What Is A Human Ear? , The Ear: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
Di: Luke
The most-striking differences between the human ear and the ears of other . This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. These openings are hidden beneath their feathers.
Human ear
The human ear has a highly dynamic hearing range, but we are most sensitive to sounds between 500 Hz and 4,000 Hz.What about 70? Three factors come into play: intensity, duration, and distance. External auditory . The eardrum, stretched across the end of the canal, vibrates as sound waves reach it.Structures of the human ear.orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Ear: Anatomy, Facts & Function
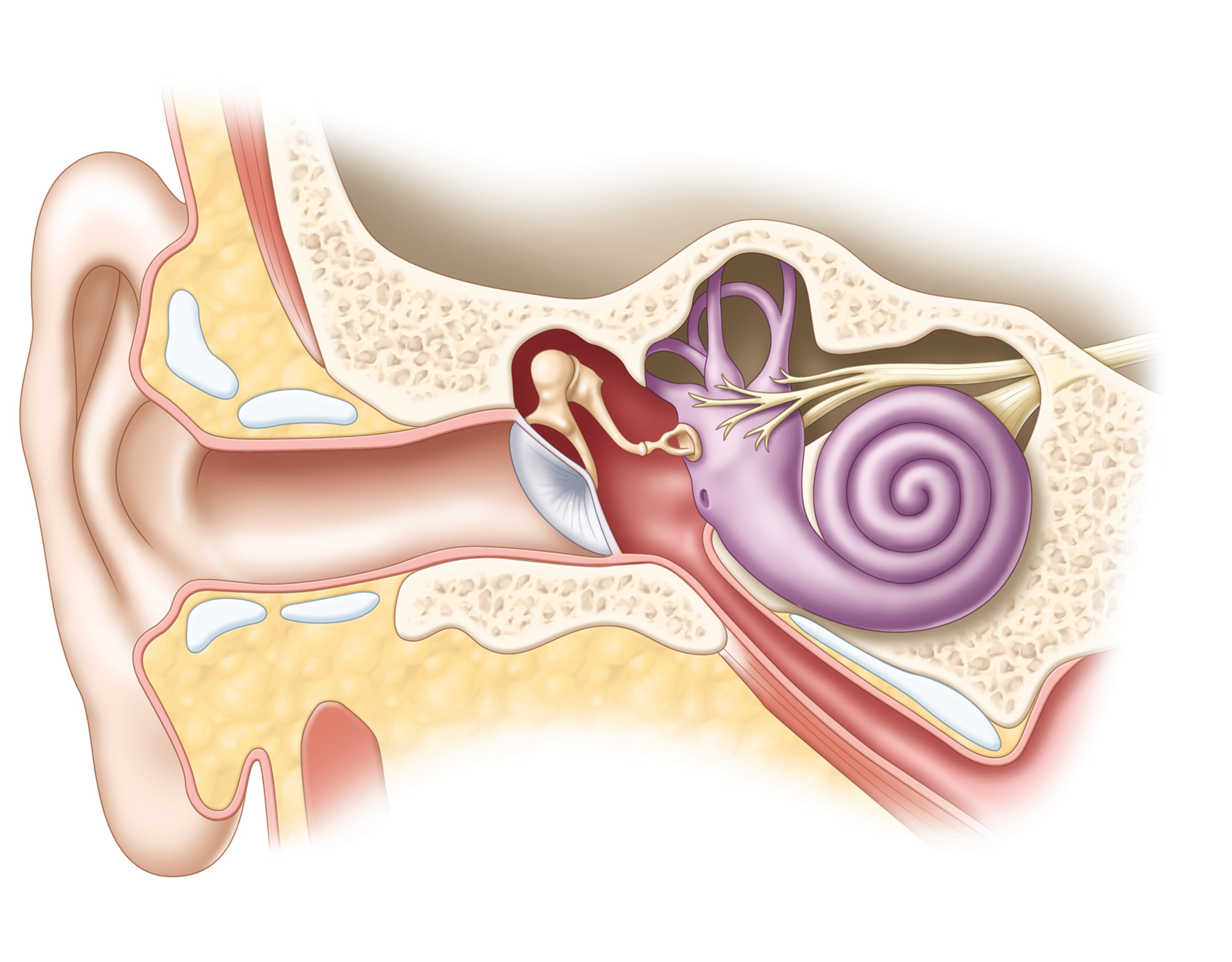
The Anatomy of the Inner Ear. Our auditory nerve then carries these signals to the brain. The parts of the ear include: Pinna or auricle. She’s had her ears pierced.Marie Donlon | April 15, 2024. The ear’s ability to do this allows us to perceive the pitch of sounds by detection of the wave’s frequencies, the loudness of sound by detection of the wave’s amplitude, and the timbre of the sound by the detection . During the 20th century, mankind witnessed great advances in the field of science. The higher the frequency, the . The signals are interpreted by the brain and connected to other impressions and experiences – the sound is then perceived as loud or quiet, speech, music or a message such as “the phone is ringing. In German, earwigs are called “earworms”; in French, “ear piercers. Watch tympanic membrane and auditory ossicles transmit sound wave .It consists of the outer, middle, and inner ear.Sound is measured in decibel units and is most often reported in reference to something.In a statement, Molly’s carers said we are just so happy to be together again. [countable] either of the organs on the sides of the head that you hear with. Anatomy of the human ear.Health Information. For lower or higher frequencies, the dynamic is narrowed. The outer ear includes the pinna (the part you see that is made of cartilage and covered by skin, fur, or hair) and the ear canal. The outer ear is the visible part, .
Crus of the Helix: It is the landmark of the outer ear, situated right above the pointy protrusion known as the tragus. The ear’s height size varies from geographical region . Or in my case the part . The cartilaginous auricle and the auditory canal of the outer ear direct sound waves to the middle ear. Hearing is the process by which the ear transforms sound vibrations in the external environment into nerve impulses that are . The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system.Humans, Blood Elves, and several other races are receiving point and round ear customization options in The War Within. When sound waves enter the ear . All acoustic systems run through it. Maintaining a sense of balance is another . Medically reviewed by Kimberly Brown, MD. It’s the part you can see and touch.
The Human Ear
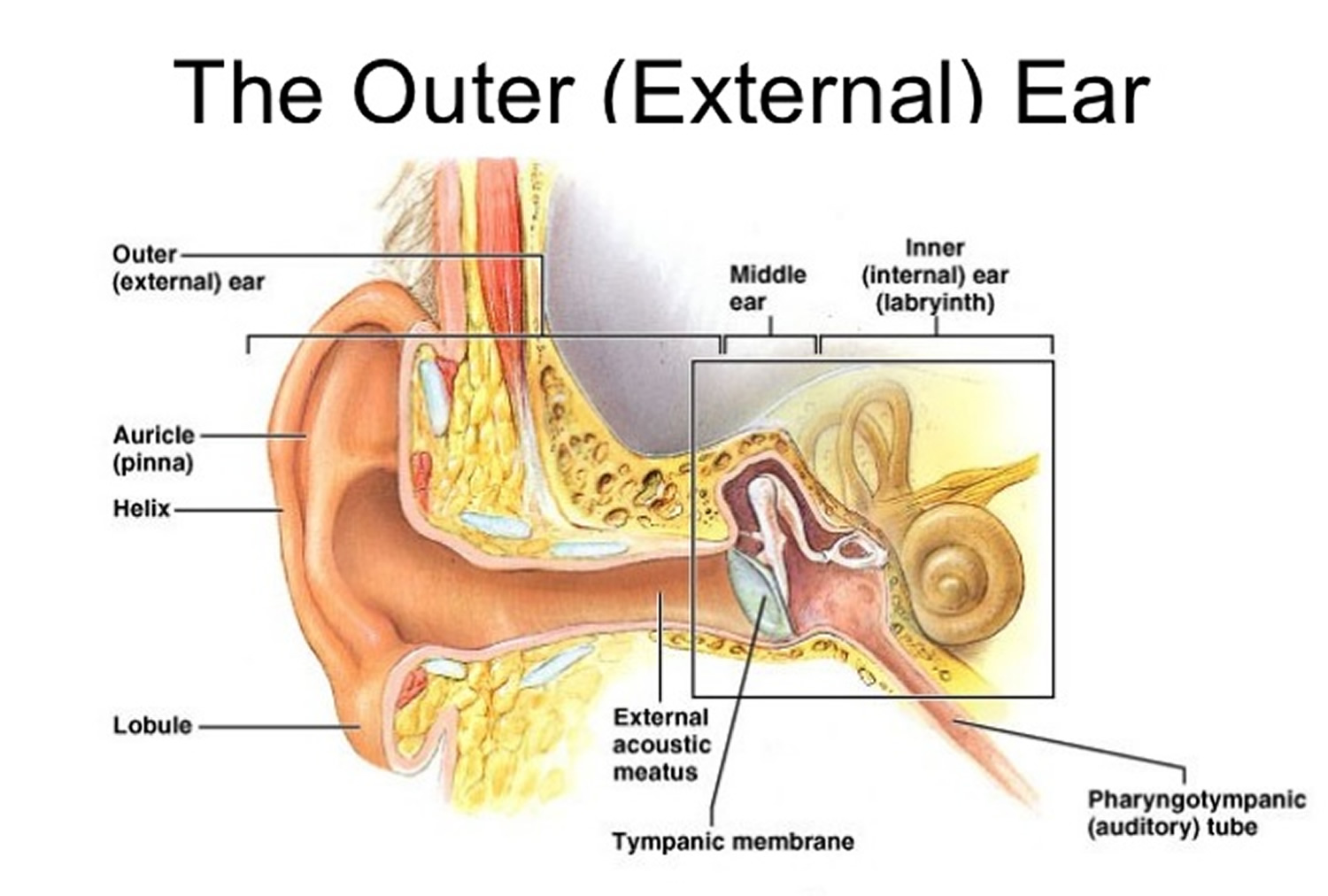
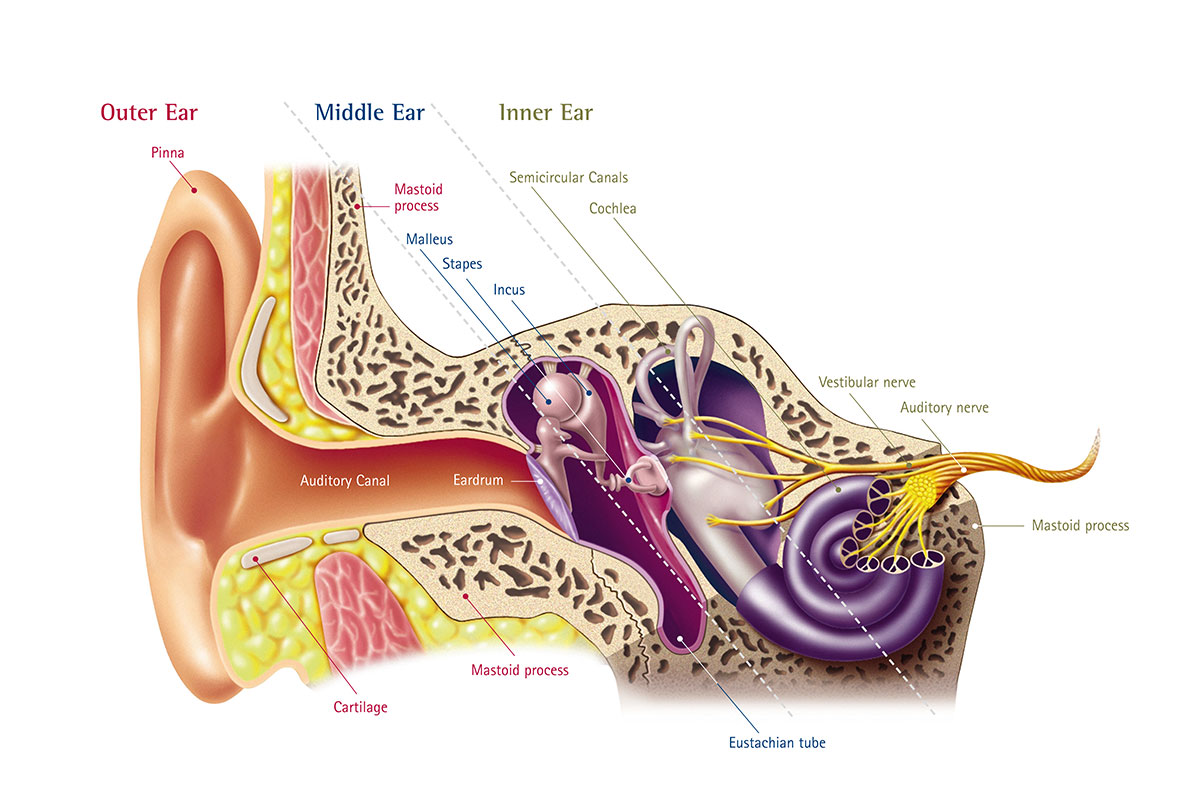
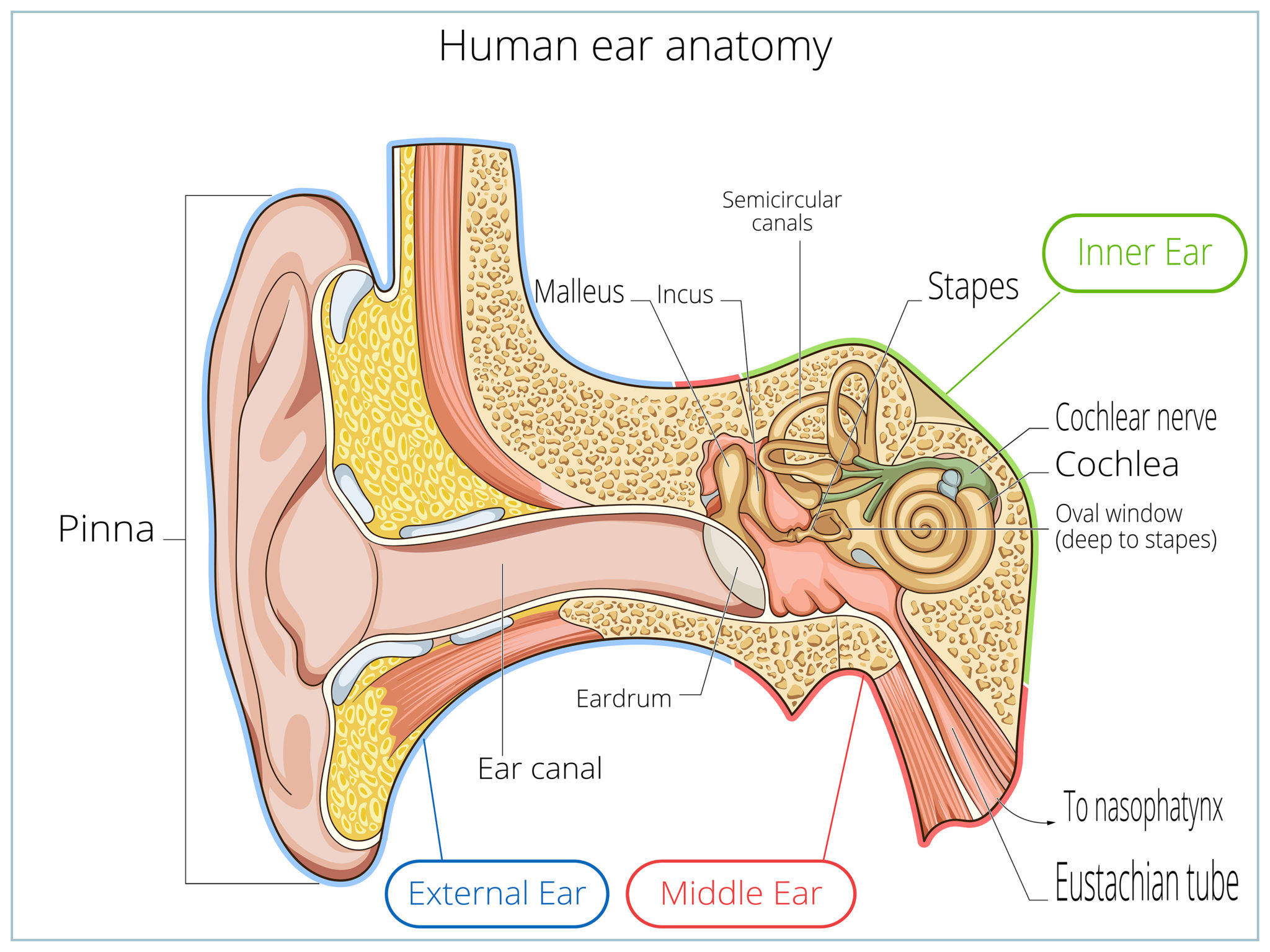
The ear can be divided into three parts; external, middle and inner.The ear has three main sections: the outer, middle, and inner ear. Helix: It is the prominent outer rim of the external ear.
The Ear: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
Your inner ear is a complicated, delicate and essential part of your body. In this section, we describe the .Anatomically, the human hearing system can be thought of in three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.The Anatomy of the Ear. The cochlea is a spiral tube that is coiled two and one-half turns around a hollow central pillar, the modiolus. either of the two organs, one on each side of the head, by which people or animals hear sounds, or the piece of skin and tissue outside the head connected to this organ: .
Scientists Behind the Lab Mouse With a Human Ear Speaks
The human ear can’t hear all sound frequencies—very low or very high frequencies, for example. Every minute of every day, your inner ear turns sound waves into sounds that keep you safe and enrich your life. The tympanic membrane divides the external ear from the middle ear. However, as shown on this graph, all sounds above 90 dB are damaging the inner ear and even doing irreversible damage above 120 dB.
Outer ear: Anatomy, blood supply, innervation
They implanted the . This means that to hear a very low-pitched frequency, like 20Hz, at the same perceived loudness as a noise of 1kHz (1000Hz), you would need to increase the dB by +50. In dogs, the pinnae are mobile and can move independently of each other. The outer ear starts with the pinna. Auditory Ossicles: The three small bones in the middle ear .

A frequency, while not the same as a pitch, is correlated to the pitch of a sound. Outer ear, middle ear . These frequencies bring us the joys of bass beats and bird songs, but it’s the middle . Updated on August 18, 2023.either of the two organs, one on each side of the head, by which people or animals hear sounds, or the piece of skin and tissue outside the head connected to this organ: The . Several studies have observed the aforementioned association between age and ear elongation. These three components are connected to each other via the ear canal. It bears a striking resemblance to the shell of a snail and in fact takes its name from the Greek word for this object. Ultrasonic Sounds and Infrasounds. The ears not only provide the ability to hear, but also . He put his hands over his ears.
This is true for the middle frequency range (1-2 kHz). published 22 April 2021. Some sources will also refer to this structure as the pinna, though that term is more appropriate for a structure . The outer ear is situated superficially next to several bony landmarks. Below you can see how the new Point ear . A plethora of anomalies and deformities exist, adding complexity to the human external ear landscape.The human ear is an astounding transducer, converting sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse that is transmitted to the brain. The tones, sounds, and speech we hear are actually nothing but oscillations of the air.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min
Ear Anatomy, Diagram & Pictures
Decibel Levels And Hearing Health: What To Know
Molly’s first 24 hours home has been wonderful for all of us, Ms Wells and Mr .The ear is a sensitive organ of the human body. Hearing loss and balance problems can come without warning and can get worse over time.
How does the ear work?
The human ear hears different frequencies differently because our ears evolved to accentuate and ignore different sounds necessary for survival.Human ear – Eardrum, Ossicles, Hearing: The thin semitransparent tympanic membrane, or eardrum, which forms the boundary between the outer ear and the middle ear, is stretched obliquely across the end of the external canal.Humans can hear sounds ranging from about 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.The myth also spans the world.You might have thought that the mouse was genetically engineered, or deformed, or the result of mad scientists “playing God. An elastic partition runs from the beginning to the end of the . Screen your hearing in less than 5 minutes. Organs of human hearing are located on either side of the head. Don’t worry, though—each part has a purpose that is easy to understand.The membrane is held in place by a thick ring of cartilage, a tough but flexible kind of tissue. Vibrations are transmitted via three small bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) to the membranous oval window, which links the middle . This is referred to as noise-induced hearing loss. The parts of the ear include: External or outer ear, consisting of: Pinna or auricle. This feature aids in pinpointing the source of sounds.Average ear size: This Post covers the Human Ear! It covers basic information such as average ear size, the earlobe size, as well as the Hearing Thresholds. Its diameter is about 8–10 mm (about 0.Hearing, or audition, is the transduction of sound waves into a neural signal that is made possible by the structures of the ear ( Figure 21.Human ear – Cochlea, Hearing, Balance: The cochlea contains the sensory organ of hearing.The human ear usually hears sounds that are 20–20,000 hertz.Autor: Mahesh Shenoy Medically reviewed by Jordana Haber Hazan, MD.

the left/right ear. However, in perfect lab conditions, some people can hear sounds as low as 12 hertz or as high as 28,000 hertz. Again, this is all due to the . It is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same . By Mark Gurarie. The Anatomy of Outer Ear. Twenty years ago, a mouse with a human ear on its body caused waves of anger and criticism, but the reality later proved the value of this experiment.The bones in the middle ear amplify, or increase, the sound vibrations and send them to the cochlea, a snail-shaped structure filled with fluid, in the inner ear. It is mainly concerned with detecting, transmitting and transducing sound.Synonyms: External auditory meatus, External acoustic pore , show more.The human ear, under normal circumstances, perceives frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz or 20 kHz. The pinna is shaped to capture sound waves and funnel them through the ear canal to the eardrum. It is posterior to the zygomatic process of the temporal bone as well as the proximal part of the mandibular process and the auricular surface of the mandibular notch. However, unlike humans, who have visible external ears, owls’ ears are openings located on the sides of their heads.
Decibels Decoded: A Guide to Understanding Loudness
The ear is the organ of hearing and balance.The ear is the organ of hearing; it enables the perception of sound.For the full article, see human ear . Tympanic membrane and middle ear.
There are several conditions that can affect your ears, including infection, .

human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction (or the conversion of sound waves into electrochemical impulses) and maintains the sense of balance . The tympanic membrane’s function is to assist in human hearing. It also helps you stay balanced. Updated on June .The ear picks up sound waves and transforms them into electrical signals which travel along nerves to the brain. Updated on August 16, 2023. Tympanic membrane (eardrum). The lower frequencies are associated with bass sounds like deep voices or bass drums, while the higher frequencies help us to hear high-pitched sounds like birds singing or a baby’s cry.
The External Ear
The Importance of Early Detection Structures of the human ear. Ears: Facts, function & disease. How Do We Hear? Hearing depends on a series of complex steps that change sound waves in the air into electrical signals.Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels.Your ears are paired organs, located on each side of your head, which help with hearing and balance.Video ansehen7:36So our ear can be divided into three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. By the age of 6 years, the ear is nearly 85% of its full size and 90% of its full size by the age of 9 years old.The world of ear shapes is more diverse than one might think. This is the outside part of the ear.What Is the Anatomy of an Ear? The ear is an unusually complex organ in human anatomy. Hearing: The eardrum vibrates .This article will focus on the anatomy of the external ear – its structure, neurovascular supply and clinical correlations. External auditory canal or tube.Home Medicine – Health Health.
Hearing range
It is known that, as technology advances, medicine will advance to the point . Home Health & Medicine Anatomy & Physiology. Researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine and Cornell Engineering have replicated an adult human ear using a combination of 3D . Some studies provided hypothetical explanations, with seemingly plausible mechanisms, but without proven .
Tympanic Membrane Pictures, Function & Anatomy
Human ear
Sound beyond the lower end of the audible range of human hearing is called infrasound, while high-frequency sounds above 20,000 Hz are called ultrasonic sounds. Anything above 85 dBA can damage the small hair cells in your ears and affect your hearing health, either over time or—if it’s loud enough—immediately. It forms a cone approximately 9 mm .The ears are organs that provide two main functions — hearing and balance — that depend on specialized receptors called hair cells. The asymmetrical placement of their ears is also another key feature that sets them apart. Antihelix: It is the cartilage curve that is situated parallel to the helix.

Although human height stays the same after approximately 20 years of age, the size of human ears seems to continue to increase. See all videos for this article. Twenty years ago, Harvard surgeons Joseph and his brother Charles Vacanti, along with MIT engineer Bob Langer, experimented with techniques to create human body parts in the lab. The large, fleshy structure on the lateral aspect of the head is known as the auricle. Any sound below 20 Hz is considered an infrasound while anything above 20 kHz is called an ultrasound. By Alina Bradford.audiologyresearch. The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts; the auricle (or pinna), and the external acoustic meatus – which ends at the .The Structure of Human Ear. Each section serves a distinct purpose in hearing. /ɪə (r)/ /ɪr/ Idioms.comEar Anatomy: Understanding the Outer, Middle, and Inner .4 inch), its shape that of a flattened cone with its apex directed inward.Anatomy of the Ear | Geeky Medicsgeekymedics. Understanding these variations isn’t just about knowing what makes us unique but also carries significant health implications.Superior to it is the squamous part of the temporal bone, while the styloid process .The human ear as a dyamic range from 0dB (threshold) to 120-130 dB.
Outer Ear: Anatomy, Location, and Function
A 2016 survey of modern central European insect folklore reported that the critter .Anatomy of the Human EarEndolymph and PerilymphCochlear Nerve, Auditory PathwaysBone Conduction, Hearing, VibrationSound Waves, Outer & Middle EarOrgan of Corti
Ear anatomy: Parts and functions
Average Ear Size. Human beings cannot hear these . Also available: . By Rachael Zimlich, BSN, RN.
- What If Moira Was 60 Years Old?
- What Is A Login Manager? – What Is Log Management? A Complete Logging Guide
- What Is A Linear Switch? – Should I use a linear charger or a switching charger?
- What Is A Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Surgery (Mavr)?
- What Is A Certificate Of Analysis?
- What Is A Strategic Approach To Hrm?
- What Is A Morph Cut Transition?
- What Is A Battle Belt , Picking The Right Holster for Your Battle Belt
- What Is A Grumman F6F Hellcat?
- What Is A Hobbit House , Hobbit Homes and Hobbit Architecture: Building with Soul
- What Is A Conflict Check In A Law Firm?
- What Is A Final Keyword? – The final Keyword in Java
- What Is 40S Slang? _ The 1980s Slang That Defined The Decade