What Are The Risks Of Cerebral Fluid Leaks After Traumatic Brain Injury (Tbi)?
Di: Luke
Cerebral edema, the dangerous brain swelling that occurs after traumatic brain injury (TBI), can increase risk of death tenfold and significantly worsen prospects for recovery in brain function .August 19, 2021. Initial treatment consists of ensuring a reliable airway and maintaining adequate ventilation, oxygenation, and blood pressure.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak: When Are Symptoms Serious?
It is reported that approximately 45 % of dysoxygenation episodes during critical care have both extracranial and intracranial causes, such as intracranial .4 million are evaluated and discharged from an EDs.

Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a major cause of mortality and morbidity, and almost half of these patients are admitted to the intensive care unit. Tumor at the skull . Causes of TBI are variable, including: Post-traumatic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage is one of the most troublesome conditions associated with head trauma.Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a major cause of death and disability worldwide. Poor coordination or balance.Cerebral edema (CE) and resultant intracranial hypertension are associated with unfavorable prognosis in traumatic brain injury (TBI).Reviewed/Revised Feb 2023. More serious TBI can lead to severe and .
Brain Injury > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine
This further leads to lactic acid accumulation, increased permeability, and the formation of oedema. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are one of the common complications after traumatic brain injuries (TBI).
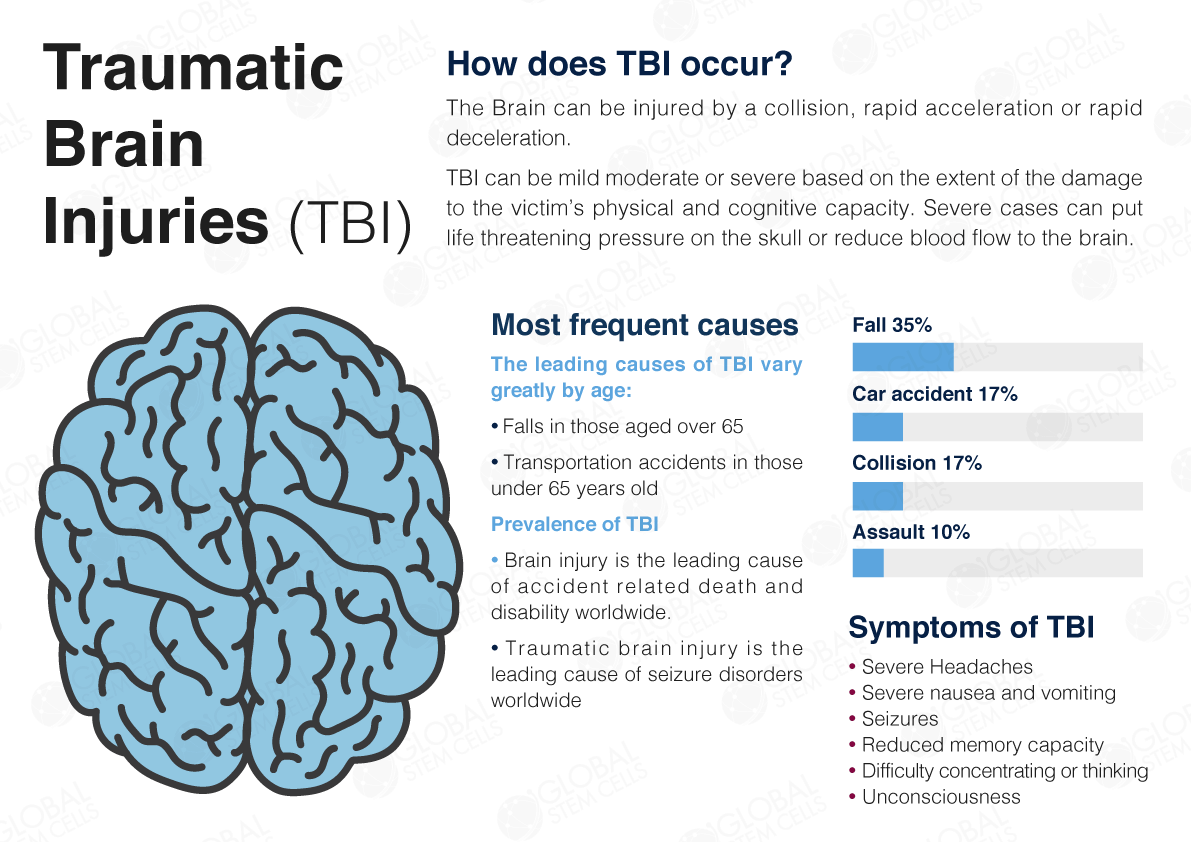
32 Pediatric patients are at greater risk of . Despite improved supportive and rehabilitative care .[] Of those, approximately 52 000 will die, 275 000 are hospitalized, and 1. Early diagnosis and proper management is imperative for it is strongly .In 2010, the CDC reported that each year approximately 1. Severe cases of traumatic brain injury (TBI) require neurocritical care, the goal being to stabilize hemodynamics and systemic oxygenation to prevent secondary brain injury.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are one of the common complications after traumatic brain injuries (TBI). Patients complicated with CSF leakage manifested a more rigorous clinical course and poorer outcome compared to patients with other TBI features: in mild head injury, patients with brain injury complicated with CSF leakage alone had a 24.Post-traumatic CSF leaks are seen 1% to 3% of all closed traumatic brain injuries (TBI) in adults and 80% to 90% of all the causes of CSF leaks in adult patients .What Are The Signs Of A CSF Leak & Best Way To Treat .This article discusses the epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of traumatic cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks. Blood collects or pools within your skull and brain.Post-traumatic CSF leaks are seen 1% to 3% of all closed traumatic brain injuries (TBI) in adults and 80% to 90% of all the causes of CSF leaks in adult patients are due to head injuries. Neurochemical changes: Energy-dependent sodium-potassium ATPase pumps regulate ionic changes across the membrane.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackFast facts on traumatic brain injury.Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain. It is a major cause . The brain is the most complex, delicate and well-protected structure in the human body—wrapped by the skull and layers of tissue called meninges. Traumatic brain injury . 1 Older adults, aged over 75 years, have the highest rates of TBI-related .
Traumatic cerebrospinal fluid leaks
The risks of CSF leaks can be detrimental to the outcomes of the patients.
Response of the cerebral vasculature following traumatic brain injury
orgCerebrospinal fluid leakage–reliable diagnostic methodspubmed.[1] According to Cushing and Weed’s seminal . 22, 28) The risk of meningitis from the traumatic CSF leak can present with high morbidity and even mortality depending on the cause and site of CSF . People at greatest risk are those with a history of minor head trauma, degenerative changes to the spine, . Obstructive sleep apnea. Some types of TBI can cause temporary or short-term problems with normal brain function. Trouble walking, often described as shuffling or the feeling of the feet being stuck. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks may be one of the mechanisms that link traumatic brain injury (TBI) with dementia, according to a hypothesis in Alzheimer’s . It consists predominantly of 99% water, and 1% accounts for electrolytes, proteins, neurotransmitters, and glucose.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid found in the subarachnoid space (SAS) that fills the neuroaxis cavities and surrounds the central nervous system (CNS).Anyone can experience a cerebrospinal fluid leak.It is frequently accompanied by haemorrhagic shock (HS) [2-5].5% risk ratio for developing intracranial hemorrhage, and the presence of post-traumatic . Some injuries are considered primary, meaning the damage is immediate.Patient Demographics If left untreated, a CSF leak can cause serious complications, such as meningitis. There are substantial practice variations in fluid management in patients with traumatic brain injury in the intensive care unit (ICU), with a new study published in .More serious TBI can lead to severe and permanent disability, and even death.Among adults 60 and older, the more common symptoms of hydrocephalus are: Loss of bladder control or needing to urinate often.
Brain-lung interaction: a vicious cycle in traumatic brain injury
The authors found that CSF leaks occurred in 1.Conclusion: Post-traumatic CSF leakages had higher mortality rates than those without CSF leakages in TBI cases, and the cases with CSF rhinorrhea had worse outcomes . Management decisions are discussed based on the current literature.A brain bleed (intracranial hemorrhage) is a type of stroke that causes bleeding in your head.A traumatic brain injury (TBI) can be caused by a forceful bump, blow, or jolt to the head or body, or from an object that pierces the skull and enters the brain.7 million people sustain a traumatic brain injury (TBI), of whom 275,000 are admitted to the hospital and 52,000 die.Post-traumatic cerebral infarction (PTCI) is one of the most severe secondary insult after traumatic brain injury (TBI), with a frequency ranging from 1.
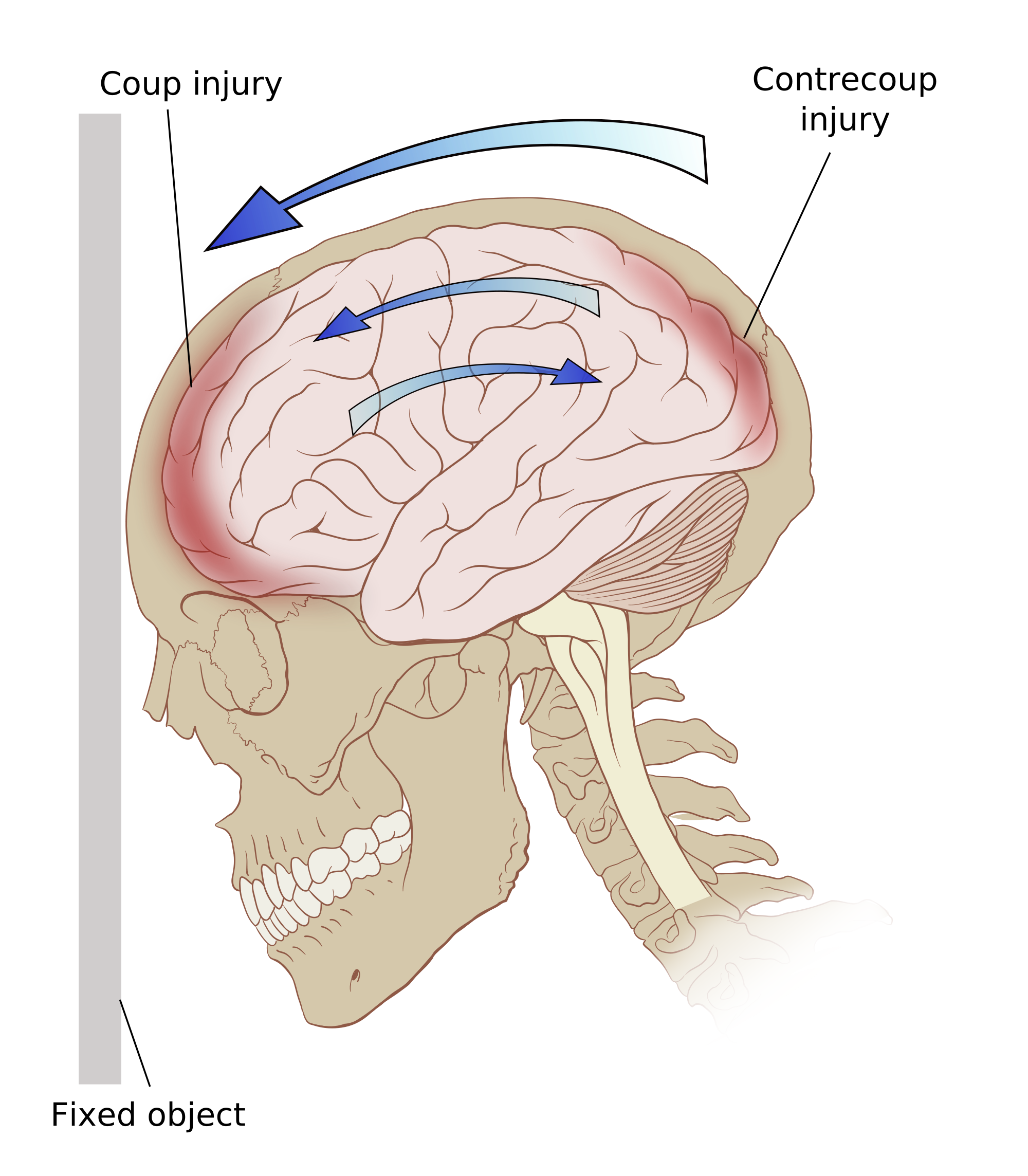
Early diagnosis .
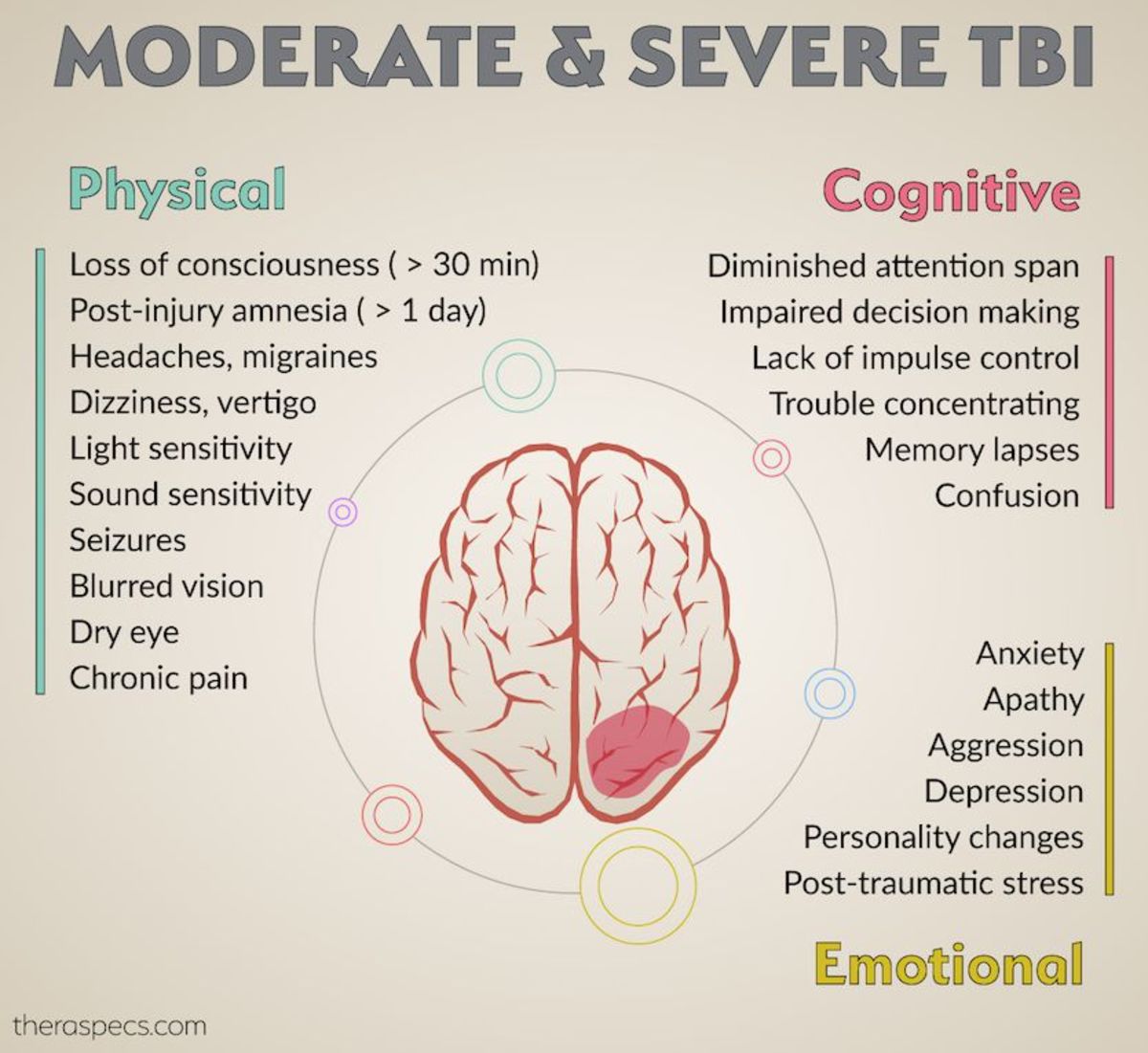
Risk factors for cranial CSF leaks include: Having a previous surgery on or around the skull. CSF fistulae, .Cerebral edema, the excess accumulation of fluid within the brain, accounts for 50% of deaths in severe head injuries. CE is a leading cause of in-hospital mortality, occurring in >60% of patients with mass lesions, and ~15% of those with normal initial computed tomography scans. Diagnosis is suspected clinically and confirmed by imaging (primarily CT). Early diagnosis and proper management is imperative for it is strongly associated with a better long-term prognosis of the patients. Since younger patients are often involved, this causes a large person-year burden of morbidity.Fluid balance and outcome in critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (CENTER-TBI and OzENTER-TBI): a prospective, multicentre, comparative effectiveness study – .comWhen A Runny Nose Is Brain Fluid Leaking: Here Is What To . Pediatric patie . Despite all of this insulation, traumatic brain injuries are still common, affecting as many as 3 million . As your brain can’t store oxygen, it relies on a series of blood vessels to supply its oxygen and nutrients.

TBI is one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity following trauma.

orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Traumatic Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak: Diagnosis and Management
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks may be one of the mechanisms that link traumatic brain injury (TBI) with dementia, according to a recently published hypothesis . The precise incidence is difficult to quantify, given variable definitions of exactly what constitutes TBI. A CSF leak in the skull base can be caused by a traumatic injury, a spontaneous .
Fluid Resuscitation in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury: A
A CSF leak of the skull base is a condition in which the clear fluid that surrounds and cushions the brain leaks out of the skull through a defect or hole in the base of the skull.govCSF Leak (Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak) Clinical Trials – Mayomayo. Not all blows or jolts to the head result in a TBI.A traumatic brain injury can cause problems in memory, cognition, language and motor skills. 12, 19, 21, 22) It is occasionally associated with poor outcome and high mortality rate.Cerebral edema is one of the most important prognosis markers observed in TBI.We also identified 7 proteins (GM2A, Calsyntenin 1, FAT2, GANAB, Lumican, NPTX1, SFRP2) positively associated with an unfavorable outcome at 6 months post .The selection and administration of fluids to trauma and traumatic brain injury patients may be especially helpful in preventing subsequent ischemic brain . Of those, 10% develop acute kidney injury (AKI) and 2% even need kidney replacement therapy (KRT).7 million people present to US emergency departments (EDs) after sustaining traumatic brain injury (TBI) each year.govManagement of CSF leak in base of skull fractures in adultspubmed.
Fluid Therapy Following Traumatic Brain Injury
1 Children, adolescents, and adults aged over 65 are most likely to suffer a TBI; most are men.The pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury (TBI) requires further characterization to fully elucidate changes in molecular pathways.Conclusions: The authors found that CSF leaks occurred in 1.Because CSF leaks are identified in ≈1% to 3% of all TBIs in adults, 4 individuals with a history of TBI may thus be at risk of dementia symptoms and diagnosis partly due to .46% of pediatric patients with skull fractures and that skull fractures were associated with significantly . Although clinical trials in patients with TBI who have AKI are lacking, . The brain-lung interaction can seriously affect patients with traumatic brain injury, triggering a vicious cycle that worsens patient prognosis.
CSF leak (Cerebrospinal fluid leak)
After treatment of mass lesions in severe TBI, an .The Management of Cranial and Spinal CSF Leaksbarrowneuro.The mechanism for adverse outcome in patients with combined TBI and HS may be due in part to the secondary ischemic injury of already vulnerable brain following loss of .Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is physical injury to brain tissue that temporarily or permanently impairs brain function.Traumatic brain injury (TBI) refers to damage to the brain caused by an external physical force such as a car accident, a gunshot wound to the head, or a fall. Progressive loss of other thinking or reasoning skills.We review the history of modern fluid therapy, complications after traumatic brain injury, and the use of fluid treatment for decompressive craniectomy and traumatic . Various mechanisms have been suggested for this complication, including direct .
Traumatic Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak: Diagnosis and Management
The effect of a TBI, such as concussion, depends on the severity of the injury and where it occurs.Traumatic brain injury leads to impaired regulation of cerebrospinal fluid and metabolism. In the early stages of TBI, the cerebrospinal fluid compensates the cerebral edema.eduDiagnosis – Spinal CSF Leak Foundationspinalcsfleak.
Fluid therapy and traumatic brain injury: A narrative review
When a brain bleed occurs, a blood vessel leaks blood or bursts. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) provides a rich repository of brain-associated proteins.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks may be one of the mechanisms that link traumatic brain injury (TBI) with dementia, according to a hypothesis in Alzheimer’s & . Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major public health problem and a leading cause of death and disability []. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is physical injury to brain tissue that temporarily or permanently impairs brain function. Diagnostic tools for CSF leaks . In this retrospective observational study, we implemented high-resolution mass sp .
Traumatic brain injury: A case-based review
An overview of traumatic CSF leaks is presented, and both conservative and operative therapies are reviewed. Although the mechanisms of the interaction are not fully elucidated, several hypotheses, notably the “blast injury” theory or “double hit” model, have been proposed and constitute the .46% of pediatric patients with skull fractures and that skull fractures were associated with significantly increased rates of neurosurgical intervention and risks of meningitis, hospital readmission, and neurological deficits at 90 days. Increasing evidence indicates that TBI is an important risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and chronic traumatic encephalopathy.[] Distribution of age is trimodal with predominance in the age .
- What Are The Best Alternatives To Artificial Grass?
- What Are Some Inspirational Quotes By Whitney Houston?
- What Do Pokemon X And Y Wear? : 15 tips for getting the most out of Pokemon X and Y
- What Are The Etiologies Of A Seizure?
- What Are Some Fun History Facts About The Oldest People?
- What Are The Main Themes In Kendrick Lamar’S Dna?
- What Does $1 Mean In A Bash Script?
- What Are Some Funny Movies To Watch Around Halloween?
- What Are The Different Types Of Improvisational Comedy?
- What Does Amigo Mean In Spanish?
- What Are Solar Cars – Solar Cars Are Still Baking Along, Kind Of
- What Documents Do I Need To Travel To France?