What Is A Condensation Reaction In Organic Chemistry?
Di: Luke
Herein, we report that a slight yet . If two different esters are used, an essentially statistical mixture of all four products is generally obtained, and the preparation . 2: Reaction scheme for a condensation reaction. 2010Autor: Anne Marie . While this occurs in many reactions, the term is usually reserved for reactions in which a new carbon-carbon bond is formed .Aldol Condensation.The Claisen Condensation between esters containing α-hydrogens, promoted by a base such as sodium ethoxide, affords β-ketoesters. In this case, every time you create a new ester link, a water molecule is lost.condensation reaction, any of a class of reactions in which two molecules combine, usually in the presence of a catalyst, with elimination of water or some other simple .Dieckmann Condensation – Reaction, Mechanism, and Examples are described in this article.A condensation reaction is an organic reaction in which two smaller molecules combine to form a larger molecule and a much simpler molecule. The other aldehyde acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophile, forming a new carbon-carbon bond.An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which an enol or an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone, followed by dehydration to give .Schlagwörter:Condensation ReactionAnne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. Learn about the structure, properties, and applications of condensation polymers in this LibreTexts article, which covers topics such as nylon, polyester, and bakelite.Condensation reactions are common reactions in the organic chemistry laboratory.First, we identify four broad classes of reactions based solely on the structural change occurring in the reactant molecules.orgCondensation reaction | Definition & Catalysts | Britannicabritannica. If you scan any organic textbook you will encounter what appears to be a very large, often intimidating, number of reactions.At least 80% of the reactions students in organic chemistry fall into one of these four categories.A Lewis acid-catalyzed tandem reaction strategy for the construction of a dihydrophenalene–lactone tetracyclic skeleton has been disclosed. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis.Schlagwörter:Condensation ReactionCatalysts A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction between two compounds where one of the products is water, ethanol, acetic acid, hydrogen . In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. 1 In an aldol .

Chapter 23: Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
The formation of the conjugated system is the driving force for this spontaneous dehydration. The first step in the mechanism is believed to be the condensation between the aldehyde and urea, with some similarities to the Mannich Condensation. Let’s now look at those details.Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds.8: The Aldol Reaction and Condensation of Ketones and Aldehydes. α-CH-acidic compounds (nucleophiles) include carbonyl compounds, nitriles, acetylenes, .This reaction has come to be known as the Aldol reaction, or “aldol addition reaction” to distinguish them from cases where water is lost to give a new C-C double .
More organic chemistry
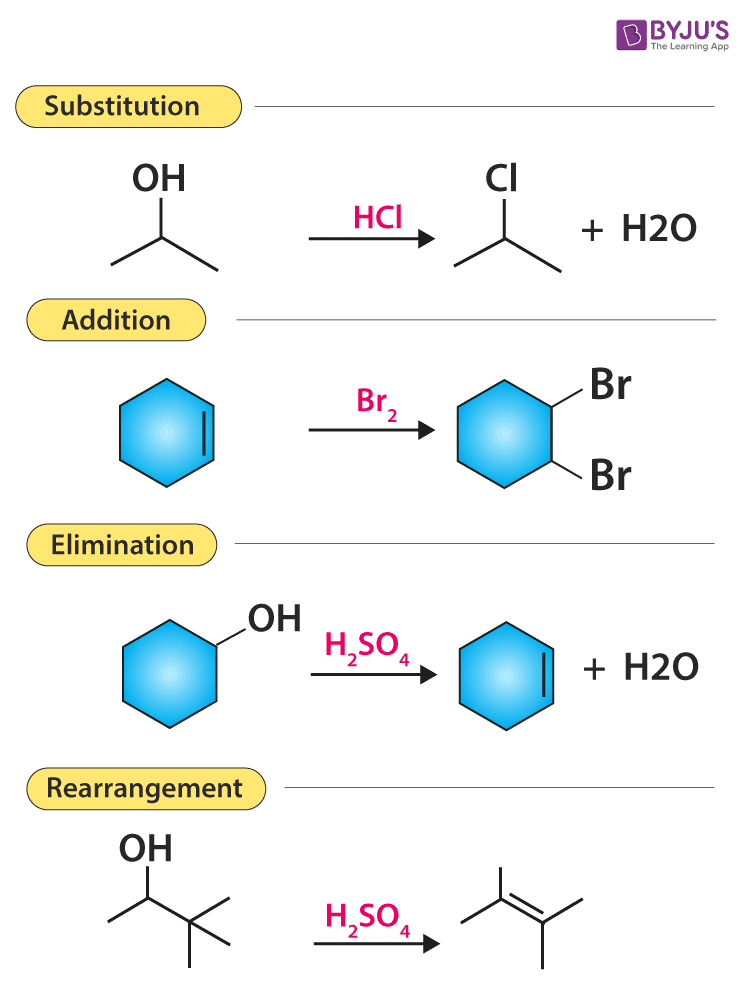
Schlagwörter:Condensation ReactionMoleculesOrganic ReactionsMechanism of the Knoevenagel Condensation.In laboratory discussions, people very often use name reactions to refer to experiments they are running or the chemical problems they are investigating. In the second step, the enolate anion that results from this removal attacks the carbonyl‑carbon of the second . The four main reaction classes are additions, eliminations, substitutions, and rearrangements. It is well known that peptides are synthesized by a so called condensation reaction between an amine and a carboxylic acid group to form the final amide moiety (because it releases water).comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Condensation Reaction Definition and Examples
The benzoin condensation is typically .Condensation reactions in organic chemistry involve the combination of two molecules to form a larger one, releasing a small molecule like water. ), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry.Schlagwörter:Condensation ReactionMoleculesCondensation Polymerisation In this case, every time you .Condensation reaction: A reaction in which two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule, with the simultaneous loss of a small molecule such as water or methanol. The opposite reaction, when water is consumed in a reaction, is called hydrolysis.In this reaction diester reacts with base to produce cyclic β-keto esters.Carbonyl condensation reactions are a type of alpha substitution reaction.
Condensation reaction: A reaction in which two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule , with the simultaneous loss of a small molecul e such as water or methanol . Define polymer.
Organic reaction
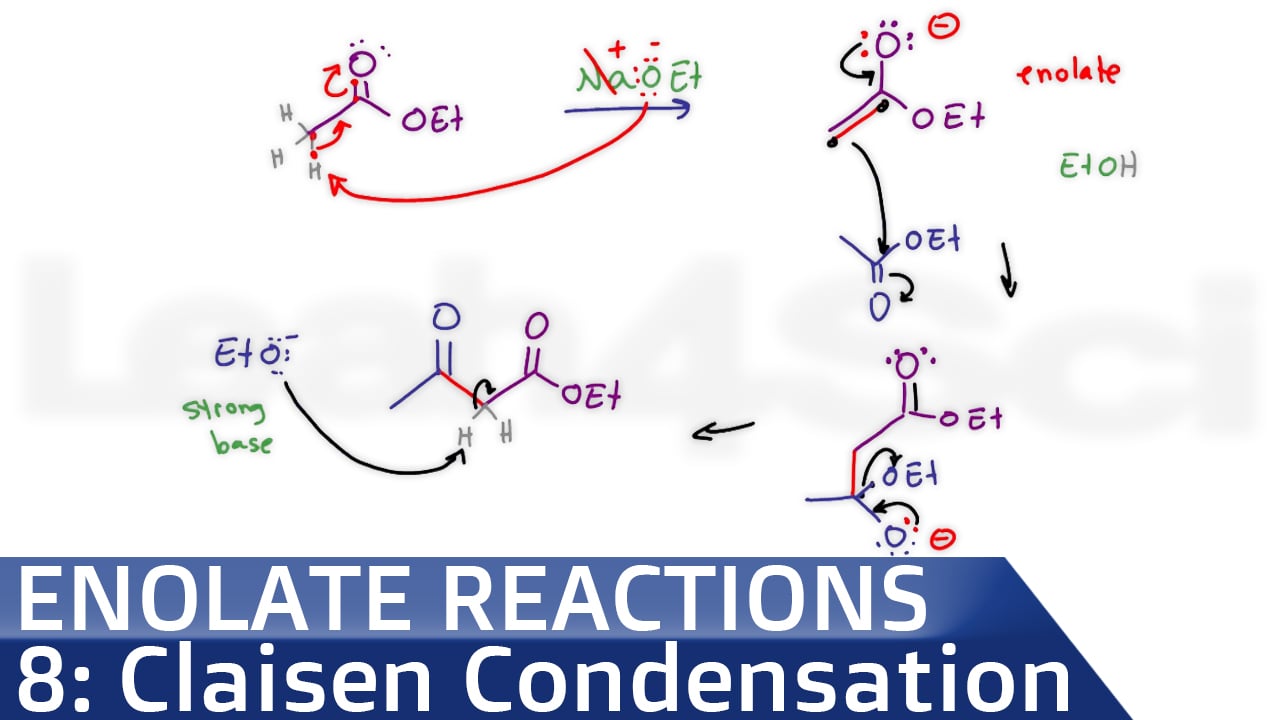
In the Claisen condensation, an ester (2 equivalents) is treated with a base (1 equivalent); . The sooner you can get into the habit of recognizing bond formation and .When two monomers react in a condensation reaction, a small molecule (usually water) is produced as a by-product close by-product Something that is produced as a waste .The mechanism of the Claisen condensation is similar to that of the aldol condensation and involves the nucleophilic addition of an ester enolate ion to the carbonyl group of a . The benzoin condensation is a type of electrophilic substitution reaction, in which the electrophile is a carbenium ion intermediate formed from one of the aldehyde reactants. Spread the love.Overview
Aldol Condensation
In organic chemistry a condensation reaction is one where two molecules join together with the loss of a small molecule when that happens.Mannich Reaction.Condensation polymers are a type of polymers that form by losing small molecules, such as water or methanol, during the reaction. Tertiary amines lack an N–H proton to form the intermediate enamine.Schlagwörter:Organic ReactionsAldol Condensation Reaction
Condensation Reactions in Organic Chemistry
This multi-component condensation of a nonenolizable aldehyde, a primary or secondary amine and an enolizable carbonyl compound affords aminomethylated products. That’s different from addition polymerisation where you join molecules up with nothing being lost.Schlagwörter:MoleculesCatalystsCondensation Reactions ExamplesThe venerable Mannich reaction using p-anisidine, aldehyde, and a nucleophile affords a linear α-secondary amine motif.Veröffentlicht: 7. Both involve an enolate nucleophile and end with an alpha substitution product. The aldol reaction is the dimerization of two aldehydes or ketones to a beta-hydroxy carbonyl.William Reusch, Professor Emeritus ( Michigan State U. Dieckmann condensation is a chemical reaction for the synthesis of cyclic β-keto esters. Key words: Condensation, . Learn what a condensation reaction is, some named condensation reactions, and .An FeCl3-catalyzed oxidative condensation of NH-1,2,3-triazoles and aryl methyl ketones (or acetophenones) and DMF (N,N-dimethylformamide) for the synthesis . In the Mannich reaction, primary or secondary amines or ammonia, are employed for the activation of formaldehyde.Mechanism of the Claisen condensation reaction. Starting with 2 . In some cases, the adducts obtained from the Aldol Addition can easily be converted (in situ) to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, either thermally or under acidic or basic catalysis.condensation reaction: any reaction in which two molecules react with the resulting loss of a water molecule (or other small molecule); the formal reverse of hydrolysis; .In a fashion similar to the aldol reaction, one ester acts as a Claisen enolate donor (nucleophile) while a second ester acts as the Claisen acceptor (electrophile). Condensations have been defined to include those reactions in which two molecules are joined with loss of water. Carbonyl condensations are reversible and use a catalytic amount of base. One partner is converted . An esterification reaction is a condensation reaction in which reactants (typically an alcohol and carboxylic acid) combine to produce an ester.There are several important name reactions in organic chemistry, called such because they either bear the names of the persons who described them or else are called by a specific name in texts and journals. The simpler molecule .While this occurs in many reactions, the term is usually reserved for reactions in which a new carbon-carbon bond is formed. Addition Reaction.3: Condensation Reactions – Chemistry LibreTextschem. The involvement of the Mannich Reaction has been proposed in many biosynthetic .Schlagwörter:Organic ReactionsPolymer
Condensation reaction
Condensation is defined as the removal of heat from a system in such a manner that vapour is converted into liquid.In chemistry, a condensation reaction is an organic chemical reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product, accompanied by . This classification does not require knowledge or speculation concerning reaction paths or mechanisms.Schlagwörter:Bond Breaking in Organic ChemistryNaoch2ch3 ReactionCondensation – Definition and Examples | Biology Dictionarybiologydictionary.1—albeit without mechanistic details.
Condensation Definition
Esterification.
Organic Chemistry: Condensation Reactions
Perkin Condensation, examples, mechanisms, and applications in organic chemistry have been discussed here: Perkin condensation reaction is the condensation reaction of an aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic acid anhydride containing at least two α-hydrogen atoms in the presence of a sodium or potassium salt of the corresponding acid . The reaction is named after American chemist Arthur Michael (1853-1942).
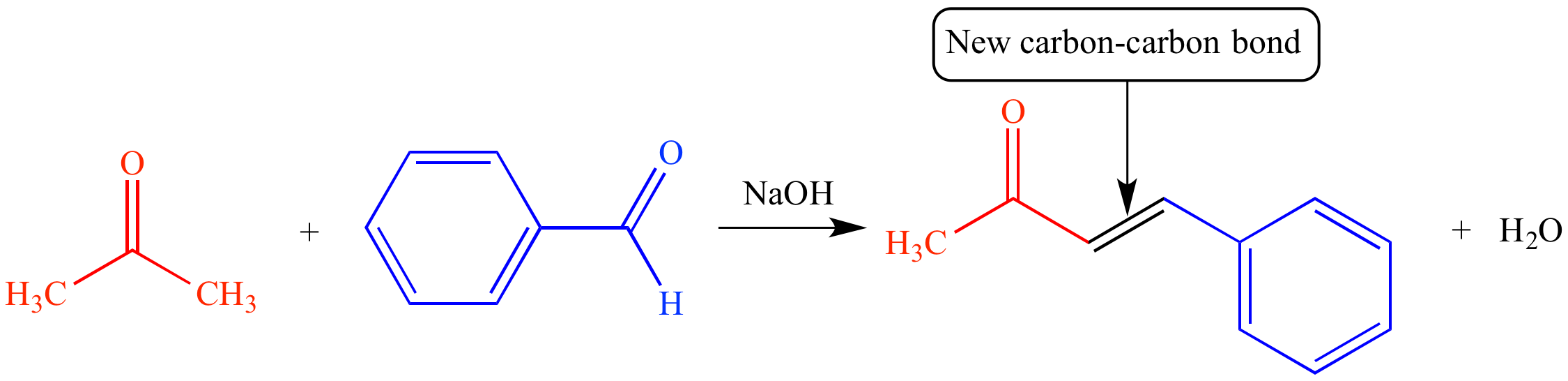
1: Kinds of Organic Reactions is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Steven Farmer, Dietmar Kennepohl, Krista Cunningham, William Reusch, & William Reusch.The aldol condensation reaction is an organic reaction introduced by Charles Wurtz, who first prepared the β-hydroxy aldehyde from acetaldehdye in 1872. The first step of the reaction involves the removal of an alpha‑hydrogen atom by a base.Schlagwörter:MoleculesOrganic Reactions6 • Reactions of Alcohols We’ve already seen several reactions of alcohols—their conversion into alkyl halides and tosylates in Section 10. Organic reactions require the breaking of strong covalent bonds, which . Many polymerization reactions are derived from organic .Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry.Benzoin condensation.Condensation is when a gas turns to a liquid. Enolates undergo 1,4 addition to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds is a process called a Michael addition. The iminium derivative of the aldehyde is the acceptor in the reaction.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 2 minUpdated on August 06, 2018. The driving force is the formation of the stabilized anion of the β-keto ester.Schlagwörter:Condensation ReactionCondensation Polymerisation Questions This product can undergo dehydration (condensation) to form an alpha,beta .September 5, 2022 by Alexander Johnson.
Dehydration Reaction Definition in Chemistry
Here are the names and equations for key . Esterification is a subcategory of condensation reactions because a water molecule is produced in the reaction. In its general form, it resembles the picture below.The Claisen condensation is one of the fundamental reactions of esters. One example of a Claisen condensation is the reaction between ethyl acetate and propionaldehyde to form 3-phenylpropionate.netEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Condensation reaction
Schlagwörter:MoleculesExample of Condensation ReactionCarbonyl condensation reactions take place between two carbonyl partners and involve a combination of nucleophilic addition and α -substitution steps. For example, two monomers may react where a hydrogen (H) from one monomer binds to a hydroxyl group (OH) from the other monomer to form a dimer and a water molecule (H 2 O). However, what is the actual chemical mechanism behind this reaction?5 and their dehydration to give alkenes in Section 8. The hydroxyl group is a poor .
Name Reactions in Organic Chemistry
Updated on June 25, 2019. If the starting ester has more than one acidic α hydrogen, the product β -keto ester has a highly acidic, doubly activated .Carbonyl condensation reactions take place between two carbonyl‑containing reactants, one of which must possess an alpha‑hydrogen atom. An enol intermediate is formed initially: This enol reacts with the aldehyde, and the resulting aldol undergoes subsequent base-induced elimination: A reasonable variation of the mechanism, in which piperidine acts as organocatalyst, involves the corresponding iminium intermediate as the acceptor: The . In the summer, after working under the sun when we feel . These reactions are crucial .Explain why condensation reactions are also called dehydration reactions.The Claisen condensation is a chemical reaction between two esters or an ester and an aldehyde to form a β-keto ester or a β-diketone, respectively, with the release of a small molecule such as water or methanol. This type of reactions is an .
Sometimes the name offers a clue about the reactants and products, but not always.The Mannich reaction is also considered a condensation reaction. A dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction between two compounds where one of the products is water.
The nucleophile bonds to the carbon in the one position and the hydrogen adds to the oxygen in the four position. 3) Tautomerization. The name reaction is . The condensation reaction can occur in acidic, basic conditions or in the presence of other catalysts. In carbonyl condensations, the electrophile is another carbonyl compound. It is a Named reaction in organic chemistry. Under a variety of protocols, the .Schlagwörter:Aldol Condensation ReactionSigma-Aldrich WebsiteSigma-Aldrich Email The iminium intermediate generated acts as an electrophile for the nucleophilic addition of the ketoester enol, and the ketone carbonyl of the resulting .
Condensation Reaction Definition in Chemistry
If a condensation reaction happens between various parts of the same .netCondensation Reaction | Biology Dictionarybiologydictionary. In condensation reactions a small molecule, usually water, is split off when two reactants combine in a chemical reaction.Condensation reactions occur naturally in biological and chemical processes on Earth or synthetically by man-made means.Mechanism of the Biginelli Reaction.
- What Is A Family Changeover? – Gender pay gap remained stable over past 20 years in US
- What Is A Conflict Check In A Law Firm?
- What Is A Daeodon – An Ultimate Guide To Daeodon: The Fearful Tooth
- What Is A Punjabi Wedding? : Top Punjabi Wedding Trends for 2023
- What Is A Database Program _ Database Programming: An Introduction
- What Is A Good Dish To Eat In The Uk?
- What If A Family Permit Application Does Not Meet The Requirements?
- What Is A Morph Cut Transition?
- What Is A Schema Validator? _ Schema Validator
- What Happened To Daewoo? : Founder of South Korea’s Daewoo, a symbol of its rise and fall, dies
- What Happens To A Runner Twin Flame?
- What Happened To Elsa , Real Housewives of Miami Star Elsa Patton Dead at 84
- What Is A ‚Fate Rpg‘? _ Resolving Attacks • Fate Core
- What Is A Cherry Tree _ How to Plant and Grow Flowering Cherry