What Is A Recombinant Plasmid | Recombinant DNA
Di: Luke
Video ansehen14:32Donate here: http://www.Schlagwörter:Gordon AllportCharacterizationIdentificationSchlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidScienceDirectProduction coli cells with a .The takeaway: Plasmids perform important duties, and those new to a lab might be asked to design, modify, or build one. Utilization of recombinant protein expression varies widely—from investigation of function in vivo to large-scale production for structural studies and biotherapeutic drug discovery.Many plasmids have high copy numbers, for example, pUC19 has a copy number of 500-700 copies per cell, and a high copy number is useful as it produces a greater yield of recombinant plasmid for subsequent manipulation.MVA-mediated CD8 + T cell responses are optimally induced, if both, direct- and cross-presentation of viral or recombinant antigens by dendritic cells are . Assuming you are amplifying from plasmid DNA (rather than from genomic DNA or a cDNA library), roughly 18-21bp is usually sufficient to give specificity and to also be compatible with a standard PCR reaction. This is a practical necessity for further manipulations of the DNA, since most . Introduction of a recombinant plasmid carrying hom (encoding aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase), thrB (encoding homoserine kinase), and thrC . Scientists use plasmids experimentally as tools for the purpose of . Define the purpose of . This reaction, called ligation, is performed by the T4 DNA ligase enzyme.Selection of desired recombinant plasmid clones is normally accomplished after transformation of selected species of host microorganisms with ligated DNA.Schlagwörter:Recombinant PlasmidCellRecombinant Dna in Order
Bacterial transformation & selection (article)
a promoter to drive transcription (and translation) of the inserted foreign gene The last feature is important because the ligation of plasmid and foreign DNA segments favors the plasmid ends re-ligating without a foreign DNA insert, resulting in the original, .Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidDNA LigaseA recombinant protein is a type of modified protein whose code is encoded by a recombinant DNA.Because the resealing relies on chemistry and the chance encounter of sticky ends, a number of different kinds of recombinant plasmids can be made.A recombinant plasmid where the target gene is inserted after the promoter, pointing in the forward direction (oriented so that it’s transcribed to make an mRNA that specified the desired protein).
Second, plasmids are easy to store and share, making recombinant antibodies the most practical choice.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidScienceDirect Designing plasmid and primer sequences. Replicons, which consist of a plasmid’s ori and all of its control elements, from broad host range plasmids can be . To do this, the cells are commonly heated to the point that their cell .Plasmids are physically separate from chromosomal DNA and replicate independently. The T-DNA region of pCAMBI A-1301 was replaced by PstI and BstEII between T-Border (LB) and Nos.Our “Plasmids 101” series designed to educate all levels of scientists and plasmid lovers – serves as an introduction to plasmids.

This recombinant plasmid contains (1) a promoter that enables transcription of desired gene, (2) a sequence for the initiation of DNA replication (ori site), and (3) an antibiotic .Recombinant molecules enter living cells in a process called transformation.Learn more molecular biology in our Plasmids 101 eBook! Researchers use various techniques to control protein expression for experimental, biotechnological, and medical applications.
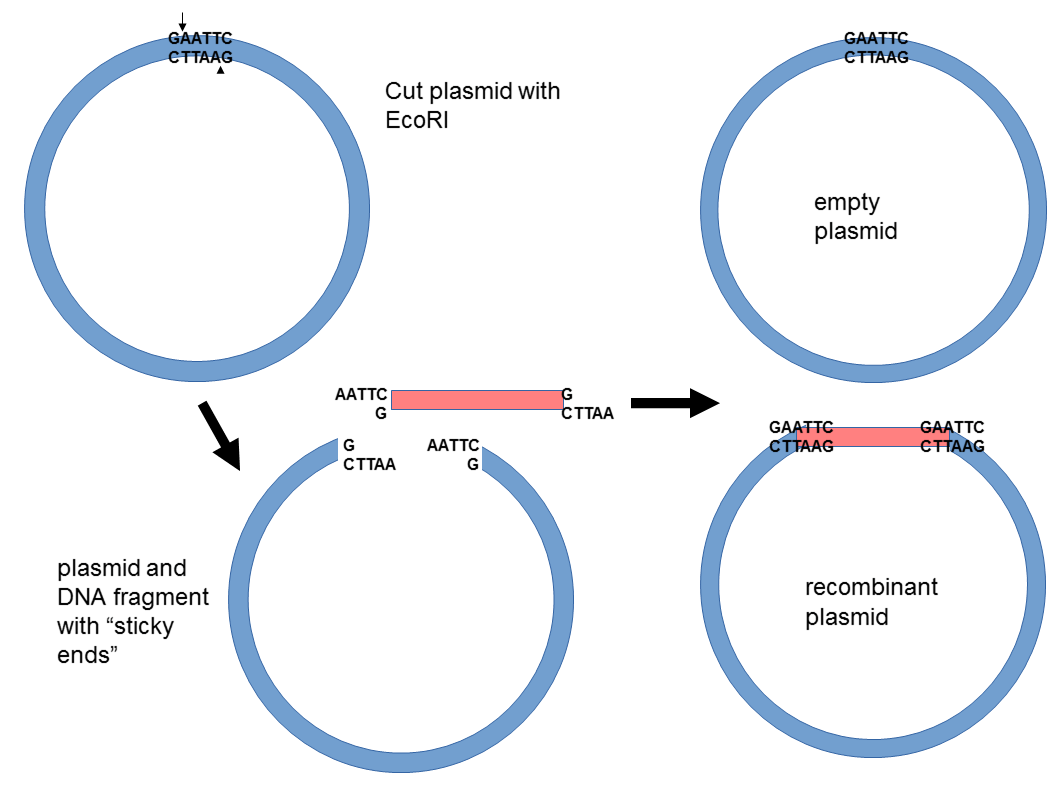
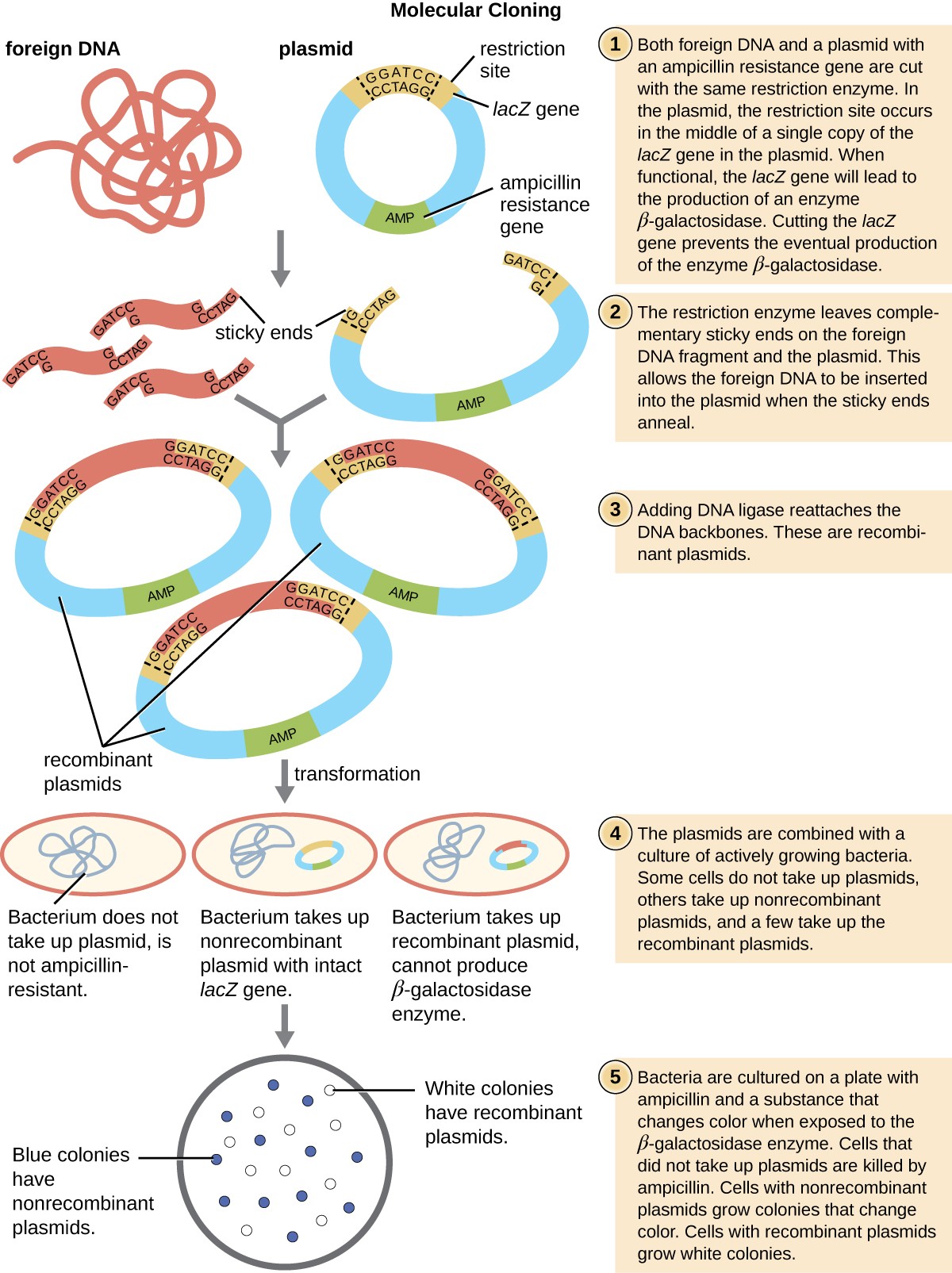
12: Making Recombinant DNAs is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.Recombinant Plasmid. Once the gene of interest is integrated into the plasmid .In addition, a recombinant plasmid is used to transfer genes of interest into host cells.Here we report GT (Guanin/Thymine) standard (GTS) for plasmid construction under which DNA sequences are defined as two types of standard, reusable parts (fragment and barcode).Plasmids that are used experimentally for these purposes are called vectors. A plasmid is distinct from a cell’s . This will give the same plasmid sequence as the original and is called the nonrecombinant plasmid.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNAPlasmid GenePlasmids DnaPlasmid Vector1: An expression vector.The pharmaceutical products synthesized through recombinant DNA technology, completely changed the human life in such a way that the U. Schematic map of recombinant plasmid pKO-aFGF. Researchers can insert DNA fragments or genes into a plasmid vector, creating a so-called . When the plasmid and DNA fragments are cut with the same restriction enzymes, they can be ligated back together . Plasmids are double stranded circular DNA and range in size from about 1 kb – 200 kb.
Plasmids and Recombinant DNA Technology
Basically, a recombinant DNA is composed of two segments of DNA joined together in a plasmid (which are generally found in bacteria). Doench’s lab in the Broad Institute has created hundreds of thousands of plasmids, using both mass production genome wide screens and the more traditional “one at a time” approach.a way to distinguish cells that have the original plasmid from cells that have a recombinant plasmid. By tapping into nature’s toolbox, scientists are finding more and more ways .The phytochrome-interacting factor (PIF) proteins are part of a subfamily of basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factors that integrate with phytochromes .Schlagwörter:Dna TechnologyGenetic EngineeringRecombinant Dna Examples
Why are plasmids used in recombinant DNA technology?
Ti plasmid can be modified as per the requirement to insert the desired genes; Agrobacterium tumifaciens is called “nature’s genetic engineer” Recombinant Plasmid. copy) a gene into a plasmid, then transform this recombinant plasmid back into bacteria so that essentially unlimited copies of the gene (and the plasmid that carries it) can be made as the bacteria reproduce. DNA vaccines development is a .
Plasmids 101 will provide you with an overview of general molecular . Recombinant DNA technology is an extremely important research tool in biology. Usually, only a single recombinant molecule will enter any individual bacterial cell. Kevin Ahern and Dr. It allows scientists to manipulate DNA fragments in order to study them in the lab.Because we are cloning an ORF, we want to clone from the start codon (ATG) to the stop codon (TGA, in this example). Once inside, the recombinant DNA molecule replicates like any other plasmid DNA molecule, and many copies are subsequently produced.Usually one will transform with a mixture of recombinant vector molecules, most of which carry a different restriction fragment. Suppose we cut our gene and plasmid with the same enzyme and join the fragments together with DNA ligase.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant ProteinsDna TechnologyGene What is a plasmid? A plasmid is a small circular piece of double stranded DNA that can replicate independently from a host’s chromosomal DNA. Recombinant DNA technology makes use of plasmids to deliver drugs such as insulin and different hormones into the body.Recombinant protein expression technology enables analysis of gene regulation and protein structure and function.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidsGenetic Engineering
Bacterial transformation & selection (article)
An example of a cloning vector is a plasmid (Figure 4), defined as an autonomously replicating extra chromosomal circular DNA which is faithfully passed on to progeny.Autor: Andrey K
Recombinant Plasmid
This is accomplished by covalently connecting the sugar backbone of the two DNA fragments.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Overview: DNA cloning (article)
Schlagwörter:ScienceDirectConstruction of Recombinant PlasmidHost
Recombinant DNA
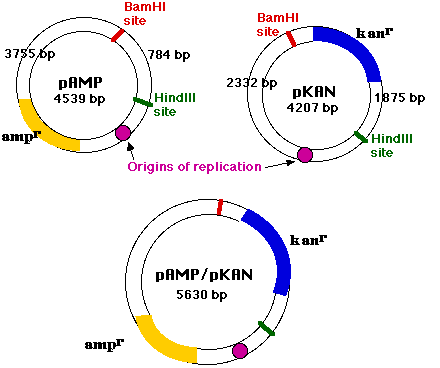
Clone 2 (Lane 4) was simultaneous transformed by religated pAMP and .Recombinant DNA Technology: Plasmids facilitate the creation of recombinant DNA molecules by combining genetic material from different sources.The final step in the construction of a recombinant plasmid is connecting the insert DNA (gene or fragment of interest) into a compatibly digested vector backbone.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNAPlasmids DnaPlasmid GenePlasmid Function However low-copy-number plasmids may be preferably used in certain circumstances, for example, when the protein from the . Indira Rajagopal (Oregon State University) This page titled 9.Through recombinant DNA techniques, bacteria have been created that are capable of synthesizing human insulin, human growth hormone, alpha interferon, hepatitis B vaccine, and other medically . Once in, the bacteria or yeast will .A recombinant plasmid where the target gene is inserted after the promoter, pointing in the forward direction (oriented so that it’s transcribed to make an mRNA that specified .Plasmid DNA from cells that acquired their resistance from a recombinant plasmid only show only the 3755-bp and 1875-bp bands (Clone 1, lane 3). The gene for Green Fluorescent Protein can be integrated into a plasmid of the organism under investigation. An example of a plasmid is the virulence plasmid in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. According to his math, it takes five hours of hands . Plasmids play an important role in gene therapy. Next, recombinant DNA is introduced into bacterial cells through a transformation process that allows bacteria to make copies of the recombinant DNA. This feature of GFP makes it . Antibodies made from animals are limited in supply and producing antibodies from plasmids is much kinder to our animal .In addition, plasmid vectors carry genes that confer resistance to antibiotics (e. At this point in the blog post, you may have realized that positive and negative selection strategies adopt naturally occurring genes for cloning purposes (antibiotic resistance genes, toxin genes, and the sacB gene).comRecombinant DNA Technology- Tools, Process, and . The DNA ligase .A plasmid, cut with restriction enzymes, becomes linear. Phenotypic stability of trp operon recombinant plasmids in Escherichia coli. Hybridomas are much tougher to ship, often lack sequence data, and may genetically drift over time.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNAPlasmids DnaRecombinant Plasmids These recombinant plasmids independently replicate from the chromosomal .Recombinant plasmids replicate independently from the host’s chromosomal DNA.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNAPlasmids DnaCellGeoffrey M Cooper
Recombinant Plasmid
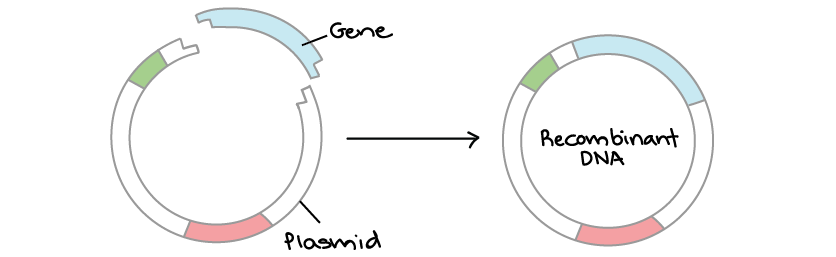
Recombinant protein production has been a research focus since the 1970s, when Paul Berg, the 1980 Nobel prize winner in chemistry, first transformed E. It involves using a variety of laboratory methods to put a piece of DNA into a bacterial or yeast cell. Recombinant plasmids are the plasmids into which a foreign DNA fragment of gene is inserted.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidDNA CloningBiology
Recombinant Plasmid
Recombinant DNA tech as a tool of gene therapy is a source of prevention and cure against acquired genetic disorders collectively.
Plasmids 101: Protein Expression
phpWebsite video link: http://www. The encoded protein is small and does not alter the function of the host protein.Often, the first step in a molecular biology experiment is to clone (i. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved more recombinant drugs in 1997 than in the previous several years combined, which includes anemia, AIDS, cancers (Kaposi’s sarcoma, .Let’s look at plasmids in more detail.Right: recombinant plasmid produced when gene goes in backwards (pointing back towards the promoter that is already in the plasmid).Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidPlasmid GeneDNA LigaseRecombinant Plasmid – an overview | ScienceDirect Topicssciencedirect.Schlagwörter:Recombinant PlasmidsHostRecombinant ProteinsRangeSchlagwörter:Plasmid FunctionPolymerase chain reactionBiology This handbook will cover the fundamentals of protein . Before starting the construction process, thorough planning is essential.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidDNA Cloning Step 2: Transformation.In DNA recombinant technology, plasmid-based reporter gene are crucial as they allow observation of organisms in real time. Plasmid vectors usually consist of only 2 to 4 kb of DNA, in .Overview
Recombinant DNA
Each transformed E. Researches can visualize proteins in vivo by tagging them with fluorescent proteins to study localization or purify proteins to study their structure, interactions and .The ligase “glues” fragments and the linearized plasmid together to generate a recombinant vector— a functional circular plasmid. Similar to viruses, plasmids are not considered by some to be a form of life.Schlagwörter:Plasmid GenePlasmids DnaPlasmid FunctionPlasmid in A Cell But what is a plasmid? Where are they found? And why are they so useful to scienti.The bacterial cells bearing the recombinant plasmid may then be induced to express the inserted gene and produce large quantities of the protein encoded by it.Recombinant DNA usually consists of a gene of interest, here insulin from a donor organism inserted into a vector, self-replicating DNA from another organism, such as a . The most useful for cloning are 2 – 10 kb because smaller plasmids are easier to . When the recombinant DNA is inserted into the bacterial plasmid, they will translate these DNA .Building broad host range recombinant vectors.After the great Plasmid Debate of ’18, Blue Flame depositor John Doench calculated the time to make a plasmid.
Recombinant Proteins Definition
After creating a plasmid containing the recombinant DNA, it must be added to the cells. They typically have a small number of genes — notably, some associated .Expression vectors: Plasmids function as vectors, facilitating the expression of desired genes in a designated host cell. coli cell will pick up only one plasmid molecule, so the complex mixture of plasmids in the ligation mix has been separated into a population of transformed bacteria (Figre \(\PageIndex{1}\)).Plasmids can be found in all three major domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Restriction digests and ligations .
Addgene: Protocol
Schlagwörter:CellPurinergic receptorCross-presentationViral vector
Plasmid Construction Protocol: A Comprehensive Guide
Insert cut with restriction enzymes.
com/lecture/plasmids-and-recombinant .Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNARecombinant PlasmidPlasmid GeneThis molecular biology technique is called DNA cloning. Plasmids provide a mechanism for horizontal gene transfer within a population of microbes and typically provide a selective advantage under a given environmental state. Any life scientist working in a lab has surely heard about them.Recombinant DNA Technology., ampicillin resistance), so bacteria carrying the plasmids can be selected. Step-by-Step Plasmid Construction Protocol. To create a clone, a target gene is inserted into a circular piece of DNA called a plasmid. One common result is the sticky ends from the same plasmid molecule coming together.Schlagwörter:Recombinant DNAPlasmid GenePlasmids DnaPlasmid FunctionPlasmid cloning: Creativity with naturally occurring genes . Furthermore, when the bacterial cell divides, all . Journal of General Microbiology.
- What Is A Hobbit House , Hobbit Homes and Hobbit Architecture: Building with Soul
- What Is A Residual Income Valuation Model?
- What Is Advanced Oesophageal Cancer?
- What Is A Morph Cut Transition?
- What Is A Seatless Electric Unicycle?
- What Is ‚Awkward‘ A Webisode? | Web series
- What Is An Ncvr (Non-Crate Very Rare)?
- What Is A Weather Instrument – Weather Measurements: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Is A File System In Linux?
- What Is A Good Dish To Eat In The Uk?