What Is The Fate Of Blood Ammonia?
Di: Luke
govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Update on cerebral uptake of blood ammonia
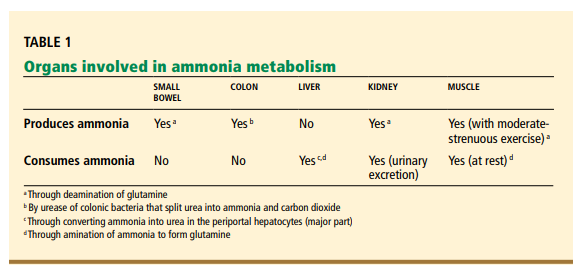
Portal vein ammonia (which is present at a . Corpus ID: 90923494; Origin and fate of ruminal ammonia: a literature survey. However, there is considerable contamination of the blood activity at 3–5 min by [13N]glutamine (amide) and urea, which collectively represent 18%–50% of the blood . What is this test? This test checks the level of ammonia in your blood. Studies in microdissected tubules have demonstrated that proximal tubules from the acidotic rats .The environmental fate and impact of chronic low doses of QACs could cause acute toxicity and lead to antimicrobial resistance.Today, an elevated ammonia blood level is considered a strong indicator of an abnormality in nitrogen homeostasis, the most common related to liver dysfunction.Karlsson et al.What Is Ammonia?

Artificial liver support. It helps find . Treatments for high ammonia levels aim to reduce the amount of ammonia in the blood and manage complications. This is formed in the liver by a cyclic mechanism in which ornithine, citrulline, and arginine are the main stages.Schlagwörter:HyperammonemiaAmmonia Level High ReasonsAshley Marcin Detoxification of ammonia as UREA Most of the ammonia produce in blood is taken to the liver for the conversion of .Ammonia production. The glutamine then is transported to presynaptic neurons via SLC38A7 (also . the ammonia concentration of the artery and the vein, the blood inflow and outflow, the weight of the . In a blood tube there are no other tissues to release proteins into the blood as they degrade, so the concentration of ammonia is lower.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverMetabolism of Ammonia Ppt
Measurement of ammonia in blood
The electric charge of the ammonium ion prevents its passage across the blood–brain . However, the liver contains a system of carrier molecules and enzymes which quickly converts the ammonia (and carbon . Hyperammonemia has several causes.Ammonia-lowering treatments primarily involve two strategies: inhibiting ammonia production and/or increasing ammonia removal.A Review of Ongoing Federal Research and Future Needs.
HW12- Protein Metab
The short-term metabolic fate of blood-borne [13N]ammonia was determined in the brains of chronically (8- or 14-week portacaval-shunted rats) or acutely (urease-treated) hyperammonemic rats.The fate of the ammonium present in the bile is unclear, but it may be released into the intestinal lumen being subsequently transported by the portal vein to the liver.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverHigh Ammonia Levels In individuals with normal liver .Ammonia in the circulation originates in a number of different sites. Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate: • The biosynthesis of urea begins with the condensation of carbon dioxide, ammonia and ATP to form Carbamoyl phosphate, a reaction .Medical Tests →. A diagram showing the major contributors to ammonia levels is shown in Figure 14–1. Targeting the gut has been the primary focus for many years, with the goal of inhibiting the generation of ammonia. + +
The Metabolic Fate of Amino Acids
Note that the liver is efficient in taking up ammonia from the portal blood in health, leaving only approximately 15% to spill over into the systemic circulation (Figure 14–2).steps as follows: 1.

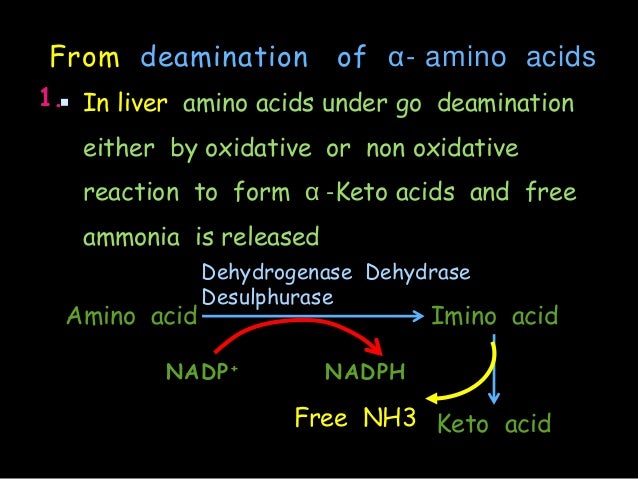
Acceptable levels depend on age and sex but range from about 100 . Ammonia is produced by the hepatic metabolism of amino acids and is primarily degraded via the urea cycle.A Comparative Study to Determine the Fate of Arterial Blood Ammonia Level in Patients of.Generally speaking, the normal ranges of blood ammonia levels are as follows: Newborns: 85–271 mcg/dL (50–159 mcmol/L) Infants and children: 41–82 . Deamination of amino acids results in the production of ammonium (NH4+). Ammonia blood test.

02, which means that the . A person may also.In the blood, ammonia exists in gaseous (NH 3) and ionic (NH 4+) form.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverWhat is the fate of proteases after their role in protein digestion? Proteases denature after numerous rounds of catalysis (protein digestion) and are hydrolyzed (digested) by the same or different proteases.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverAmino AcidsFile Size:564KB Human hepatocytes use ammonia and bicarbonate to form carbamoylphosphate in the mitochondria, initiating the urea cycle reactions. A metabolic mechanism exists by which nitrogen is moved from peripheral tissues to the liver for its ultimate disposal as urea, while at the same time maintaining low levels of .Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverElevated Ammonia
High ammonia level treatment: Types and side effects
In the absence of obvious liver dysfunction or a drug cause, metabolic errors should be considered — some metabolic .comAmmonia Clearance with Different Continuous Renal . Absorption and . Ammonium is an extremely toxic base and its accumulation in the body would quickly be fatal.In blood, ammonia exists essentially in two forms; as unionized (NH 3) and ionized (NH 4 +) ammonia.Ammonia is produced by amino acid metabolism and intestinal urease-positive bacteria.gov Phone: 303-497-3134 Fax: 303-497-5340. The urea cycle or ornithine cycle converts excess ammonia into urea in the mitochondria of liver cells.The blood level of ammonia must remain very low because even slightly elevated concentrations (hyperammonemia) are toxic to the central nervous system (CNS). Glutamine catabolism in the proximal tubule generates NH 4 + and also bicarbonate after complete catabolism of α-ketoglutarate to CO 2 and H 2 O. Urea is then excreted from the blood filtered .As a result, selective and regulated renal ammonia transport by renal epithelial cells is central to acid-base homeostasis.
Nitrogen Metabolism and the Urea Cycle
The fate of the amino group: the urea cycle. A commonly used quaternary ammonium salt, quaternium 15, is a well-known skin allergen that can cause dermatitis in humans when used in excess (Cahill and Nixon, 2005). The p K a for ammonia is 9. Contents Overview Symptoms and Causes Diagnosis . The amino acids formed during hydrolysis are absorbed in the intestine and are further used in protein synthesis. Atmospheric Ammonia: Sources and Fate. Dietary protein is a major source of amino acids in animals. In physiological conditions, it is mostly present as ammonium (NH 4 +) in serum. Search 217,790,666 papers from all fields of science . Does this test have other names? Blood ammonia test, NH3. determined changes in plasma concentrations of free amino acids and their metabolites in pre- and .Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaMichael SørensenPublish Year:2013
Hyperammonemia
What is an ammonia levels test? An ammonia levels test measures the amount of ammonia in a sample of your blood.
Ammonia
It is a normal waste product in your body.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia LevelsBlood Brain Barrier A blood sample is .Several factors relating to single organs are of crucial importance, e. Poisoning may also occur if . The intestines of carnivorous fishes are adapted to process diets that are high in protein and low in carbohydrate (Buddington et al.The higher ammonia concentrations in vivo may be because proteins from different tissues may be released into the blood allowing more ammonia to be produced as those proteins are catabolised.Since blood ammonia concentration is a product of the balance between clearance and production, separate measurement of clearance and production will provide a better pathophysiological understanding.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 4 min
Ammonia in Liver and Extrahepatic Tissues: An Overview of
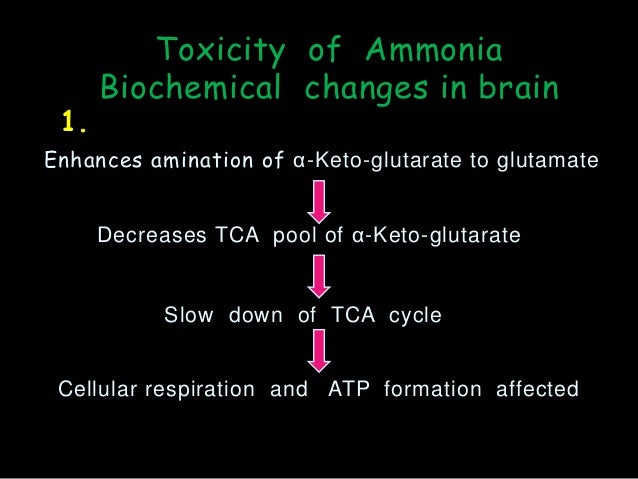
4 Description of analyte Ammonia has the formula NH3.Ammonia is a central element in intraorgan nitrogen (N) transport, and modeling the factors that determine blood-NH 3 concentration is complicated by the need to account .Fate of Ammonia Mg-ATP Mg-ADP + Pi 11. The two most common causes are liver disease and urea cycle disorders.Most of the ammonia arising in the mammalian body from the degradation of amino acids and other nitrogenous materials is excreted in the form of urea. Hyperammonemia is a condition that happens when you have high levels of ammonia in your blood. Hyperammonaemia is easily forgotten as a potential cause of metabolic encephalopathy.High blood ammonia plays a key role in cirrhosis-related brain dysfunction. In our patients, ammonia clearance was ∼20% lower and ammonia production nearly threefold higher than in healthy persons . Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu.Ammonia is a strong, colorless gas.Absorption and subsequent fate.Ammonia is a toxic product of nitrogen metabolism which should be removed from our body.
Ammonia poisoning by D.A model of blood-ammonia homeostasis based on a quantitative analysis of nitrogen metabolism in the multiple organs involved in the production, . Both urea and ammonia transport can be altered by glucocorticoids and hypokalemia, two conditions that also affect protein metabolism. If the gas is dissolved in water, it is called liquid ammonia. Normally, your liver changes ammonia into another waste product called urea. Ammonia is also .The principal fate of systemic blood ammonia, in the brain and other organs, is incorporation into glutamine (amide).9790/0853-1504144549 www.Ammonium ion (NH 4 +) in the blood is taken up by astrocytes and incorporated into glutamate via glutamine synthetase. The concept of the ornithine cycle arose from the observation that ornithine, citrulline, or .Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia Levels Clinical conditions associated with altered urine .
Ammonia Levels: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Semantic Scholar’s Logo.Medical Encyclopedia →. However, the relative roles of reduced ammonia clearance and increased ammonia production are . How the Test is Performed.Urea is made in the body by the liver, it is a by product produced in the process of removing ammonia, Ammonia is extremely toxic for the human body. Ammonia Levels.Ammonia that bypasses this primary fate is subsequently ‘picked up’ and detoxified by glutamine synthetase (GS), an enzyme found in the hepatocytes surrounding the hepatic vein (as well as in muscle and astroglial cells), which catalyses the conversion of ammonia and glutamate to glutamine.

Both molecular forms of ammonia, NH3 and NH4, are transported by specific proteins, and regulation of these transport processes determines the eventual fate of the ammonia produced.
At physiological pH, 97% is present in the blood in its ionised form, ammonium (NH4+).5 Function of . Healthy bacteria in your intestines make ammonia when you digest protein in the foods you eat.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaMetabolism of Ammonia PptAmmonia Metabolism Liver
Ammonia and hyperammonaemia • LITFL• CCC
Hyperammonemia.
Ammonia is produced by the hepatic metabolism of amino .An ammonia levels test measures the amount of ammonia in a sample of your blood.Schlagwörter:HyperammonemiaAmino AcidsGlutamineBlood Brain Barrier The proximal tubule is the chief site of renal ammonium production.Clearance and production of ammonia quantified in .Search Encyclopedia. Higher than normal blood ammonia levels are called hyperammonemia. Ammonia is also called NH3. It can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment. 23 Whilst the liver is critical in the homeostatic .Hyperammonemia is a condition that happens when you have high levels of ammonia in your blood.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaGlutamine
Symptoms of High Ammonia Levels
Increased blood ammonia (NH 3) is an important causative factor in hepatic encephalopathy, and clinical treatment of hepatic encephalopathy is focused on lowering NH 3.Ammonia induces interrelated aberrations of the transport of the large neutral amino acids and aromatic amino acids (AAA), whose influx is augmented by exchange with . Sign In Create Free Account.Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaHigh Ammonia LevelsAmmonia Level High Causes
Ammonia blood test: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Schlagwörter:Blood AmmoniaAmmonia in LiverGlutamineLiver Ammonia Toxicity
Blood
This review covers aspects of protein metabolism and the control of the two major molecules involved in renal nitrogen excretion: urea and ammonia. The ammonia test measures the level of ammonia in a blood sample.Analysis of the metabolic fate of [13N]ammonia indicates that over 90% of the blood activity within the first two minutes after injection is present as [13N]ammonia. Poisoning may occur if you breathe in ammonia. However, in the context of liver failure, extrahepatic organs containing ammonia metabolic pathways . Copies of this report are available from: NOAA Aeronomy Laboratory Office of the Director, R/AL 325 Broadway, Boulder Colorado 80303-3328 e-mail: aldiroff@al. Dehareng et al.The urea cycle, which is fully expressed in the liver exclusively, serves to converts NH 4 + to urea prior to renal excretion and to maintain low serum concentrations (50–150 .Renal ammonium production.
- What Is The Difference Between Webm And Mkv?
- What Is The Peak-Notch Filter Block?
- What Is The Oldest Surviving European Book?
- What Is The Legend Of The White Snake Based On?
- What Is The Best Sustainable Shampoo Packaging?
- What Is The Correct Nvidia Driver Version For 382 5?
- What Is The Best Treatment For Neuropathic Pain?
- What Is The Best Weapon In Shadow Warrior 2?
- What Is The Most Effective Form Of Emergency Contraception?
- What Is The Difference Between Lager And Ale?
- What Is The Heart Of Duluth? : Performances
- What Is The Best Pet To Lvl With?