving a modal verb).
Konjugation des Verbs haben
This verbs is used in its infinitive form and – attention! – is used in the very end of the sentence. But first, we . The modal verbs are pretty commonly used in German, also in their KII form. sollen – should, shall, to be supposed to.Modal verbs show possibility, intent, ability, or necessity. They provide more information about the nature of the action expressed .The six modal verbs in German are: dürfen, können, mögen, müssen, sollen, wollen.‘Möchten’ conjugations translate to ‘I would like to, etc. You use a form of “haben”, because none of the modal auxiliaries are intransitive verbs and the past participles are all regular except “mögen”, which becomes “gemocht”.In German, there are six modal verbs: können, müssen, sollen, dürfen, möchten and wollen. They help you talk about what you have to do, want to do or are allowed to do and can be used in the present, past and conditional tenses. In this exercise, you will practice conjugating these common German modal verbs in the present tense.So, in this case, the modal verb in German is “ kann, will, muss ” and the main verb of the sentence is “spielen”.Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb in German that express possibility, necessity, or ability. to be able to/can.
How do you use German modal verbs?
FOLLOW OUR JOURNEY ON INSTAGRAM: http://www. On this page I’ll explain how „können“ is used, how to conjugate it, and things to watch out for, as well as provide some examples to help you really understand this important verb that you’ll use very often when speaking German. Modal verb können: Description of a possibility or ability: Ich .There are three types of reflexive verbs in German: 1.
Using the Six German Modal Verbs
’ The infinitive verb ‘möchten’ (to ‘would like’ in English) is one of the very first German verbs you should learn. I can help you. Common examples are: sich bedanken, sich beeilen, sich befinden, sich benehmen, sich betrinken, sich eignen, sich erholen, sich erkälten, sich schämen, sich verspäten .5 modal verbs, if you will, because the one –möchten (to ‘would like’) is the subjunctive subsidiary of the modal verb ‘mögen’ (to like). They usually occur in a sentence with a second verb.

The modal verbs in German are: können (can) dürfen (may) mögen (like) müssen (must) sollen (should) wollen (want).Modal verbs (Modalverben) come before main verbs and express things like permission, obligation, advice, ability, etc. Ihr (müssen) noch viel lernen.
- What Are The Benefits Of Rf Skin Tightening?
- What Are The Biggest Hurdles To Bullet Journaling?
- What Are The Top Email Marketing Agencies In Usa?
- What Are The Main Organs Of The United Nations?
- Wg Zimmer Paderborn Kostenlos : WG-Zimmer in Paderborn: 11564 Angebote
- What Are Aggressive Cognitions?
- What Are The Best Rpgs On Playstation 2?
- What Are The 7 Chakras? : What Are the 7 Chakras? A Beginner’s Guide to the Chakra System
- Weycor Ar 480 Test : AR 380 AGRAR
- What Are The Benefits Of Eating Rice Regularly?
- What Are The Most Common Uti Causes In Women?
- What Are The Different Types Of Buildings In Green Hell?
- What Are The Best Family Resorts In Portugal?