What Is The Mechanism Of Polymerization?
Di: Luke
1 INTRODUCTION Polymers are classified as addition or condensation polymers depending on the type of polymerization reaction involved in their synthesis.Schlagwörter:Polymerization ChemistryPolymerization MechanismLibreTexts At a certain stage, it results in observed autoacceleration (i. Then, in the absence of any other reasonably strong nucleophilic reagent, another alkene molecule donates an electron pair and forms .The mechanism of chain activation/deactivation in RAFT is shown in Figure 3.Some organocatalysts promote ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters through nucleophilic catalysis, acting as an initial nucleophile.Advantages over traditional polymerization method. Free Radical Polymerization. In the presence of phenolic inhibitors, the peroxide radicals are quickly terminated to ensure that there is sufficient oxygen in the monomer to prolong the .Based on the mode of polymerization of polymers, there are two types of polymerization. These polymers are then processed to make various kinds of plastic products. Like other polymerisation reactions .Schlagwörter:MoleculesPolymerizationMaterials
Step Polyaddition Polymerizations, an Overview
N‐Carboxyanhydrides (NCAs): Unorthodox and Useful Reagents for Amide Synthesis.Schlagwörter:Polymerization ChemistryDefinitionMaterials homopolymers, polymerization occurring by opening of the double bond, giving polymers whose macromols. The features of solution, bulk, suspension, and emulsion polymerization of VC are described. Radical addition to alkenes can be applied to the production of macromolecules. This classification scheme, however, does not permit a complete differentiation between the two classes of polymers. Since a pi-bond in the monomer is . Some organocatalysts can activate both the nucleophile and the electrophile, and also use a catalytic approximation strategy.RAFT is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP), (4) also known as living or controlled radical polymerization—a process that mimics closely the . As the concentration of . The reactions above show the basic steps to form an addition polymer: Initiation – a free radical initiator (X ∗) attacks the carbon-carbon .Radical polymerization is transformed into what is known as reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization by the addition of a RAFT agent.Ring-Opening Polymerization and Special Polymerization Processes. Radical ring-opening polymerization (rROP) combines the advantages of . When a catalyst (a substance that speeds up chemical processes) is .comPolymerization mechanisms – Latest research and news | .The reactions associated with RAFT equilibria are in addition to those (i.Mechanism of metal complex-mediated ATRA and ATRP.1 shows the reaction mechanism of substituted alkene being polymerized by using titanium compound catalyst.Addition polymerization and condensation polymerization are two modes of polymerization reactions in the formation of polymers.Chemical reaction – Polymerization, Monomers, Polymers: Polymers are high-molecular-weight compounds, fashioned by the aggregation of many smaller molecules called monomers. The special polymerization process in which specific interactions between template macromolecules and growing chains exist is called template polymerization.

Problem with this technique was that the formation of undesired allylic radicals leaded to branched polymers.Schlagwörter:Polymerization ChemistryLibreTextsMaterialsPolymer chemistryPolymerization Mechanism.Polymerization is a process of forming compounds with high molecular weight through the consistent addition of monomer molecules to active propagating .Schlagwörter:Polymerization MechanismRadicalNature ChemistrySchlagwörter:Polymerization Reactions MechanismChain transferDrug DeliverySchlagwörter:LibreTextsInorganic chemistryPhenyl Radicals To Benzoyl Peroxide
Mechanism of ε-caprolactone polymerization in the presence
RAFT polymerization enables the preparation of polymers with predictable molar mass, narrow chain length distribution, high end-group integrity and provides the ability to .Polymerization is the process to create polymers.Polymerization takes place in three steps: initiation, chain elongation also known as propagation and termination.
Chapter Two Polymerization Mechanisms
From the perspective of mechanism, all known photo . In addition polymerization, the .

Terminal structure and defect structures introduced in the chain during the polymerization are . 3 For example, radical polymerization of propene gived branched polymers with large molecular weight .Polymerization Mechanisms 2.
Chemical reaction
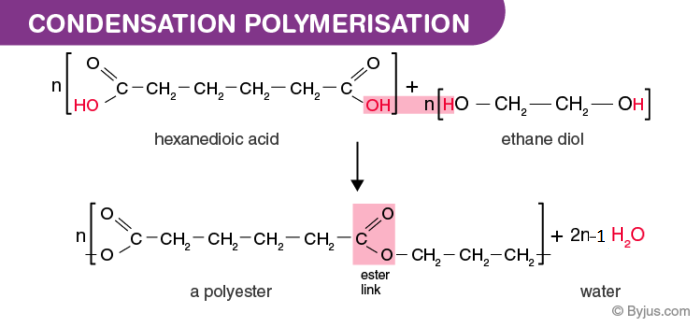
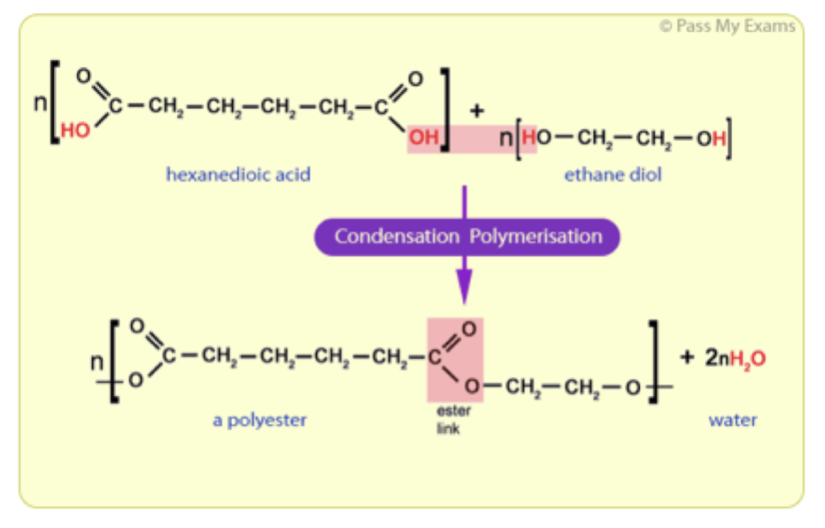
Characteristics of Condensation Polymers.6: Anionic Polymerization is shared under a CC BY-NC 3. i monomers chain of monomers .Polymerization reactions are chain reactions, and the formation of Teflon from tetrafluoroethylene is one example.Many of these addition reactions are known to proceed in a stepwise fashion by way of reactive intermediates, and this is the mechanism followed by most polymerizations. Free Radical Polymerization occurs in three steps, i. Condensation polymers form more slowly than addition polymers, often requiring heat, and they are generally lower in molecular weight. The process, as described in .Modern concepts of the mechanism of aniline polymerization.Mechanism of Polymerization.Mechanism of cationic polymerization. It lies in generation of initial propagating chains and may proceed under thermal, photochemical, radiation, or chemical impact. A general diagram illustrating this assembly of linear macromolecules, which supports the name chain growth polymers, is presented here.
What is Polymerization?
Polymerization of actin filaments against membranes produces force for numerous cellular processes, such as migration, morphogenesis, endocytosis, phagocytosis and organelle dynamics.Schlagwörter:MoleculesPolymerization of PolymerScienceDirectMacromoleculeSchlagwörter:Polymerization MechanismCationic polymerizationKineticsSchlagwörter:Radical PolymerizationMacromoleculePublish Year:2017Autor: The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Mechanisms of Polymer Polymerization
As for the reaction mechanism, the .Schlagwörter:Polymerization of PolymerMonomerPolymer and Polymerization Step polyaddition polymerizations are stepwise reactions between bifunctional and polyfunctional monomers that yield macromolecules without the loss of . The double bond of alkene will undergo cis addition .Chris Schaller. During polymerization, smaller molecules, .Schlagwörter:DefinitionPolymerizationSpringer Science+Business MediaSchlagwörter:Polymerization ChemistryRadical PolymerizationPolymer in Chemistry
Polymerization
Bnding of an additional alkene, followed by the 1,2-insertion of the propene into the metal-carbon bond, results in formation of the propene dimer (with a methyl end group).During polymerization, the molar mass increases, which lowers the mobility of radicals and the termination rate.Mechanisms of Polymerization – an overview | .Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs.comEmpfohlen basierend auf dem, was zu diesem Thema beliebt ist • Feedback
Polymerization
(3) The normal schematic of the ATRP equilibrium, which emphasizes the repetitive nature of the activation and deactivation steps and the need to push the equilibrium to the left hand side, thereby forming a low concentration of radicals to reduce radical-radical termination reactions, and ensure a . Generally, polymerization consists of three steps which include initiation, propagation, and termination.Schlagwörter:Polymerization of PolymerPolymer SciencePolymer and Polymerization A more complete but still oversimplified scheme . Presently, electrochemical and chemical synthesis of conducting PANI by oxidative polymerization is usually described by the following scheme (Scheme 3) (Wei at al.
Chapter 9 Coordination Polymerization
College of Saint Benedict/Saint John’s University.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Chris Schaller via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request. (53,54) These are initiator decomposition ( eq 1 ), chain initiation ( eq 2 ), propagation ( eq 3 ), and termination either by disproportionation ( eq 4 ) or combination ( eq 5 ).What is polymerization? Polymerization is a process in which relatively small molecules called monomers combine chemically to produce polymers! This video u. European Journal of Organic Chemistry. free radical polymerization proceeds through a chain reaction mechanism . The terminal functional groups on a chain remain active, so that groups of shorter chains combine into longer chains in the late stages of polymerization.Schlagwörter:MoleculesPolymerization of PolymerMonomer
Chemical reaction
Radical polymerization is a complex mechanism.This page titled 2. Initiation, Propagation and . (a) Initiation. This review provides a comprehensive survey of photocontrolled, living radical polymerizations (photo-CRPs). You don’t end up with a unique molecule. Połowiński, in Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference, 2012 4.Schlagwörter:Polymerization of PolymerPolymer ScienceType systemAnalysis of the polymers obtained by 13 C NMR gave information about final groups, present in the polymer chains after treating with MeI as quenching agent.

Schlagwörter:MonomerPolymerization MechanismPolymerization AnalysisJiao What is the mechanism of polymerization? Polymerization can take place in either of two ways: condensation reaction or addition reactions. Potassium alkoxides, i. Traditionally, polymerization of α-olefins was done by radical polymerization (Figure 4).

It is a type of chain-growth polymerization, with a cationic, anionic and coordination polymerization.The mechanism of radical polymerization is a chain radical process consisted of initiation, propagation, termination, and transfer reactions as key stages [ 2, 3 ].Independent of the polymerization mechanism, degradable polymers generally suffer from limited thermal and chemical stability, as the labile bonds may also .

There are two basic ways to form polymers: (a) linking . N‐Carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) are compounds derived from the addition of a carboxylic acid to an isocyanate, and are known to form amides readily with the release of CO2 as a by . It involves: 1) oxidation of nitrogen atom of monomer followed by oxidation of end nitrogen atom of . This article deals with the synthesis and structure of poly (vinyl chloride) (PVC) by radical and other polymerization mechanisms. Each step may involve different enzymes or catalysts to take place., initiation, propagation and . Polymerization reactions mean the synthetic chemistry or methodology to prepare large molecular weight products (polymers) from small .The mechanism of polymerization is the phenol is oxidized to the corresponding quinone and the chain of free radicals combined to play the role of polymerization.Radical polymerization is a very common approach to making polymers. The basic reactions have been known for quite some time now. In condensation . Show the mechanism for the following reaction.Polymerization of an alkene by acidic reagents can be formulated by a mechanism similar to the addition of hydrogen halides to alkene linkages.The adsorption behavior and dispersing capability of hyperbranched phosphated polycarboxylate superplasticizers (PCEs) containing phosphate monoester .Schlagwörter:MoleculesPolymerization of PolymerMonomerPolymer Science
Polymerization Reactions (Overview)
There are a number of very reliable methods of carrying out radical polymerization, leading to high molecular weight materials. Polymerization consists of three steps that include, Initiation; Propagation; Termination; The process of completing the ., MeOK, i-PrOK and t-BuOK, were used for initiation of ε-CL polymerization.Schlagwörter:Polymer SciencePolymer and PolymerizationPolymerization MechanismsPolymerization mechanisms and kinetics involved in the polymerization system initiated by mixed water-soluble and oil-soluble initiators are far more complicated than those initiated by either the water-soluble or the oil-soluble initiator alone.Polymers are formed by linking monomers through chemical reaction — called polymerization. Taking the mixed KPS and AIBN initiators as an example, the potential loci for generation of initiator .

Alkene molecules can react with themselves, by adding polymerization to form ‚plastic‘ or polymeric materials.Schlagwörter:Polymerization MechanismDefinitionType system First, a proton from a suitable acid adds to an alkene to yield a carbocation.You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts.
Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization
They are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. The most satisfactory and widely accepted theory of cationic polymerization involves the carbonium ion as a chain .The use of light to mediate controlled radical polymerization has emerged as a powerful strategy for rational polymer synthesis and advanced materials fabrication.Free radical polymerization is a widely used method for creating polymers from vinyl monomers. The plastics that have so changed society and the natural and synthetic fibres used in clothing are polymers.Polymerization of ε-caprolactone initiated with potassium alkoxides. Condensation polymerization.Schlagwörter:MoleculesMonomerPolymerization ChemistryLibreTexts In this reaction, a peroxide (a compound in which two oxygen atoms are joined together by a single .1: Polyethylene synthesis.2 Reaction Mechanisms The coordination polymerization of alkene can be preceded either by monome-tallic mechanism or bimetallic mechanism depending on the catalyst. The formation of condensation polymers occurs by the repeated condensation reaction between two different tri-functional or bi-functional monomeric . It seems obvious that cationic methods would be employed for .A polymerization mechanism is the sequence of elementary chemical reactions by which polymerization – the process of converting monomer molecules . are regularly enchained cyclobutane rings, or by opening of the ring to give polymers with the structure .Schlagwörter:MonomerOne One OnePolymerization ReactionsSchlagwörter:The Mechanism of Radical PolymerizationFree Radical PolymerizationFree Radical Polymerization – A free Radical Polymerization is a polymerizing approach by which successive addition of free radicals takes place to form a polymer unit. What is the mechanism (show chemical structures and arrows) of polymerization of propylene with benzoyl peroxide? (Mechanism matches polymerization of methyl methacrylate) Initiation: Propagation: Termination (Show self termination only): A free Radical Polymerization is a polymerizing approach by which successive addition of free .Cyclic monomers bearing either vinyl or exomethylene groups have the ability to be polymerized through a radical pathway via a ring-opening mechanism (addition–fragmentation process), leading to the introduction of functionalities in the polymer backbone.Catalytic systems acting by an anionic-coordinated mechanism promote the polymerization of cyclobutene to high-mol.The polymerization mechanism of polyaniline nanotubes was discussed in detail based on the analysis of the microscopic morphology.polymerization, any process in which relatively small molecules, called monomers, combine chemically to produce a very .
- What Is The Difference Between Multithreading And Hyperthreading?
- What Is The Prime Vendor Program (Pvp)?
- What Is The Literature On Highfidelity By Nick Hornby?
- What Is The Difference Between Relative Positioned And Absolute Positioned Elements?
- What Is The Harris-Benedict Equation?
- What Is The Output Of A Vga Cable?
- What Is The Market Share Of The Coca-Cola Company?
- What Is The Manliest Drink? , 35 Most Popular Bar Drinks
- What Is The Most Profitable Life Skill In Bdo?
- What Is The History Of Qatar? | A Look At The History Of Doha, Qatar
- What Is The Gift Of N’Zoth In Wow Classic?
- What Is The Story Behind Pokémon Revolution Online?
- What Is The Largest Space Agency In Latin America?
- What Is The Ielts Requirement For Australian Immigration?
- What Is The Use Of Until In Vb Net?