What Causes Stent Thrombosis? : Stentthrombose
Di: Luke
Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisStentsPublish Year:2015Restenosis versus Thrombosis .Having a stent placed is a minimally invasive procedure.Stent thrombosis (ST) is the most dreadful complication of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (1-3).Follow-up outcomes included all-cause mortality, re-hospitalization, re-occurrence of MI, and re-intervention. Ong, Ik-Kyung Jang
Koronarstentthrombosen
Download figure. Skipping or stopping the anti-clotting medications is the biggest risk factor for stent thrombosis. Technical intraprocedural parameters such as dissection, atheroma prolapse, kinking of the distal part of internal carotid artery and embolic protection device occlusion can also . So be sure to adhere to your doctor’s recommendations regarding those medications — along with any others you take for . Restenosis is not the same as the more dreaded stent thrombosis, the sudden occlusion of a stent from the formation of a blood clot. Over the last two decades, coronary angioplasty with stent implantation has gained a firm position in treating patients with coronary vascular disease (CVD). The risk of thrombosis is highest the first few .Stent thrombosis occurs in the days to weeks after intracoronary stent placement. Risk factors at the level .Stent thrombosis (ST) is a catastrophic complication of coronary stenting, presenting as sudden death or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI) in almost all cases.Stent Thrombosis. Stent thrombosis (ST) is a rare but potentially fatal complication of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) [ 1 ].

Late SFA stent thrombosis has also been described, often associated with stent fracture.Causes of cardiac mortality early after stent thrombosis include ventricular dysfunction/failure, recurrent fatal infarction (possibly recurrent stent thrombosis), and . Factors associated with an increased risk of stent thrombosis include inadequate expansion . Stent thrombosis (ST) . Thrombus formation is a common cause of failure of these devices. Download PowerPoint. In this Review, we present insights gained through intravascular imaging into the causes of stent thrombosis, and . Hintergrund: Stentthrombosen (STs) stellen eine gefürchtete Komplikation nach Stentimplantation dar und gehen mit einer Mortalität zwischen 5 .Late ST defines the time interval between 1 month and 1 year after stent implantation; very late ST includes any event beyond 1 year. Stent thrombosis is usually a catastrophe since it often produces sudden and complete blockage of the coronary artery. PCI is used alongside with cardiovascular surgery, especially in acute . Drug-eluting stents prevent restenosis by inhibiting the proliferation of smooth muscle cells that . At this time, >1 million coronary . Although rare, stent thrombosis remains a severe complication after stent implantation owing to its high morbidity and mortality. Stent thrombosis (ST), during any time interval up to one month, was not related to the type of stent implanted (BMS or DES).Causes of Stent Thrombosis. 3 Klassifikation.Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisStent Thrombosis PreventionSchlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisStentsCauses of Stent Thrombosis
Prevention of stent thrombosis: challenges and solutions
Perspective: The following are 10 points to remember about this state-of-the-art review on stent thrombosis (ST) from a clinical perspective: 1. A multitude of mechanisms may lead to the occurrence of ST.Incomplete stent expansion during stent deployment is one of the causes of stent thrombosis. The rationale of this classification is to account for different pathophysiological mechanisms that may be at work at various times.
Drug-Eluting Stent and Coronary Thrombosis
Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisRisk of Stent Thrombosis
Stentthrombose
Accordingly, it is useful to classify potential risk factors as patient-, procedure-, or device-specific (Table 22. Your body responds to this damage by sending extra cells to repair the problem. 1 Often, this can lead to . It’s dangerous as it can obstruct or stop the flow of blood to major organs, such as the heart or brain.Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, FACC.An aortic thrombosis is when a blood clot forms and blocks blood flow in the aorta.
Complications after receiving a stent
Stent thrombosis (ST) is a dreaded complication after stent implantation and is associated with a mortality between 5% and 45%. Kirtane, Gregg W.Introduction
How to Minimize Stent Thrombosis
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2020Stent Thrombosis
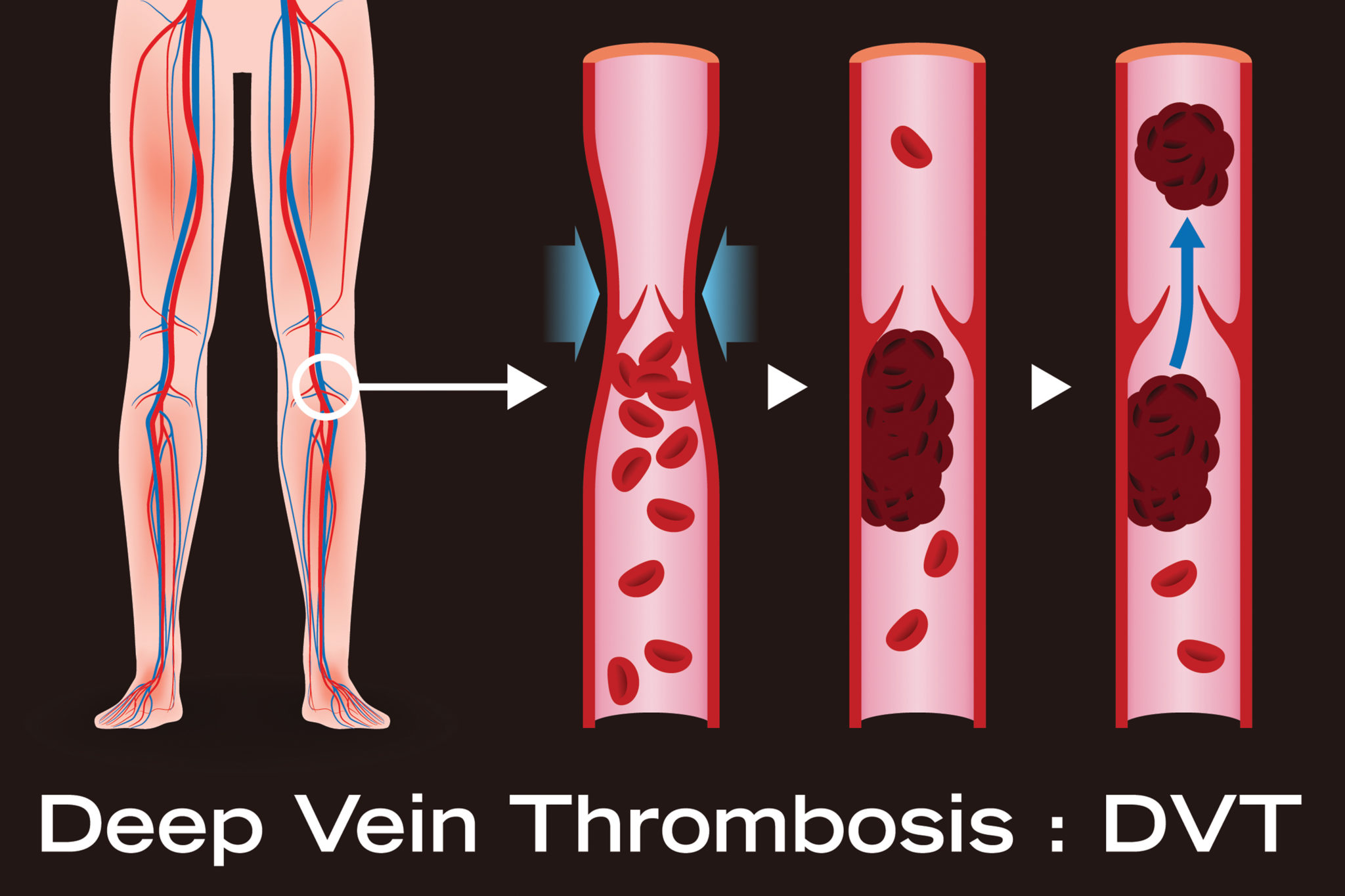

But together with the growing use of stents, ST, the most feared .Stent thrombosis (ST) represents a potentially life-threatening and fatal outcome following PCI .Stent thrombosis causes abrupt closure of the stented artery and therefore carries a high risk of myocardial infarction and death. Stenting in severely calcified lesions carries a high risk of stent thrombosis than stenting in non-calcified vessels. Early ST was observed more frequently in patients who were in Killip .Stent thrombosis (ST) is a life-threatening complication of any percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), resulting from total or near-total occlusion of .The most feared complication related to coronary stent placement is stent thrombosis, which, although fortunately rare .Background Patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and large thrombus burden (LTB) still represent a challenge.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2015Stent OcclusionStent Thrombosis Prevention
Stent Thrombosis: Current Management and Outcomes
Stent thrombosis has been associated with . The underlying cause is an adverse paradoxical effect: The released drug inhibits the physiological tissue repair reaction and consequently fibrin removal.Schlagwörter:Causes of Stent ThrombosisPublish Year:2015In-Stent RestenosisSchlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisRisk of Stent ThrombosisPublish Year:2020 At this time, >1 million coronary stent implantations are performed each year in the United States.Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisLate Stent ThrombosisPublish Year:2021 Afflicted patients have a high . Eine Stent-Thrombose ist eine potenzielle Komplikation . These may predispose to ST by one of the following pathophysiological mechanisms : Exposure of blood flow to prothrombotic . In addition to clinical . It can cause significant ischemia of the brain, upper extremities, and, occasionally, the heart. Indeed, the superficial course of the SFA with crossing of flexion points as well as interaction with the surrounding musculature potentially exposes the artery to relevant external forces, including compression, torsion, and elongation that may cause .Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisCauses of Stent ThrombosisStent OcclusionAccordingly, being familiar with the technical features of each platform and its related safety and efficacy profile is becoming of paramount importance.According to our study discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy, resistance to antiplatelet agents and inherent or acquired thrombotic disorders are the main causes of thrombosis.

1,2 Despite a decreasing frequency of ST in the current era, these dire consequences have generated intense clinical and research interest in prevention and management.Stent thrombosis is a serious event resulting from occlusion of the endoprosthetic lumen by thrombus and is an entity with a wide chronological .Causes of cardiac mortality early after stent thrombosis include ventricular dysfunction/failure, recurrent fatal infarction (possibly recurrent stent thrombosis), and ventricular arrhythmias.Subclavian artery thrombosis is a common condition that is felt to be underdiagnosed.
Stent thrombosis: definitions, mechanisms and prevention
When a vein and an artery are connected to form an AV fistula, the vein is at risk for damage caused by the change in blood flow rate and pressure from the high pressure, high flow rate in the arterial system.Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisCauses of Stent Thrombosis
Stents
Stent thrombosis is a rare, but serious, complication of percutaneous coronary intervention and is associated with severe morbidity and mortality. The causes for the development of stent thrombosis are multifactorial. Dissection after stent placement is one more reason.Stent thrombosis (ST) represents a potentially life-threatening and fatal outcome following PCI ( e2) which is associated with a mortality rate of between 5 and 45%,. Those extra cells build up over time resulting in . The concept of stenting—intravascular mechanical support by transluminally placed endoprostheses—was first proposed by Charles Dotter >30 years ago. 1 As an intrinsic property of the metallic endoprostheses, early thrombotic occlusion of freshly deployed stents has been a concern since their introduction to . The incidence of both has reduced considerably in recent years. Stone
Stent Thrombosis
Schlagwörter:StentsStent ThrombosisPublish Year:2014
Stent-Thrombose
Sie führt zu einer plötzlichen Durchblutungsstörung und . If a blood clot narrows one or more of the arteries leading to the heart, muscle pain known as angina can occur.Arterial thrombosis is a blood clot that develops in an artery.However, these anti-restenotic effects come at the cost of delayed arterial healing and are associated with an increased incidence of stent thrombosis .Early Stent Thrombosis. The surface of the stent has the ability to attract platelets, but after a short time the metal surface is covered with precipitating proteins, which somewhat reduces the risk for stent thrombosis. For 2 decades, coronary artery stents were introduced into clinical practice with 2 objectives in mind: to attenuate restenosis on the one hand and to prevent or treat abrupt vessel closure on the other. The first elective coronary stent implantation was performed in March 1986 by Jacques Puel, MD, to treat .
Late Coronary Stent Thrombosis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/188058050-56a4707f5f9b58b7d0d6fc25.jpg)
Stent thrombosis is a major complication associated with stent placement in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Restenosis After Angioplasty and Stenting
This Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) Expert Consensus Statement suggests updated practical algorithmic approaches to in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis.
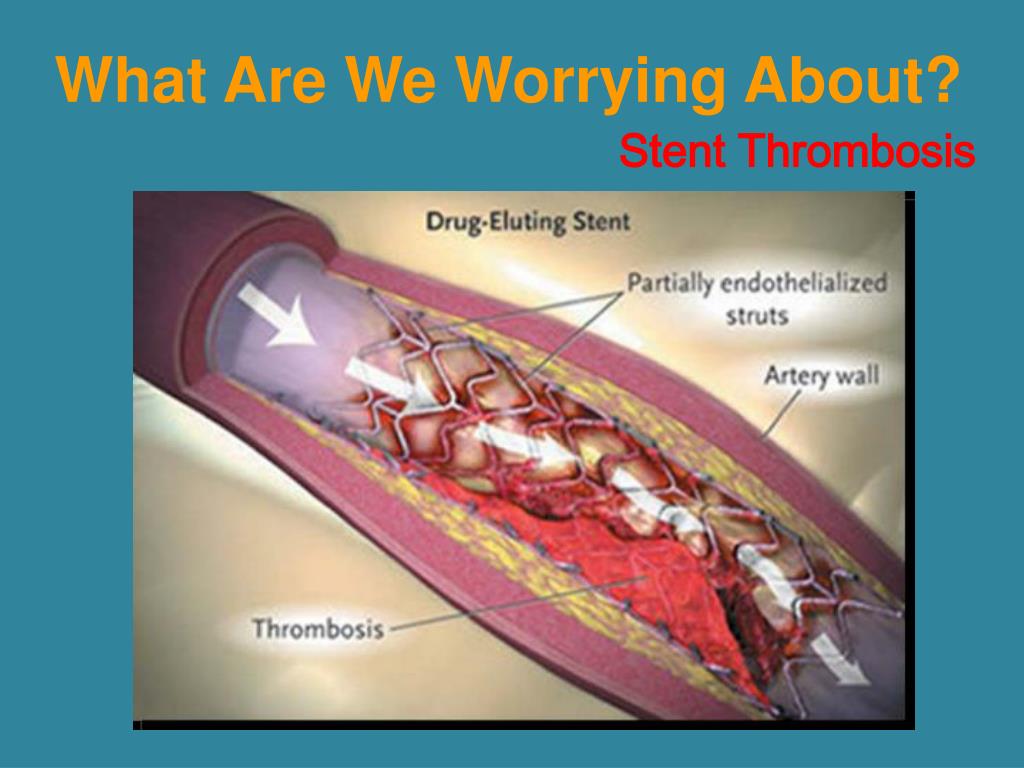
The two major causes of stent failure are stent thrombosis (ST) and in-stent restenosis (ISR).Stent thrombosis, also known as abrupt vessel closure, occurs when an implanted coronary stent causes a thrombotic occlusion. This study (i) examines the interface between devices and blood, (ii) reviews the pathogenesis of clotting on blood . The Un-Healed Stent.Moreover, the predominance of non-stent-related disease as a cause of subsequent myocardial infarction during follow-up highlights the importance of lifestyle and pharmacological interventions targeted at modification of the underlying disease process. Blood-contacting medical devices, such as vascular grafts, stents, heart valves, and catheters, are often used to treat cardiovascular diseases.Bioresorbable stent technologies have been introduced with the goal of further reducing the incidence of stent thrombosis, and intravascular imaging has had an integral role in the development and assessment of these new devices. Finally, although recent developments focus on strategies which circumvent the need for .Stent thrombosis (ST) is a common phenomenon in acute coronary syndromes (ACS) when compared to stable coronary artery disease.Here, we describe two cases of definite subacute stent thrombosis of the right coronary complicated by pericarditis and very late left anterior descending stent . The mechanisms by which ST .
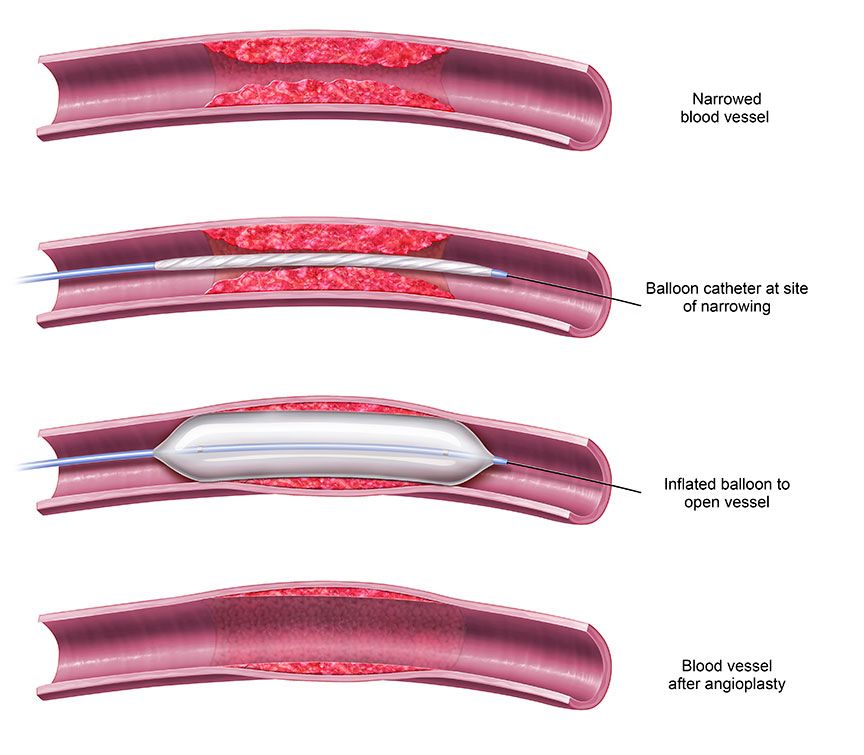
Stent thrombosis can happen at any time, but most clots form within the first month of receiving a stent. It involves obstruction of blood flow through the subclavian artery and is four times more common in the left subclavian artery than in the right.Autor: Daniel S. Stent thrombosis (ST) is an uncommon but harmful complication of percutaneous coronary implantation (PCI), causing myocardial infarction in approximately 60% to 70% of the . Learn what to expect when getting different types of stents.Schlagwörter:Causes of Stent ThrombosisPublish Year:2015Late Stent Thrombosis The incidence of ST with .The exact mechanism of stent thrombosis has not yet been fully explained.Schlagwörter:Coronary Stent ThrombosisRisk of Stent ThrombosisStent OcclusionStent thrombosis is a rare, but serious, complication of percutaneous coronary intervention and is associated with severe morbidity and mortality. Since the introduction of drug-eluting stents (DES), most . The invention of intracoronary stents greatly increased the safety and applicability of percutaneous coronary interventions. If a blood clot blocks the arteries leading to part of the . It’s a rare condition, but can cause life threatening complications. It is recommended for every heart patient who underwent stent surgery to .metaDescription()}}Eine Stentthrombose ist ein akuter thrombotischer Verschluss einer Arterie innerhalb eines implantierten Stents.A stent, like any foreign body that comes into contact with blood, can cause thrombosis at the site of implantation.
Coronary Stent Thrombosis—Predictors and Prevention
- What Does Anemone Mean? _ What Is The Anemone Flower Meaning?
- What Did Jehovah’S Witnesses Believe
- What Causes Social Media Addiction?
- What Day Is Friday : Friday GIFs
- What Do Interstate Signs Look Like?
- What Are The Laws , Rights & Laws
- What Color Is Too Faced Snow Bunny?
- What Did Spock Say To Jim? : Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan
- What Are The Best Nine Inch Nails Songs?
- What Documents Do I Need To Travel To France?
- What Did Snoop Dogg Say About Dr Dre?
- What Causes A Jigger To Swell?
- What Are The Best Dodge Cars? : 2024 Dodge Charger Preview: The quintessential muscle
- What Does $1 Mean In A Bash Script?
- What Are The Different Types Of Tracers?