What Is Cross Site Forgery , What Is CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery)?
Di: Luke
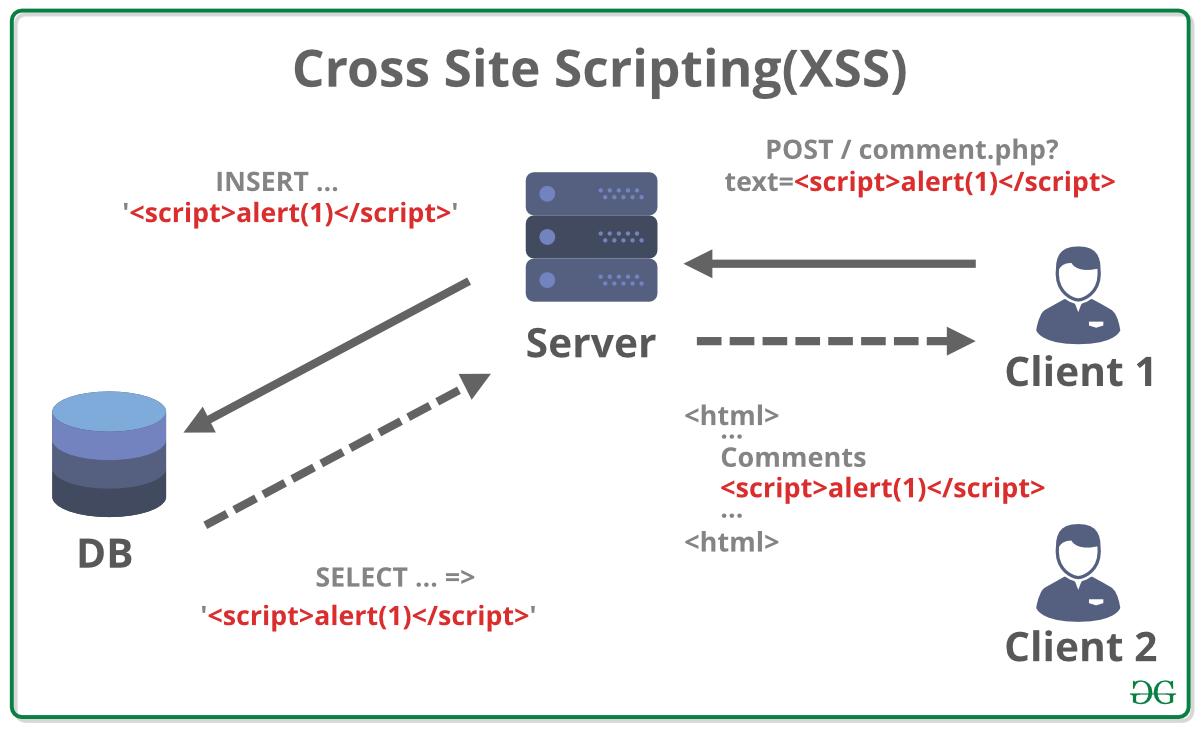
Anti-CSRF and AJAX. Specifying the SameSite Attribute on your session cookie. This makes a CSRF attack different from a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack because although an XSS—and a reflected XSS—attack also changes information on the .Cross-site request forgery (CSRF), also referred to as Session Riding or XSRF, is an attack vector that exploits the trust a website has in an authenticated user’s browser, tricking it .
What is Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)?
A CSRF attack tricks users into submitting a malicious request.
Complete Guide to CSRF/XSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery)
What is Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) – GeeksforGeeks. The entire premise of CSRF is based on session hijacking, . Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack where a malicious site sends a request to a vulnerable site where the user is currently . CSRF attacks exploit the trust a Web application has in an authenticated user.Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they’re currently. In general, it doesn’t directly steal the user’s identity, but it exploits the user to carry out an action without their will. Cross-site request forgery or CSRF attacks are also sometimes . The attacker can use this attack to steal sensitive information such as login .Übersicht
Cross-site request forgery
CSRF attacks can: Alter the target’s records in an application. Last Updated : 08 Mar, 2019.

The server authenticates the user.
Cross-Site Request Forgery: An Explanation with real-life Example
This security flaw exploits the trust that a site has for the user’s browser, potentially leading to unauthorized commands being transmitted .Cross-site request forgeries (CSRF) and state changes.Cross-site scripting (or XSS) allows an attacker to execute arbitrary JavaScript within the browser of a victim user.Overview
What is cross-site request forgery?
CSRF attacks specifically target state-changing requests, not theft of data, since the attacker has no way to see the response to the forged request. During a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attack, a hacker does something under a victim’s authentication. It allows an attacker to circumvent the same origin policy, which is designed to segregate different websites from each other. These attacks are possible because web browsers send some types of authentication tokens automatically with every request to a website. (Conversely, cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks exploit the trust a user has in a .
CSRF Attacks: Anatomy, Prevention, and XSRF Tokens
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is an attack in which a malicious web site, email, blog, instant message, or other program makes the victim’s web browser perform a function without the victim’s initial knowledge, on a trusted site where the user is currently authenticated.

Therefore, the attacker abuses the trust that a web application has for the .跨站点请求伪造(Cross Site Request Forgery)又被称作 CSRF,是恶意站点或程序通过已认证用户的浏览器在受信任站点上执行非正常操作。可进行的恶意操作局限于已在网站通过身份验证的用户的功能。 例如,Jane 可能会在查看电子邮件的同时登录了她的网上银行,然后可能会点进钓鱼邮件中的自带转账 .Cross-Site-Request-Forgery (CSRF oder XSRF abgekürzt) ist eine Angriffsmethode, die meist für Internetbetrug genutzt wird. Such attacks take advantage of the fact that a website completely trusts a user once it can confirm that the user is .Description Cross-site Request Forgery (moving forward, CSRF) is a security vulnerability usually found in web applications. Dies geschieht über HTTP-Request. 2 — Cross Site Request Forgery Proof of Concept. Spring provides two mechanisms to protect against CSRF attacks: The Synchronizer Token Pattern. This simply means that the attacker sends a request to modify the data on the server on the victim’s behalf.Cross-site request forgery is an attack against web-hosted apps whereby a malicious web app can influence the interaction between a client browser and a web app that trusts that browser. A user logs into a website, and somehow, that person’s login .Cross-Site Request Forgery, also known as Session Riding or One-Click attack, and abbreviated to CSRF or XSRF, is a type of attack that exploits the user’s identity and privileges to execute unintended actions on a web application.
Was ist Cross-Site Request Forgery?
To protect against CSRF attacks, we need to ensure there is something in the request that the evil site is unable to provide so we can differentiate the two requests. One of the first things you need to wrap your head around is that cross-site request forgeries involve changing the state of data on a website’s server. A successful CSRF attack can be devastating for both the business and user.A CSRF (cross-site request forgery) tricks authenticated users into granting malicious actors access through the authentic user’s account.Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) A Cross Site Request Forgery or CSRF Attack, pronounced see surf, is an attack on an authenticated user which uses a state session in order to perform state changing attacks like a purchase, a transfer of funds, or a change of email address.Cross-site request forgery (CSRF), also referred to as Session Riding or XSRF, is an attack vector that exploits the trust a website has in an authenticated user’s browser, tricking it into executing unwanted actions. Environment A web application being delivered to .A Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attack occurs when a malicious web site, email, blog, instant message, or program tricks an authenticated user’s web browser into .The impact of the attack depends on the level of permissions that the victim has.Cross site request forgery (CSRF), also known as XSRF, Sea Surf or Session Riding, is an attack vector that tricks a web browser into executing an unwanted . Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is one of the most severe .Cross site request forgery (CSRF), also known as XSRF, Sea Surf or Session Riding, is an attack vector that tricks a web browser into executing an unwanted action in an application to which a user is logged in.Examples of Cross-Site Request Forgery Attack Cross-Site Request Forgery attack is executed when a cybercriminal copies the layout, design, or website format from where data is being pulled [1] . Here is an example of a CSRF attack: A user logs into www.com using forms authentication.Cross-site scripting (also known as XSS) is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to compromise the interactions that users have with a vulnerable application. The response from the server . This can be done, for example, by including malicious parameters in a URL behind a link that purports to go somewhere else:
CSRF Attack: Cross-Site Request Forgery Definition & Defense
A typical Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF or XSRF) attack aims to perform an operation in a web application on behalf of a user without their explicit consent. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack that forces authenticated users to submit a request to a Web application against which they are currently authenticated.Cross site request forgery (CSRF or XSRF) refers to an attack that makes the end-user perform unwanted actions within a web application that has already granted them . These attacks typically involve malicious social engineering, such as emails or links, that deceive the user into sending .Cross-site request forgery (CSRF), also known as session riding, is a type of cyberattack in which authenticated users of a web application are forced to submit malicious, state-changing requests created by an attacker. Submit a transaction. Cross-site request forgery (or CSRF) allows an attacker .CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) is an attack that impersonates a trusted user and sends a website unwanted commands.Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that occurs when a user clicks on a malicious website, email, or another message that causes the user’s web browser to perform an unwanted action on a trusted site on which the user is currently authenticated. It can result in damaged client relationships, .
How to test for Cross-Site Request Forgery?
Cross-Site-Request-Forgery
Back to all learning paths.Cross-Site Request Forgery ( CSRF) testing is the procedure of finding and remediating CSRF vulnerabilities in web applications. CSRF lets attackers partly bypass the same-origin policy (SOP) and cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) . Kriminelle übernehmen eine .Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they’re currently authenticated.
Since this is a PoC, we would click on .The attacker is able to trick the victim into making a request that the victim did not intend to make.Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) tricks victims into performing unwanted actions on web applications where they’re authenticated, often without their knowledge.Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF or XSRF) is a type of attack on websites.Ein Cross-Site-Request-Forgery-Angriff ist eine Art Confused Deputy* Cyberangriff, der einen Nutzer dazu verleitet, versehentlich seine Anmeldedaten zu verwenden, .Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a web security vulnerability that allows attackers to trick users into performing actions they did not intend to do on web applications where they are authenticated. Once this HTML page is opened, it shows a “Submit request” button, as shown in the below image. Let’s understand a CSRF example in the context of a user logging into an e-commerce portal to purchase a product. An application vulnerable to CSRF allows an attacker to force a victim user to execute unwanted actions in a web application to which they are currently authenticated.Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) – PortSwigger. With a successful CSRF attack, an attacker can mislead an authenticated user . Cross-site scripting vulnerabilities .
What are Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks?
What is Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
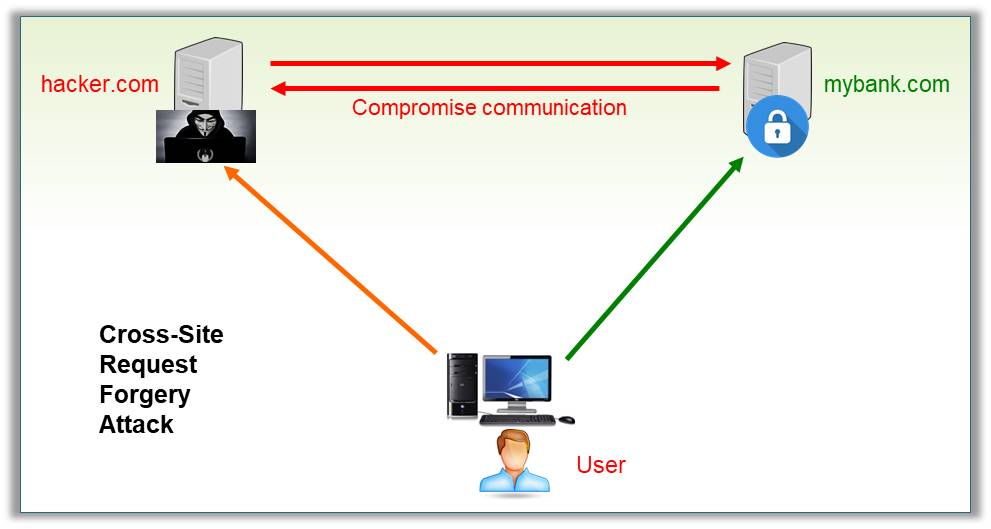
By performing a CSRF attack, the attacker inherits the identity and privileges of the victim to perform an undesired function on behalf of the victim.

This form of exploit .Cross-site Request Forgery, also known as CSRF, Sea Surf, or XSRF, is an attack whereby an attacker tricks a victim into performing actions on their behalf.Cross-site request forgery attacks (CSRF or XSRF for short) are used to send malicious requests from an authenticated user to a web application. Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) This learning path covers CSRF .Cross Site Request Forgery, or CSRF occurs when a malicious site or program causes a user’s browser to perform an unwanted action on a trusted site .Cross-site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF), also sometimes called sea surf or session riding, refers to an attack against authenticated web applications using cookies. Kriminelle übernehmen eine vom Nutzer autorisierte Session (Session Riding) und können so schadhafte Aktionen durchführen. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is an attack where a malicious site sends a request to a vulnerable site where the user is currently logged in.
What Is CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery)?
Cross site request forgery (CSRF or XSRF) refers to an attack that makes the end-user perform unwanted actions within a web application that has already granted them authentication.
XSS vs CSRF
Cross-site request forgery is an attack against web-hosted apps whereby a malicious web app can influence the interaction between a client browser and a .
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
If the request is . eine Überweisung von seinem Konto, die Änderung seiner E-Mail-Adresse und seines Passworts oder eine andere .
Definitions: An attack in which a subscriber currently authenticated to an RP and connected through a secure session browses to an attacker’s website, causing the .A cross site request forgery attack is a type of confused deputy* cyber attack that tricks a user into accidentally using their credentials to invoke a state changing activity, such as .Cross-Site Request Forgery – जिसे CSRF, XSRF या Cross site reference forgery के रूप में भी जाना जाता है – एक प्रकार का हमला है जो तब होता है जब कोई Malicious website किसी अन्य वेबसाइट या वेब एप्लिकेशन को अपना .Ein Cross-Site-Request-Forgery-Angriff ist eine Art Confused Deputy* Cyberangriff, der einen Nutzer dazu verleitet, versehentlich seine Anmeldedaten zu verwenden, um eine Aktivität auszulösen, die den Status verändert, z. It’s a bit like a magic trick.
- What Is Dynamic Dns? _ What is DNS & Dynamic DNS?
- What Is Fitt Exercise? – The FITT Principle Explained
- What Is Asu Logo? – About ASUS
- What Is Chi Square Test In R? – What is a Chi-Square Test? Formula, Examples & Uses
- What Is F In Chemistry – Chapter 9: Reaction Systems
- What Is Diffusion Process In Probability Theory
- What Is Copy And Paste : How to Copy and Paste in CorelDRAW
- What Is Cn Tower In Canada , CN Tower in Toronto
- What Is Crawling – Website Crawling: The What, Why & How To Optimize
- What Is Gta 5 Online Download?
- What Is Cake Mania About? , Buy Cake Mania Main Street CD Key Compare Prices
- What Is Arial Rounded Font? , Arial® Rounded Bold
- What Is Font Color? , HTML Font Color Chart, Codes & Complete List of Color Names
- What Is Chapter 1 Of World Of Goo?