What Is Fastidious Bacteria? | Growing Fastidious Microorganisms in the Laboratory
Di: Luke
indigenous human flora and oral biota. It has been implicated in cases of bacterial endocarditis. The most important feature of fastidious bacteria is that they have a very complex set of nutritional requirements. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1.
Specialized media are used in the identification of bacteria and are supplemented with dyes, pH indicators, or antibiotics.

One type, enriched media, contains growth factors, vitamins, and other essential nutrients to promote the growth of fastidious organisms, organisms that cannot make certain nutrients and require them to be added to the . Growth media contain a variety of nutrients necessary to sustain the growth of microorganisms.Propagation of bacterial strains can vary significantly between species. A 1 log reduction in the number of viable organisms was . The media can be made suitable for the cultivation of other fastidious organisms by the addition of different biological fluids such as horse or sheep blood, serum, egg yolk, etc. There are two commonly used physical forms of growth media: liquid media and solid growth media.
eucast: AST of bacteria
Bacteria of the genus Gemmata, phylum Planctomycetes 1 form a group of organisms of interest in environmental sciences and medicine 2.Fastidious bacteria. The basis of all susceptibility testing is the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). – Other examples of non-fastidious bacteria are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus. Click the card to flip ?.
Growing Fastidious Microorganisms in the Laboratory
Recalcitrant bacteria are known collectively as fastidious bacteria, 1 and they have a predilection to cause, although not limited to, endocarditis. They are among the earliest known life forms on earth. Bordetella pertussis is readily inhibited by many normal constituents of media and the .
Bacterial Infections: MedlinePlus
Lithoautotrophic nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) are known as fastidious microorganisms, which are hard to maintain and not many groups are trained to keep . So, these bacteria do not . Walled bacterial pathogens also inhabit the water-transporting cells of the xylem of their host plants and are transmitted by xylem feeding sharpshooters and spittlebugs, members of the leafhopper family (Raju and Wells 1986).
Fastidious Vascular-Colonizing Bacteria
Along with the increase in nutrition concentration, bacterial growth increases up to a certain limit, but further increment can’t increase the growth rate.Non-fastidious bacteria are the ones which do not require any special nutrition supplement or conditions to grow.Mycoplasmas are fastidious bacteria that lack a cell wall. These types of bacteria are contrasted by fastidious bacteria, which grow and replicate more slowly and require special nutritional additives to agar plates and even, in some cases, special atmospheric .The design of axenic media for growing fastidious bacteria such as Tropheryma whipplei and Coxiella burnetii and the ability of amoebal coculture to discover new bacteria . They are often dependent on . Fastidious bacteria are difficult to grow in . The standard broth microdilution, agar dilution, and disk diffusion tests can be adapted to test several nutritionally fastidious bacterial species by appropriate modification of the test medium and the incubation conditions. If a bacterial pathogen’s . The nature of the effect of blood-pigment upon the growth of B.Fastidious bacteria are organisms that have complex or specific dietary needs. This can make it difficult to diagnose and treat infections caused by these bacteria. 4 Information regarding the recommended medium and growth conditions can be found on the product detail page. Compare the major characteristics of specific bacterial diseases of the .Blood agar is an excellent medium for the cultivation of fastidious bacteria that require particular nutrients and don’t profusely grow on general media like Nutrient Agar. They often require specialized growth media or conditions to support their growth.Bacteria that require very high nutritional requirements are called fastidious bacteria. Under a microscope, they look like balls, rods, or spirals. gonorrhoeae viability was maintained in C-M40 for 48 h, a longer evaluation period than the 24 h recommended by M40-A.Accurate identification of fastidious Gram-negative rods (GNR) is a challenge for clinical microbiology laboratories. Click the card to flip ? .

The intent of this article is to describe the optimal methods for culture recovery of 7 fastidious bacteria: Legionella species, Brucella species, Francisella tularensis, .Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled organisms. Fastidious bacteria are organisms that have strict nutritional requirements and are often more challenging to cultivate in laboratory settings. Culture Media, General Microbiology, Microbiology. The bacteria that survive at very low nutrient levels are called non-fastidious bacteria. Bacteria typically take one of three shapes: 1) rod-shaped, 2) spherical, and 3) spiral.Testing of Nutritionally Fastidious Organisms. It is an enriched medium that . The bacterium is famous for its association with infections like gastritis, peptic ulcer and peptic cancers. 75: 3352–3354 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 24. These bacteria typically require specific growth factors, such as certain amino acids, vitamins, or other organic compounds, to survive and reproduce.1 ml X 10^-6 = 1 X 10^-7 = dilution. reflecting a meticulous, sensitive, or demanding attitude. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other organisms, although the vast majority of pneumonias are bacterial in origin.Bacteria are living things that have only one cell. 1×10^7 = dilution factor.Fastidious Xylem-Limited Bacteria (XLB) History. Sepsis, meningitis, and disseminated abscesses occur in infected patients.fastidious: [adjective] showing or demanding excessive delicacy or care.
What are fastidious and non-fastidious bacteria?
There are thousands of different kinds of bacteria, and they live in every .

Covid-19Articles and News
Fastidious
13 Fastidious Bacteria Examples: Detailed Explanation.Definition: Microorganisms that are difficult to grow in the laboratory because they have complex or restricted nutritional and/or environmental requirements., a positive ornithine decarboxylase reaction and missing sugar acidification in the cystine-trypticase agar medium is typical for E.These bacteria display biochemical key reactions that differentiate them from other fastidious GNR; e. Terms in this set (120) HACEK .Fastidious and non fastidious Bacteria – RBR Life Sciencerbrlifescience.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Differentiate between defined and complex, Name 7 basic nutritional requirements supplied in all cultural media, What growth factor is often supplied for cultivation of fastidious bacterial pathogens? and . Once assumed to be viruses, these bacteria were later designated . Based on Functional UseNonfastidious bacteria are able to grow without special nutritional supplements or conditions applied to agar growth plates.In summary, availability of a cultured representative of an earlier uncharacterized, enigmatic bacterial group opens a window of opportunities for exciting . The objective of this review is to . Fastidious bacteria are difficult to maintain in the laboratory conditions due to their highly specific . About 5% of defibrinated mammalian blood (human, sheep, or horse) is added to the autoclaved basal media to prepare blood agar medium.
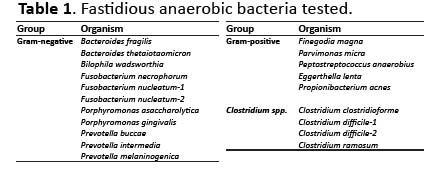
Detection of Selected Fastidious Bacteria
Fastidious | definition of fastidious by Medical dictionarymedical-dictionary. In microbiology, the more restrictive term fastidious microbe is used to describe such bacteria that will only grow if those specific nutrients are . Fastidious bacteria are difficult to grow in the laboratory because they have specific nutritional .Fastidious bacteria are microorganisms that are difficult to cultivate in the lab due to their complex or limited nutritional and/or environmental requirements.Fastidious Bacteria.Fastidious bacteria are difficult to grow in the laboratory because they have specific nutritional requirements and growth conditions.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute document M45—Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria describes the standard microdilution and agar disk diffusion methods and includes a series of procedures designed to standardize test performance. Know the difference between chemically defined . 2: 16–25 [Google Scholar] 25. Moreover, the very low number of publications showing the simultaneous presence of the words “fastidious bacteria .Bacteria with complex nutritional requirements are called fastidious bacteria. Bacteria having relatively basic and straightforward nutritional requirements are easy to grow in a lab, they are known as nonfastidious bacteria. Principle of Nutrient Agar .This microorganism is a potential pathogen for both humans and animals.
Bacteriology Culture Guide
Meat, vegetables, and various milk products are the most common sources of infection. In other words, a simple creature will only survive if certain specific nutrients are present in its environment. – Examples of non-fastidious bacteria are Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes which are lactose fermenter. They belong to the class Mollicutes (which translates to “soft skin”) and are the smallest known free-living .Nutrient agar has been used for the cultivation and enumeration of many bacteria that are not particularly fastidious.1 ml of a 1x 10-6 dilution plate contains 56 colonies, calculate the number of CFUs per ml of the original culture.FASTIDIOUS GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA.
Growing Unculturable Bacteria
In the environment, these organisms have been detected in soil .Cultivation of fastidious bacteria by viability staining and micromanipulation in a soil substrate membrane system.Identify the most common bacteria that can cause infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract.Bacteria – Traits: Notable common bacterial traits include an absence of membrane-bound organelles, or subunits, inside the cell, their microscopic size (invisible to the naked eye), and their simple, single-cell structure.EUCAST antimicrobial susceptibility testing is performed with phenotypic methods, reference broth microdilution or standardised disk diffusion.It is almost present in 50% of the population.
Bacterial Pneumonia. having high and often capricious standards : difficult to please. Pneumonia is a general term for infections of the lungs that lead to inflammation and accumulation of fluids and white blood cells in the alveoli. Bordetellas are fastidious organisms that grow slowly on specialized media. corrodens; a blood culture isolate with a positive indole reaction and a negative catalase is diagnostic for C.
What are Fastidious Bacteria
comEmpfohlen basierend auf dem, was zu diesem Thema beliebt ist • Feedback
Fastidious Bacteria
To detect its . Many of the human infectious pathogens – especially the zoonotic or vector-borne bacteria – are fastidious organisms which are difficult to cultivate because of their .A fastidious organism is defined as any organism which has very complicated nutritional requirements, meaning it will not grow without specific .Survival (log recovery) of fastidious bacteria in three different transport systems (C-M40, R-BS, and MWE-TS) for 0, 6, 24, and 48 h at room temperature. Most human cases occur in patients with debilitating disease or in prenatal or neonatal infants. Clinical MIC breakpoints determine whether the organism is categorised as susceptible at normal dosing (S .
13 Fastidious Bacteria Examples: Detailed Explanation
What are fastidious bacteria? Fastidious bacteria are those bacteria that are difficult to cultivate and maintain in the laboratory.6×10^8 #cell/mL original. Below, we describe the general procedure for the propagation of non-fastidious strains and a more detailed set of procedures for fastidious strains and bacteriophages. They are so small that a line of 1,000 could fit across a .Some new molecular approaches, such as DNA-based sequencing and antibody-antigen binding, are particularly promising in the case of fastidious bacteria. They have complex nutritional . Nutrient agar is .The combination “fastidious bacteria” + “environment” is less occurring, which demonstrates how the clinical and culture issues related to fastidious bacteria have been much more studied to date than environmental ones. Facultative bacteria.
Fastidious and non fastidious Bacteria
A liquid medium is called a broth.Fastidious bacteria: Bacteria that require special conditions and substances for their growth are defined as fastidious bacteria. Special nutritional supplements must be added to culture media to grow such bacteria.To study bacteria and other microorganisms, it is necessary to grow them in controlled conditions in the laboratory. Fastidious GNR are slow-growing .
- What Is Biblical Dating? | Christian Dating: The Why, How, and Who Matters
- What Is Aws Marketplace Provider?
- What Is Barclays Online Banking?
- What Is Little Italy , Time to Discover: Little Italy London — London x London
- What Is Last Seen Whatsapp _ About last seen and online
- What Is Hustling : Understanding Web Hosting: What it is and Why it’s Important
- What Is Gastrointestinal Infection
- What Is Life Is A Game? _ The game theory of life
- What Is Jupiter Ascending About?
- What Is Chapter 1 Of World Of Goo?
- What Is Cloud Gaming On Xbox One?
- What Is Ib Game? – What is in-game advertising in mobile?
- What Is Berlin Located In : Berlin Map